Excess weight is blamed on carbohydrates, fats, or individual foods, including potatoes, cottage cheese or fruits. There are horror stories on the Internet: if we had cereal for breakfast, but didn’t go to work out and didn’t work off the carbohydrates, they will be stored as fat. Or that carbohydrates and fats cannot be eaten together, because one goes for energy, and the second, as unnecessary, goes into fat. How do we actually get fat?
We get fat when we get more energy from food than we have time to expend. And from this point of view, it doesn’t matter which foods we exceeded the calorie norm. However, different macronutrients (protein, fat, carbohydrates) make us fatter in excess calories through different mechanisms.
How fat accumulates in the body. Fat. How it accumulates and how to get rid of it.
Jerry Brainum.
Most people think that fat cells are these inert, little globules that make us look fat. Although the main function of adipocytes (fat cells) is to store triglycerides, which consist of three fatty acids bound to a glycerol backbone, fat cells are not called “sleeping” globules. In fact, they produce a range of chemicals that affect health, metabolism and appetite.
. They are even able to regulate their own metabolism using signals sent to the brain.
There are several categories of fats in our body. The main ones are white adipose tissue and brown adipose tissue. Most fats belong to the first category. Brown adipose tissues are darker because their cells contain more mitochondria, where fat oxidation occurs. Brown adipose tissues are the body's main thermogenic tissues, converting fat calories into heat. Scientists debate their importance, but one thing is clear: these tissues have a greater impact on the functioning of the body of children than adults.
All fats in our body can also be divided into deposit, essential and sex-determining. Deposit fats are fats deposited under the skin; they are the most abundant. Essential fats are located in areas such as the bone marrow, heart, lungs, liver and kidneys, and they also surround nerve fibers. In men, they make up about 3% of all body fat, and in women - 9%, if you take into account fats determined by gender. These fats in women are found in the breast, pelvic and thigh areas. They are put aside in case of conceiving a child. Nature is interested in rationality, and not in a woman’s wishes regarding her figure.
Men tend to store fat around the waist, while women tend to store fat in the chest, pelvis and thighs. This difference in the type of fat deposits by gender is regulated by hormones, for example, estrogen determines the deposit of fat according to the female type. It is also responsible for the internal deposition of fat, as well as for a small additional layer of fat, which makes women's skin softer than men's.
Testosterone in men is quite the opposite when it comes to fat, especially in the abdominal area. Research consistently shows that low testosterone levels in men promote fat storage around the waist. Other studies have found that anabolic steroids, which are synthetic versions of testosterone, lower overall body fat, especially in the abdominal region. But excess estrogen in men leads to the deposition of excess fat.
This fat around the waist is associated with insulin resistance and increases the risk of developing cardiovascular disease and diabetes. This applies to both men and women. Abdominal fat is unstable; it is constantly released from visceral fat cells and sent to the liver, where it serves as a starting material for enhanced cholesterol formation. Excess fat prevents the liver from using glucose, which gradually leads to insulin resistance.
The number and size of fat cells depend on various factors, including heredity and what you ate during the first four years of life, when fat cells formed very quickly. Obese people usually have both larger cells and more cells compared to other people. It used to be believed that you couldn't lose or add fat cells, but recent research has shown this to be wrong. Attention! Only when a person reaches a certain level of obesity do fat cells begin to divide, forming new adipocytes, a process called hyperplasia. This is one of the reasons why you shouldn’t follow the example of many bodybuilders who gain too much weight in the off-season. Only if you loosen control will you end up with more fat cells than before, which will make subsequent drying more difficult. This becomes especially noticeable with age.
Savvy readers here might be thinking, “why bother with added fat cells when you can get rid of them with liposuction? » Indeed, such an operation can remove local deposits of fat, for example, on the abdomen, but fat cells can return to the same place if you consume too many calories and do not exercise enough. It is a myth that fat cells, once removed, will never return.
Recent studies have shown that the sequence of fasting-overeating cycles in animals leads to improved functioning of lipogenic enzymes that promote fat synthesis (1. so far this has only been demonstrated in rats, but humans have similar lipogenic enzymes, so the same scenario can be assumed and in humans.We should avoid diets that are too low in calories and involve overeating, as the body may respond by increasing the activity of fat-producing enzymes.
Several years ago, a bodybuilding magazine described a diet called the Abcd. Its essence was alternating high- and low-calorie diets. The goal of the diet was to lose fat and maximize the release of anabolic hormones through dietary manipulation of insulin, testosterone, and growth hormone levels. Although on paper.
All this seemed quite reasonable; it did not help most people who tried this diet, and recent experiments on rats showed exactly why. Reducing the diet of rats for some time, followed by a period when they were allowed to eat whatever they wanted, led to an increase in the rate of fat deposition three times compared with the control group of animals on a regular diet (2. in rats fed according to the Abcd diet, The resting metabolic rate was 30% lower than in control animals, which led to a slowdown in fatty acid oxidation. When animals were allowed to eat everything after a period of restriction, all excess calories were immediately stored as fat. The same thing happened in humans who tried the much-praised but disastrous Abcd diet.
The simplest cause of most cases of obesity is an excess of calories with a lack of physical activity. Consuming excess calories, regardless of their source, will increase your body fat unless you burn them off through exercise. Although this sequence of events leading to the appearance of excess fat is considered obvious, proponents of various diets argue that it is not so simple. They talk about the influence of various hormones and enzymes on the physiology of the fat cell and believe that the issue is not only an excess of calories, but also systemic disturbances in the process of their distribution.
Obese people suffer from disorders of lipid metabolism, as a result of which fat tends to be stored rather than burned. Even in physical activities, such people often achieve less success than their leaner comrades. There is heated debate about why this happens.
Everyone thought the answer was found in 1994, when scientists discovered a protein in fat cells called leptin. In experiments on mice and rats that were “Programmed” for obesity using genetic engineering methods (obesity in them can only be achieved using such methods, since wild rodents never gain more than 10% fat), leptin deficiency was discovered in the animals. Researchers injected it into obese rats, and they quickly lost almost all their fat. When this information was leaked to the press, leptin was touted as a cure for obesity.
But subsequent experiments on humans cooled the initial enthusiasm. The genetic defect that leads to leptin deficiency in rodents is rare, if at all, in humans. In fact, obese people produce more leptin than thin people. Leptin serves as a regulator of fat cells in the body, and in humans the problem is not due to a lack of leptin, but rather, it involves disruption of the brain's connections to fat cells via leptin, and scientists are still trying to figure out why this happens.
Another popular cause of excess fat deposition is slow metabolism. According to this theory, the rate of calorie burning in obese people is not optimal. The thyroid gland is often blamed for this, since it is the hormones it produces that control the rate of metabolism.
But in fact, obese people not only have normal levels of thyroid hormone production, but their resting metabolism is much higher than one would expect. Resting metabolic rate is related to muscle mass, and it turns out that underneath all that fat, these people have enough muscle to maintain a normal or even elevated metabolic rate. On the other hand, recent studies have shown that in many cases, thyroid hormone therapy can speed up fat burning, although excess thyroid hormones can also lead to loss of lean muscle mass.
That is, it’s not just a matter of slow metabolism. We are not at all trying to say that obese people do not have any hormonal defects or disorders of fat cells. The problem with a slow metabolism is that the wrong hormones were blamed. Most scientists who have studied obesity in humans now talk about disorders of thermogenesis (the process by which the body gets rid of excess calories) and defects in insulin metabolism. In short, too much subcutaneous fat leads to the development of insulin insensitivity and further to excess insulin secretion.
Insulin control is the basis of all low-carb diets. Their critics say that insulin does not promote fat storage unless accompanied by an increased intake of calories. However, this is only true for people with normal size and number of fat cells. In addition, recent studies have shown that insulin regulates its own release in normal people and loses this ability as body fat levels increase (3.
Let us recall the recent discovery of resistin. Resistin, like leptin, is produced directly in fat cells, making them insensitive to insulin and is believed to be linked to the development of diabetes. Since enlarged fat cells work differently than normal fat cells, all these ideas about calories and insulin don't apply to them.
Although the larger number and size of fat cells make it more difficult to lose excess fat, the fact that many people have succeeded in losing it suggests that weight control is possible. So, if you have excess fat, you will have to deal with impaired sympathetic hormonal response (i.e., thermogenesis) and excess insulin activity. Simply reducing your calorie intake will lead to fat loss, but will be accompanied by an increase in appetite, which is not only difficult in itself, but can also lead to weight gain again.
Thermogenesis defect can be managed with reasonable training and certain nutritional supplements. Aerobic exercise causes the release of catecholamines such as epinephrine and norepinephrine, which not only have a beneficial effect on thermogenesis, but also directly promote the release of fats from fat cells by activating an enzyme called hormone-sensitive lipase.
People with a high percentage of body fat should start with light aerobic exercise as they lack the oxidative enzymes needed to burn fat. Over time, you can gradually increase the intensity of your workouts and move on to interval-type aerobics, which means alternating high-intensity loads, determined by your heart rate, with low-intensity ones during the same workout. This combination of loads produces the most powerful fat burning effect.
As the level of subcutaneous fat decreases, hormones such as growth hormone begin to be released more actively. Many obese people exhibit low levels of growth hormone, which also contributes to maintaining high levels of body fat. Growth hormone acts on fat cells in the opposite way to insulin; it promotes the mobilization of fat rather than its deposition.
Weight training is very important for controlling fat levels as it causes lean muscle mass to grow. As noted above, muscle mass determines your resting metabolic rate. In addition, regular resistance training improves insulin sensitivity, leading to tighter insulin and body fat control.
Dietary supplements used to regulate the thermogenic system of overweight people usually include ephedra or ephedrine, caffeine and other ingredients such as green tea. Such natural substances mimic the effects of catecholamines such as epinephrine and norepinephrine during beneficial thermogenic reactions leading to increased fat mobilization and oxidation when aerobic exercise is present. Contrary to some reports, these thermogenic supplements are safe for people who do not have cardiovascular disease or thyroid abnormalities.
Obese people are often persuaded to switch to a low-fat diet, which sounds reasonable. At nine calories per gram, fat is the most concentrated source of calories when compared to four calories from protein or carbohydrates. In addition, excess carbohydrates and proteins tend to be oxidized during their own metabolism, which is not the case with fats. The excess calories that come with them are sent directly to fat cells.
The problem with low-fat diets is that they do not differentiate between different forms of dietary fat and do not take into account the carbohydrate metabolism disorders that occur at high levels of fat in the human body. Obese people simply cannot oxidize carbohydrates in the same way as lean people; they tend to store excess carbohydrates as subcutaneous fat due to their problems with excess insulin (4. The results of a recent experiment presented at the Experimental Biology Meeting in 2001 showed that if fat cells are exposed to the separate effects of glucose and insulin, nothing happens, but when they act together, fat cells begin to grow rapidly.
Some types of dietary fats are very useful for people who want to lose weight, and the degree of obesity does not matter. This includes monounsaturated fats found in canola oil and olives. Under dietary conditions, they maintain levels of high-density lipoproteins, which have protective properties. Another category of “healthy” fats includes omega-3 fats, which are found in flaxseed oil and fish oil. In animal experiments, they actively helped reduce the size of fat cells. In addition, omega-3 fats increased insulin sensitivity by changing the density of cell membranes, which facilitated the interaction of insulin with cellular hormonal receptors. Fats to avoid include saturated and trans fats, although both saturated and monounsaturated fats help maintain normal testosterone levels in men.
So, if you have too many enlarged fat cells, the only option is a low-carb diet. Although these types of diets are often criticized for being high in fat, many recent studies have confirmed that typical low-carb diets are both safe and highly effective in removing excess fat. They have advantages over low-fat diets because they allow for better appetite control. And the point here is not at all in the fat content, as you might think, but in the presence of a large amount of protein, which contributes to the feeling of fullness (5.
Goose fat
This type is one of those available to us. It was valued most of all for its rich composition and quick help for various ailments. The specific smell forces it to be mixed with additional components to make it easier to take orally.
Effective recipes for bronchitis:
- Mix the fat with aloe, honey (cocoa, chocolate), heat until the components form a single mass. Add 1 tbsp. composition in a glass of warm milk and take orally once or twice a day until complete recovery.
- Grind the onion into a pulp and mix with the fat to form a thick mixture. Apply it to the back and chest, cover with film and wrap warmly. It is better to do it at night, and in the morning to enhance the effect by taking a dessert spoon of the composition inside.
- Onions can be replaced with garlic and mixed with fat in a ratio of 1:5. Use for rubbing only.
How quickly fat accumulates in the body. Types of fat in the body. Subcutaneous and visceral fat
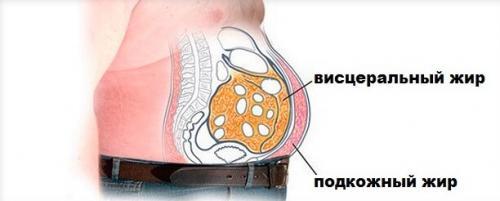
There are 2 types of fat in the human body:
1) subcutaneous
2) visceral
, as you already understood from the name, is located under the skin in our body, throughout the body. If excess calories begin to enter the body for a long time, then subcutaneous fat is deposited first. Moreover, the structure of subcutaneous fat depends on what foods you eat. For example, excessive consumption of lard (lamb, pork) leads to the fact that the fat layer becomes dense and elastic, this is especially noticeable on the stomach. But excessive consumption of high amounts leads to the fact that the fat layer becomes flabby and viscous, and has a jelly-like structure.

Also, where this fat will be deposited first depends on what gender you are, woman or man. In men, subcutaneous fat is primarily formed on the abdomen. But on women’s legs and buttocks.
is fat that accumulates around the organs of our body. When excess calories enter the human body for a long time, subcutaneous fat is deposited first, and then visceral fat. Well, when the moment comes when a lack of calories enters the human body, the opposite is true. Visceral fat “burns” first, and only then subcutaneous fat.

Both men and women are prone to the deposition of visceral fat. You have all seen people with oversized, huge bellies; in men it is also called a beer belly. So a huge beer belly is nothing more than excess visceral fat.
Badger fat
The lard from this little animal has strong antimicrobial properties. Since ancient times, it has been used for acute, chronic, protracted bronchitis, smoker's cough, and obstructive pulmonary diseases. It is active against tuberculosis, bronchial asthma, pneumonia.
The active components in badger fat can thin and remove mucus, soften the mucous membranes of the bronchi, and reduce inflammation.

There is a whole series of factory-made pharmaceutical preparations based on this healing agent for internal and external use, but they are prescribed by a doctor.
Folk remedies for bronchitis are:
- Use no more than a tablespoon of pure fat orally before meals three times a day.
- Rub the clean product onto the chest (bypassing the heart area), back, feet, and legs. After this, you need to warm up under a blanket for 1-2 hours. It is better to do the procedure at night.
- For a dry cough, to reduce an attack and facilitate the removal of sputum, fat is mixed with milk in a ratio of 1:3 and used orally. You can combine it with honey, jam or chocolate, after melting it.
- Compresses made from a mixture of badger fat, vodka and honey in equal proportions are effective. You need to apply the composition on gauze, apply it to your chest and back and wrap yourself up. This method is not used at elevated body temperatures.
Fat has a smell and taste, making it difficult to swallow. It is better for children and adults to mix it with other components when taking it orally.
How fat accumulates in the human body. Where does fat come from?
To regulate body weight, there are two mechanisms that our brain carries out: control of food intake and regulation of heat production and heat transfer. The supply of nutrients to the body is controlled by the food center of the brain. Our body has an express laboratory that analyzes the composition of blood and other media. Based on the test results, the food center gives signals about the need for food, which is usually called appetite, and in acute cases - hunger. The “opinion” of the stomach, which cannot tolerate absolute emptiness, is also taken into account. Its signals can sometimes be heard quite clearly, in the form of dissatisfied grumbling.
The body has two sources of energy: glucose from carbohydrates and fatty acids from fat stores. They are also regulators of energy consumption. The body constantly decides the question: “What to drown with? What source of energy should I use at the moment? Hormones help in solving this issue: insulin manages glucose, and growth hormone manages fatty acids. Reserves are not created to be used immediately. If food enters the body, energy is taken primarily from it. Glucose from food affects glucose receptors in the hypothalamus. This leads to a decrease in the supply of growth hormone from the pituitary gland. The concentration of fatty acids in the blood decreases. Glucose is released from the pancreas under the influence of insulin. It serves as fuel after eating. The reserve fat reserve is preserved. Excess glucose turns into fat and replenishes stores. This is a daily food type.
When food is not supplied to the body, for example at night, fat is used as fuel, the reserves of which are much greater than those of glucose. In addition, a supply of glucose is necessary for nervous tissues and in case of shortage, for example in times of stress, the body will synthesize it from proteins.
The state when such a switch from one type of fuel to another occurs clearly and without failure is called homeostat. The homeostatic mechanism can be disrupted, for example, with age. In this case, when receiving glucose, the concentration of growth hormone does not decrease, and the blood becomes oversaturated with fatty acids, glucose and insulin, resulting in obesity.
Contraindications
Despite the abundance of beneficial properties, like any medicine, animal fat has contraindications:
- Do not use externally for rubbing at elevated body temperatures.
- Pregnant and nursing mothers should avoid this treatment method unless recommended by their doctor.
- Children under 14 years of age are contraindicated from using any formulations with fat inside.
- Do not use internally for diseases of the stomach, liver, or cholelithiasis.
- If allergic reactions or individual intolerance occur, use in any form is prohibited.

How fat is stored in the body. We burn
So, the fat is released and transported along with the blood to the muscle. When it reaches this muscle, it needs to be burned in the mitochondria, the “power plants” of a person. And so that fat can burn, it needs enzymes and oxygen. If there is not enough oxygen or enzymes in the body, fat will not be able to be converted into energy and will be deposited in the body again.
This process is natural weight loss. Those. With the help of physical activity and a certain calorie intake, we create a deficit (shortage) of energy and in order to replenish its reserves the body decides to use its own resources.
Yes, breaking down fat is not everything!
A very important point for understanding when losing weight is that the process of breaking down fat does not yet ensure weight loss. Therefore, by the way, it is worth questioning cosmetic procedures that promise to provide you with the breakdown of fat and the destruction of fat cells.
Once the fat is broken down, it still won’t go anywhere. It will simply go from the cell into the bloodstream and hang around there until something is done to it. Otherwise, it comes back, filling the fat cells again, or gets stuck with cholesterol plaques in the vessels, which can lead to irreparable health problems.
Therefore, even fat released from cells must be “burned.” This can be done by using it as fuel for muscle work.
That is, to lose weight, it is necessary for the body to receive a load that would be accompanied by a large consumption of oxygen, and at the same time have all the necessary enzymes for burning fat (they are contained in food).
Let's not forget about water. This mechanism only works if there is a large amount of water in the fat cells, because the breakdown of fat occurs in the water-containing interior.
Let us repeat the above for better absorption: fat in our body is not stored as a solid mass, but is located in the form of a chemical triglyceride in fat cells, which are called lipocytes.
In order to release fat from its tenacious hands, the cell must first carry out lipolysis - break down triglyceride into fatty acids and glycerol. And only in this form the accumulated fat releases the cells and is sent through the blood vessels to its destination in order to perform the required function - supply the body with energy, build the cell membrane, etc.
The main hormones in the process of lipolysis are hormones. They are the ones who “open the door” of the cell to give it the opportunity to share the accumulated fat. The key point in this chain of interactions is that the hormones secreted by the glands circulate evenly through the bloodstream and control the fat cells.
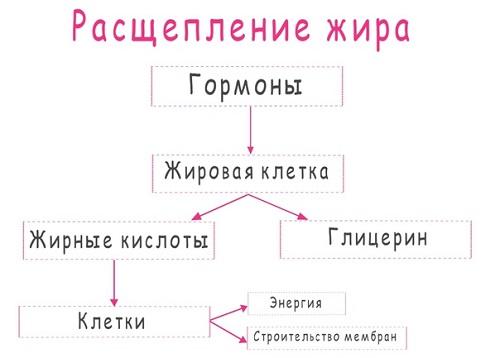
It is absolutely impossible to keep them in one place, for example, in the buttocks or abdominal area, forcing fat cells to “open” only there.
Moreover, in those very problem areas that you so badly want to lose weight locally, fat will be the most difficult and take the longest to come off. After all, despite the fact that hormones move throughout the body at the same speed and in the same quantity, they cannot immediately “open” all cells - some of them have reduced activity of cellular receptors (the very “doors” that open the cell).
In addition, lipolysis is also influenced by blood supply (capillarization), which provides greater blood flow capacity in the muscles and promotes the transfer of energy substances.
Those. alas and ah - you cannot burn fat locally. The whole body is involved in the process of fat loss, and we lose fat in a “first come first served” manner (we remind you: first visceral - then subcutaneous - and only then fat deposits based on gender).
By the way, if you want to find out where fat is actually utilized, then read the article “Where does fat go when losing weight?” !
The best option for losing weight: a calorie deficit and going to the gym, coupled with an active daily life. Why the gym: how to lose weight without harm to your health.
If for some reason strength training is contraindicated for you, then you can do cardio or any other physical activity! Skiing, skating, swimming, basketball and dancing, walking - all this burns calories, which means it burns fat.
But without nutrition control, you won’t get rid of a single gram with any training, if the nutrition is really fundamentally wrong.
Dog fat
The fat of our smaller brothers is also extremely beneficial for the body and actively fights bronchitis and other lung diseases. It has bactericidal properties, strengthens the immune system, and helps restore mucous membranes. The product helps with prolonged bronchitis.
Dog fat is used in its pure form. To do this, melt it in a water bath and drink 1 tbsp. before meals twice a day. Treatment period is 2-4 weeks. Can be mixed in equal proportions with honey.
Children under 14 years of age are not allowed to take this product internally! The chest, back, and feet are rubbed with pure fat, and then wrapped in a blanket.
What research should you listen to?
Research directly related to human health is divided into two main groups - epidemiological and interventional.
Epidemiological studies study the relationships between causes and effects : for example, smoking and lung cancer, exercise and heart disease. Such studies may show that two processes are related, but this does not mean that one is necessarily the cause of the other. For example, based on the presence of a television in the house, one cannot conclude that television causes heart disease. The issue here is not the presence of a television, but the sedentary lifestyle caused by watching television.
Causality is best identified through intervention studies . Participants in such studies are exposed to a certain effect (intervention), and then the results are compared with data from a control group.
No matter how authoritative epidemiological studies are, their results cannot end the debate about how much fat is to blame for obesity. This still requires intervention studies. If fat really makes you fat, then low-fat diets should be effective for weight loss?
In order to assess the effectiveness of a particular technique as accurately as possible, it is necessary to summarize the results of several studies. That's exactly what the respected international scientific community known as the Cochrane Collaboration did. The scientists were especially interested in the ability of the experiment participants to maintain a stable weight for a long time.
Low-fat diets were compared with diets that, while restricting calories, did not completely eliminate fat. Low-fat diets led to very modest results: after 18 months, the participants weighed the same as at the beginning of the experiment.
Diets that did not eliminate fat outperformed low-fat diets. What conclusion suggests itself? Low-fat diets are less effective for weight control than diets that contain fat.
The statement that fat does not make you fat and that reducing your fat intake does not help get rid of the body's accumulated fat reserves seems illogical. However, everything falls into place when we understand how fat deposits in our body are regulated.
Bear fat
It contains a lot of vitamins (especially B), minerals, trace elements, and other active substances that get there with food. And the bear eats a varied diet - it eats meat, fish, herbs, berries and nuts. Bear lard treats lingering and chronic bronchitis. Bear fat is used for bronchitis in adults and children over 2 years of age.
How to use bear fat for bronchitis:
- For dry cough, drink a glass of milk with 1 tbsp twice a day. facilities.
- Rubbing the chest and back at night, warming up after rubbing under the blanket.
- You can use it as a massage product. Apply to the skin, massage your back, cover with film or parchment and wrap with a woolen scarf. Do the massage for no more than 5 minutes.
It also helps with tracheitis and severe cough.
Pork fat
This available fat is effectively used for colds at the beginning, for regular and obstructive bronchitis:
- At the first sign of a cold, rub your feet with melted lard and put on warm socks.
- Make green tea with milk, add fat on the tip of a spoon, and a pinch of hot pepper. Drink before bed.
- As a rub, pre-melted fat is mixed with vodka. Rub the back and chest, cover with film and wrap in a woolen scarf. It's good to hide under the blanket. 50 gr is enough. lard and 2 tbsp. vodka.
- For obstructive bronchitis, use lard in its pure form, a tablespoon 5 times a day. To make it easier to swallow, you can mix it with honey or take it with honey and wash it down with warm milk.