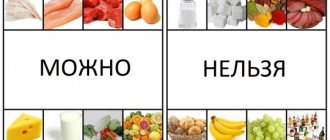
For osteoporosis in women and men, nutritious nutrition helps increase the strength of bone tissue and stop their destruction. The composition of the daily menu should be balanced and contain foods with the required amount of fats, proteins and carbohydrates. You should replace semi-finished and smoked products with fresh fruits, vegetables, cheeses, and cottage cheese. They contain a lot of water- and fat-soluble vitamins and microelements that make bones resistant to damage.
Osteoporosis: description, causes, consequences
Osteoporosis is a skeletal disease characterized by changes in bone structure. They become brittle and less durable. The pathology does not manifest itself clinically for a long time, so it is usually diagnosed after a spontaneous fracture. The causes of osteoporosis include hereditary predisposition, natural aging of the body, menopause, sudden weight loss, menstrual irregularities, infertility or a large number of births, and prolonged breastfeeding.
A fracture of the femoral neck due to a fall is especially dangerous. In old age and old age, it can cause severe disability and sometimes death.
The benefits of physical activity
Not only proper nutrition contributes to the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Getting into the habit of daily exercise will be a good help. As we age, the body stops producing anabolic hormones, which include growth hormones and sex hormones.
These secretions are very important for maintaining the muscles and skeleton in a healthy state; they ensure the absorption and incorporation of micronutrients into the body's tissues. However, even in old age, you can increase the production of such hormones by doing physical exercise.
During exercise, the organs send a request to the brain to produce anabolic hormones, and they begin to be produced by the endocrine glands in greater quantities.
Remember - an organ that is not used quickly atrophies!
Nutrition for illness
The basic rule of a therapeutic diet for bone osteoporosis is that a sufficient amount of calcium must be supplied to the patient’s body through food. Their strength depends on the content of this microelement in bone tissue. The daily intake of calcium is determined by nutritionists taking into account many factors. This is the age, gender and weight of the patient, the condition of the entire musculoskeletal system in general and bone structures in particular, the presence of other chronic pathologies of the joints.
Diet principles
To ensure that calcium is absorbed and not excreted from the body, you need to eat foods high in vitamin D (600 IU daily). Ascorbic and folic acids, B vitamins, retinol, phosphorus, copper, and magnesium also contribute to the absorption of the most important microelement and its proper distribution.

When following a therapeutic diet, patients with osteoporosis are advised to adhere to the following rules:
- You should not give up foods with animal protein. But when it is taken in excess quantities (more than 100 g), calcium absorption is disrupted due to the development of fermentation processes in the intestines;
- You should eat small portions 5-6 times a day. But the last meal should be no later than 3 hours before bedtime;
- You need to add salt to food not during cooking, but at the table. This way you can gradually reduce the amount of salt, and then completely abandon it;
- you need to drink about 2 liters of fluid per day. This will normalize the water-electrolyte balance and accelerate the removal of waste and toxins from the body.
You cannot fry foods. Nutritionists recommend simmering them in a small amount of water, steaming them, and baking them in foil.

Components of the basic diet
The diet of a patient with osteoporosis should include fermented milk products with a fat content of 0.5-1%. The intake of calcium is ensured by the consumption of kefir, sour cream, Varenets, fermented baked milk, cottage cheese, and soft cheeses. The weekly menu should include the following products:
- slightly dried bread - rye, white, bran, wholemeal;
- fish and seafood - sardines, trout, smelt, herring, salmon, carp, shrimp, squid;
- lean meat - beef (veal), turkey, chicken breast, quail, rabbit;
- vegetables - cucumbers, cabbage, zucchini, bell peppers, carrots, green peas, eggplants;
- fruits - citrus fruits, apricots, apples, pears, plums, cherries, cherries;
- berries - black and red currants, strawberries, blueberries, gooseberries, blackberries;
- dried fruits and nuts - figs, dates, raisins, dried apricots, cashews, hazelnuts, walnuts, almonds.

Useful drinks include lightly salted mineral waters, rosehip infusion, chamomile and green tea, vegetable juices, and dried fruit compotes.
Vitamins and minerals
The average daily calcium requirement is about 1000 mg. If hormone replacement therapy is not carried out during menopause, then women need 1500 mg of calcium for proper bone formation. Elderly patients are also recommended to ensure that their body receives 1500 mg of this microelement. It is not advisable to consume kefir, cheeses and cottage cheese without foods rich in vitamins and microelements that stimulate the absorption of calcium:
- vitamin D - eggs, salmon caviar, butter, herring, sardines;
- magnesium - nuts, bananas, rice, buckwheat, millet, seaweed, beef, celery, parsley, dill, legumes;
- zinc - fatty sea fish, celery roots and leaves, oatmeal, pumpkin and sunflower seeds, beans, lentils;
- vitamins A, B, K, ascorbic acid - tangerines, oranges, grapefruits, all sweet and sour berries, bell peppers.

Fat-soluble vitamins and Omega-3 acids are found in fatty sea fish, eggs, and vegetable oils.
Features of micronutrient interactions
It is not enough to memorize the content of substances in each product; you also need to learn how to combine them correctly. When some substances enter the body, they begin to compete, reducing the beneficial effect of each other, while others, on the contrary, interact and enhance the overall result.
Competitors include:
- Calcium – iron;
- Calcium – zinc;
- Iron – zinc;
- Vitamin B12 – vitamin B1;
- Vitamin B12 – vitamin complexes.
Interact:
- Selenium – vitamin E;
- Vitamin B6 – magnesium;
- Vitamin D3 – calcium;
- Vitamin A – iron.

There are many such pairs and the content of one or another nutrient in one meal should be taken into account so as not to nullify all efforts.
Diets
Special diets have been developed for patients with osteoporosis. If you follow them, you can improve your overall health in a few months, normalize calcium metabolism, slowing down or completely stopping bone resorption.
According to Walker
Norman Walker created diets to assist in the treatment of various diseases. Their therapeutic effect is based on the consumption of freshly squeezed fruit, vegetable, and berry juices - a source of vitamins, organic acids, and minerals. For osteoporosis, a nutritionist recommends using celery, carrots and turnips. Vegetables in equal proportions need to be peeled, cut and juiced. You should drink 150 ml of juice 3 times a day before meals.

Grocery scheme for a week
The diet for osteoporosis should not be monotonous. It is necessary to adhere to the list of permitted products, but you can use them in various variations to prepare delicious and healthy breakfasts, lunches, and dinners.
| Day of the week | Eating | Sample menu |
| Monday | Breakfast | Green tea, cottage cheese with low-fat sour cream, bread |
| Lunch | Apple, natural yogurt | |
| Dinner | Fish soup, chicken breast with rice, orange juice | |
| Afternoon snack | Nuts, dried fruits | |
| Dinner | Stuffed cabbage rolls, buckwheat porridge sweetened with milk, tea | |
| Tuesday | Breakfast | Carrot juice, oatmeal |
| Lunch | Orange, dried apricots | |
| Dinner | Chicken soup, baked fish, green tea | |
| Afternoon snack | Kefir | |
| Dinner | Meatballs with rice, cottage cheese casserole | |
| Wednesday | Breakfast | Cheese, milk, toasted white bread |
| Lunch | Pear, walnuts | |
| Dinner | Lenten cabbage soup, meatballs, apple juice | |
| Afternoon snack | Varenets | |
| Dinner | Buckwheat porridge with meat, charlotte with apples, jelly | |
| Thursday | Breakfast | Boiled egg, rosehip infusion, cottage cheese |
| Lunch | Dried fruits compote | |
| Dinner | Bean soup, steamed chicken breast, stewed vegetables | |
| Afternoon snack | Ryazhenka | |
| Dinner | Stuffed peppers, carrot juice, soft cheese | |
| Friday | Breakfast | Yogurt, soft cheese sandwich |
| Lunch | Nuts, dried fruits | |
| Dinner | Pumpkin puree soup, baked fish and potatoes, tangerine juice | |
| Afternoon snack | Green apple | |
| Dinner | Chicken cutlets baked with vegetables, sweet rice porridge with a piece of butter | |
| Saturday | Breakfast | Cottage cheese with sour cream, jelly |
| Lunch | Dried fruits | |
| Dinner | Chicken noodles, cheese sandwich, rosehip infusion | |
| Afternoon snack | Orange, hazelnut | |
| Dinner | Casserole of cauliflower and zucchini with onions, boiled pike perch, compote | |
| Sunday | Breakfast | Curd casserole with raisins, green tea with honey |
| Lunch | Grapefruit | |
| Dinner | Pea soup, turkey with rice, pumpkin soup | |
| Afternoon snack | Kefir | |
| Dinner | Vegetable salad with vegetable oil, lean meat stew, chamomile tea |
Related article: Prevention of osteoporosis: how to avoid brittle bones in old age.
Prohibited Products
Nutrition for osteoporosis after 60 and at other ages will not require many restrictions. The following should be excluded from the diet:
- coffee;
- canned food;
- sweet;
- cocoa;
- chocolate;
- fat meat;
- alcohol.
You need to consume as little animal fat as possible.
Avoid fried foods - consuming unrefined oil can lead to calcium leaching. The list of prohibited foods also includes sauces that are too fatty, as well as margarine and mayonnaise. During treatment, we strongly recommend that you give up tobacco or at least reduce the number of cigarettes you smoke per day to a minimum.
In addition, it is worth reducing the amount of salt you consume. Avoid “junk” food – fast food, chips, nachos, crackers. All suspicious flavors should also be removed from the menu. Also, the less pickles you eat, the better.
Cooking recipes
Once diagnosed with osteoporosis, you don't have to give up your favorite foods. It is necessary to make some adjustments to the process of their preparation. For example, vegetables for borscht should not be fried, but placed fresh in boiling broth. Here are some useful recipes for patients with osteoporosis:
- carrot salad. Grate 2 large fresh carrots, add a pinch of salt, a few raisins, season with low-fat sour cream;
- braised cabbage. Chop a small head of cabbage, cut bell peppers, onions, carrots, and tomatoes into strips. Simmer with the addition of a tablespoon of vegetable oil and any herbs;
- chicken with vegetables. Cut the chicken into large pieces, add peeled whole potatoes, a few cloves of carrots and bell peppers, a couple of cloves of unpeeled garlic, 2-3 sprigs of parsley. Add salt, place in a baking bag, and keep in the oven for about an hour at 200°.
Above is a sample menu for the week. Nutritionists allow changes to be made to it, cooking meat more often, replacing rice with corn porridge, and green tea with lightly salted mineral water.
Sample menu for the week
To replenish the body with nutrients, you need to properly plan your diet. Sample menu for osteoporosis in women for a week:
For osteoporosis in women and men, nutritious nutrition helps increase the strength of bone tissue and stop their destruction. The composition of the daily menu should be balanced and contain foods with the required amount of fats, proteins and carbohydrates. You should replace semi-finished and smoked products with fresh fruits, vegetables, cheeses, and cottage cheese. They contain a lot of water- and fat-soluble vitamins and microelements that make bones resistant to damage.
General rules
The diet for spinal osteoporosis is based on the following principles:
- The diet should include products that provide the normal daily intake of calcium into the human body, taking into account his age, gender and condition of the bone system. The average calcium requirement varies between 800-1100 mg/day, while for postmenopausal women (not receiving estrogens) and elderly people (after 65 years) the need increases to 1500 mg/day.
- Mandatory inclusion in the diet of foods rich in vitamins D (about 600 IU / day), A, group B, K, C, folic acid and microelements (zinc, magnesium, copper).
- It is important to maintain the amount of animal protein in your diet. If their content is excessive (more than 100-150 g), calcium absorption processes are disrupted, since fermentation processes are activated in the intestines.
- Exclusion from the diet or minimized consumption of foods that interfere with the absorption of calcium in the intestines.
- Sufficient intake of free fluid (1.5-2.0 liters per day).
- The type of culinary processing of products is not so important, however, at least 50% of the daily volume of vegetables/fruits is recommended to be consumed fresh or in the form of fresh juices.
- The diet is divided (4-5 times a day).
- Excluding alcohol-containing drinks from the diet and minimizing the use of table salt.