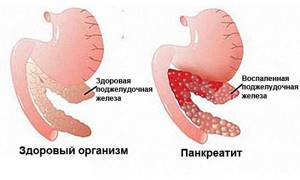
Accumulation of fat in the pancreas, defined as pancreatic obesity, is usually an incidental finding on transabdominal ultrasound. This disease without significant alcohol consumption is defined as non-alcoholic fatty pancreatic disease and, although its clinical impact is still largely unknown, disease progression could hypothetically lead to chronic pancreatitis and possibly the development of pancreatic cancer.
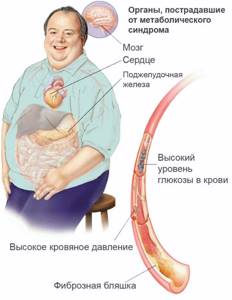
Recently, metabolic problems such as diabetes, central obesity, fatty liver, and dyslipidemia have emerged as important risk factors associated with nonalcoholic fatty pancreatic disease and cancer; however, the exact mechanism is not yet fully understood. Early detection and screening of pancreatic cancer in clinical practice is challenging due to nonspecific symptoms, anatomical location, accuracy of biomarkers in clinical practice, and the high risk of radiation and contrast agent exposure from imaging studies. Endoscopic ultrasound is still considered the best method for assessing the pancreas and for screening and diagnosing cancer. However, there is still a lot of controversy regarding its cost, availability and operator training experience.
What is pancreatic steatosis
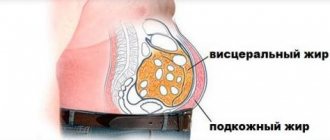
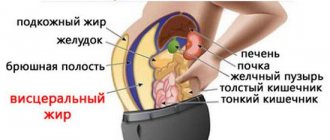
The accumulation of fat in the pancreatic tissue is called steatosis, or fatty degeneration of the organ. You can also come across such a diagnosis - non-alcoholic fatty disease. This condition often accompanies obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome (a combination of obesity, excess cholesterol, blood glucose, hypertension).
This is explained by the fact that the pancreas produces an enzyme for breaking down fat - lipase. It is the one that comes into first contact in the small intestine with foods containing lipids. With its help, fats are converted into glycerol and fatty acids. Pancreatic juice also contains soda (sodium bicarbonate), which creates an alkaline environment for lipase to work.
Pancreatic steatosis
If too much fat is consumed in food, it results in the formation of large amounts of free fatty acids. Under their influence:
- inflammation of the tissue occurs, followed by its replacement with fatty tissue;
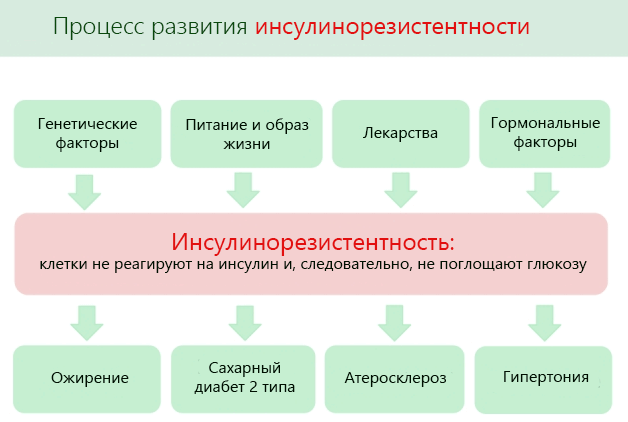
- Insulin secretion and sensitivity to it are impaired, insulin resistance appears;
- gland cells experience a lack of energy, their activity decreases, and less and less of the necessary lipase is formed.
Other biologically active compounds secreted in excess by adipose tissue are also involved in organ damage - interleukin 6, leptin, adiponectin, tumor necrosis factor.
We recommend reading the article about ultrasound of the pancreas for a child. From it you will learn about the indications for performing an ultrasound of the pancreas in a child, preparation for the study, the features of performing an ultrasound in a child, as well as about the norms in indicators and deviations, and their causes.
And here is more information about ultrasound of the pancreas.
Stages and clinic of obesity
Stages of lipomatosis depending on the composition of fat in the organ:
- 1st degree – adipose tissue makes up 30% of the organ’s weight.
- 2nd degree – fat cells make up 60% of the weight.
- 3rd degree – fat mass more than 60% of the organ’s weight.
An ultrasound examination reveals the pathology that has occurred in the gland. Lipomatosis consists of small foci located in a chaotic manner throughout the gland. The amount of fat and the size of the gland are assessed during examination. If there is little adipose tissue, then the pancreas does not experience any obstacles to normal functioning.
A sick person is prescribed medical procedures when certain areas of the gland are enlarged. This causes serious complications and diseases.
The functions of the gland are not performed normally if fat cells have accumulated near its ducts. This does not depend on the severity of obesity. The process of digestion of food is disrupted when the gland ducts are compressed. In this case, the patient develops unpleasant symptoms: vomiting, nausea, pain in the gland, heaviness in the abdomen. In this case, food is not digested enough, causing weakness in the body, bloating, and increased formation of gas.
Causes of pancreatic obesity
Conditions that increase the risk of fatty infiltration (impregnation of tissue with fat) of an organ include:
- excess body weight, especially belly fat;
- carbohydrate metabolism disorders - type 2 diabetes mellitus, prediabetes, metabolic syndrome;
- hereditary diseases with changes in absorption in the small intestine or the formation of defective lipase;
- iron deposition (hemochromatosis) in the pancreas, frequent blood transfusions, overdose of iron-containing drugs;
- excess cortisol in diseases of the adrenal glands, long-term use of synthetic analogues (for example, treatment with Prednisolone);
- viral infections - HIV, hepatitis B, reoviral diseases (intestinal flu);
- chronic inflammatory process in the pancreas (pancreatitis), liver (hepatitis), gall bladder (cholecystitis), duodenum (duodenitis);
- long-term, often uncontrolled, use of medications that lower cholesterol levels, somatostatin, hormonal drugs, and dietary supplements for weight loss.
Risk factors for pancreatic steatosis have also been established:
- unhealthy diet with consumption of fatty foods, mainly meat, lack of vegetables and fruits in the menu, overeating;
- fasting, strict poor diets, especially monotonous protein diets, ketogenic;
- adolescence and old age of patients;
- regular drinking of alcohol;
- male gender;
- smoking;
- excess triglycerides, cholesterol in the blood;
- obesity, pancreatic diseases, diabetes mellitus, insulin resistance in close relatives;
- low physical activity.
Folk remedies for obesity
Obesity causes problems in life. To cure this pathology, it is necessary to reconsider your lifestyle, exercise, pay attention and use traditional medicine and medications.
Types, symptoms, causes
Obesity is characterized by an increase in body weight through the accumulation of fat. The clinic of this process has been determined:
- accumulation of fat tissue in the mammary glands, thighs, abdomen, buttocks;
- excessive appetite, shortness of breath, fatigue.
- heredity;
- excessive consumption of foods;
- diseases of the digestive system, kidneys;
- taking hormones.
Symptoms of organ dysfunction
The difficulty in identifying this disease is that in most cases patients do not complain. An asymptomatic course is especially characteristic in the early stages of the development of steatosis, when it is still completely cured.
Subsequently, under the influence of a sluggish inflammatory process and dystrophy (depletion of reserves), the following occurs:
- pain in the epigastric region, radiating to the back. Its intensity is moderate or weak, increases when eating fatty foods, and usually appears 30-45 minutes after eating;
- nausea, less often vomiting;
- rumbling in the stomach, bloating;
- alternating diarrhea and constipation or increased bowel movements.
There is usually an increase in body weight and an increase in waist size, while with typical pancreatitis, patients lose weight. Among the accompanying diagnoses, the following are often found:
- arterial hypertension;
- coronary heart disease (angina pectoris);
- fatty liver;
- atherosclerotic ischemic colitis, enteritis (attacks of abdominal pain due to lack of blood flow to the intestines);
- stagnation of bile (cholestasis);
- xanthomatosis (fatty plaques) on the skin of the upper eyelid, elbow, face, neck;
- small vascular aneurysms - red droplets on the body (dilated capillaries that do not disappear with pressure).
Main symptoms
Can pain in the right hypochondrium after a fatty meal indicate the development of lipomatosis? We list the main signs of this disease:
- Girdle pain felt in the right hypochondrium after eating food (any food, not necessarily even fatty food).
- Periodic bloating, accompanied by flatulence.
- Constant thirst.
- The appearance of small ulcers in the mouth.
- Periodic vomiting, nausea.
- Abnormal stool. Often, inclusions of blood or fat are found in the patient's stool.
- General weakness, apathetic state.
- If the disease is advanced, the patient begins to lose weight significantly.
What are the risks of obesity if the pancreas does not work properly?
Inflammation in the tissues of the gland against the background of fatty infiltration is difficult to treat. Over time, fibrosis forms in its place - connective tissue fibers grow. At this stage, the changes become irreversible, and the release of enzymes and hormones (insulin, glucagon) rapidly decreases. This is accompanied by impaired digestion of food, weight loss, signs of vitamin deficiency, severe diarrhea, and worsening diabetes.
Excess fat can lead to blockage of blood vessels and ducts, the development of acute pancreatitis and organ destruction - pancreatic necrosis.
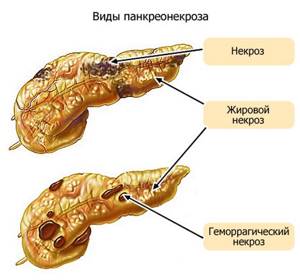
Pancreatic steatosis also causes transformation (degeneration) of normal cells into a cancerous tumor. An important feature of this pathology is that the risk of cancer is higher if obesity occurs in a teenager or at a young age.
Symptoms of deviation
The initial stages of obesity in the gland are asymptomatic. The clinical picture becomes pronounced when normal pancreatic function is impossible. The pathology progresses extremely slowly.
Symptoms appear when the pancreas begins to put pressure on neighboring organs. Gradually, the clinical picture becomes more extensive and pronounced. The manifestation of symptoms is associated with:
- dysfunction of the pancreas;
- compression of neighboring organs and tissues.

With problems with the pancreas, patients often complain of nausea
First of all, the functioning of the digestive system is disrupted. During obesity, the body finds it most difficult to digest foods high in protein. The main symptoms of glandular lipodystrophy include:
- nausea;
- painful sensation in the abdominal cavity;
- increased gas formation;
- heaviness and bursting feeling in the stomach;
- frequent fatty stools.
Pancreatic obesity is also manifested by hormonal imbalance. Glucose levels increase. Foreign impurities are observed in fecal matter.
Pain in a patient in the abdominal cavity is a sign indicating the formation of disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. If treatment is not treated in a timely manner, fat cells begin to form groups. In this case, the patient's obesity in the pancreas is accompanied by the development of a benign neoplasm. At first, the condition does not pose a serious danger.

Flatulence and bloating may occur
Deterioration of the condition occurs when a benign formation begins to grow rapidly. The neoplasm compresses blood vessels and nerve endings. In this case, the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- bloating;
- pale skin;
- frequent nausea and vomiting.
The condition requires urgent treatment.
Diagnosis of steatosis
The criteria for diagnosis are:
- external signs of obesity, body mass index (weight/height square in meters) above 27-30;
- in the blood - excess cholesterol, triglycerides, glucose. Amylase activity is reduced, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase is increased. During inflammation, high levels of leukocytes, ESR, and amylase activity are detected;
- glucose tolerance test – prediabetes, diabetes;
- Ultrasound – increased size, diffuse changes: uneven, heterogeneous structure, reduced granularity, blurred external contour. The pancreatic duct is often dilated. Often there is simultaneous hepatic steatosis;
- CT or MRI - the density of the pancreas is 20-30 units lower than the spleen, there are layers of fat between the lobules. A widespread pattern of fatty infiltration or limited accumulation of fat in the body and tail may be detected;
- Fine-needle biopsy is necessary for focal fat deposits to distinguish them from a tumor.
Nutrition for lipomatosis
There is an opinion in everyday life that reducing the amount of fat in the diet will help stop lipomatosis. This is a completely false statement.
Even completely stopping fat intake will not stop the degeneration of healthy cells into fat cells. The development of lipomatosis has nothing to do with nutrition. However, it is still better to exclude fats. This will have a beneficial effect on the body:
- relief of pancreas;
- getting rid of extra pounds.
Reducing the amount of incoming fat helps alleviate the condition; many signs of the disease recede and become less pronounced. In the absence of external manifestations of the disease, we can talk about preserved pancreatic functionality.
This means that all the ducts are functioning normally, they are not compressed by adipose tissue. With normal functioning of the pancreas, limiting fats in food will help you lose weight, but will not affect the further development of the disease.
Treatment of pancreatic obesity
The main condition is weight loss. For this purpose, a low-calorie diet is prescribed (a deficit of 500 kcal from the calculated one), physical activity of at least 45 minutes a day. In the absence of pain and digestive disorders, therapy is aimed at normalizing the metabolism of carbohydrates (treatment of diabetes, prediabetes), fats (cholesterol-lowering agents), and improving the outflow of bile.
For signs of pancreatic insufficiency (pain, bloating, unstable stool) and severe metabolic disorders, medications are prescribed:
- acidity reducing agents – Omez, Controloc;
- enzymes containing lipase in microspheres - Creon, Pangrol, Ermital;
- hypolipidemic (Crestor, Traikor) until a sustainable decrease in cholesterol and normalization of lipid ratios;
- sorbents – Enterosgel, Polysorb, Atoxyl;
- probiotics to normalize microflora - Linex, Hilak forte;
- to increase tissue response to insulin - Metformin, Januvia;
- antioxidants – vitamin E, Berlition, Mexidol;
- hepatoprotectors to improve liver function - Essentiale, Gepabene, Citrarginine;
- antispasmodics for pain - No-shpa, Riabal, Buscopan;
- vascular agents – Mikardis, Prestarium.
In severe cases, blood purification sessions are performed using plasmapheresis, intravenous administration of Heparin and short-acting insulin to enhance lipase activity.
Folk remedies against obesity
1st degree obesity:
- Dry gooseberries are poured with water and boiled for 10 minutes. Drink 4 times before meals.
- Collection of mint leaves, chamomile, rowan fruits, 10 g, pour boiling water in a thermos, infuse. Drink 0.5 cups 4 times.
2nd degree:
- Tea with healing properties: elderberry, jasmine, string, hop cones, verbena, walnut. 1 tbsp. Pour boiling water over a spoon and drink like regular tea.
3rd degree : 1 spoon of dandelion roots, mint leaves, parsley, buckthorn is brewed with boiling water. Drink 0.4 liters in the morning.
Herbal treatment
A collection of elderberry, linden, chamomile, and fennel is brewed and drunk 3 times. Obesity of the glands is cured: before meals, 25 drops of corn silk. Make a decoction: 1 tbsp. spoon for 1 tbsp. boiling water
Treatment with honey
The patient lies down on a plane, the fatty parts of the body are smeared with honey. A massage is performed for 15 minutes with palms. After the procedure, wrap it with film, then wash off the honey with water.
Treatment with leeches
Medical specialists perform a hirudotherapy procedure that cleanses the body and restores functions. Leeches lower cholesterol, break down fats, and thin the blood.
Diet to restore organ function
Drug therapy is ineffective without dietary changes. In addition to the need for a low-calorie diet, it is recommended:
- exclude fatty meats, offal, canned food, all sausages, and deli meats from the menu;
- completely abstain from alcohol in any form, drinks with dyes, flavors;
- Every day you need to eat at least 400 g of vegetables and 200 g of fruits, 30 g of nuts or seeds (not fried and without salt);
- use healthy products - pumpkin, carrots, sea buckthorn, apricots, zucchini, cauliflower and broccoli, water porridge, cucumber and herb salads, fresh cottage cheese up to 5% fat, fermented milk drinks;
- carry out culinary processing by boiling in water, steaming, baking in the oven, frying and stewing with fat is prohibited;
- prepare vegetarian first courses;
- Lean meat and boiled fish are allowed 1-2 times a day, 100-150 g, boiled vegetables are suitable as a side dish, in the absence of an inflammatory process - fresh in the form of a salad with vegetable oil.

If you are overweight, have impaired tolerance to carbohydrates or have diabetes, sugar, sweets, flour products, sweet fruits, and honey are completely excluded from the diet. If there is concomitant arterial hypertension, then table salt is limited to 3-5 g per day. In case of simultaneous fatty liver damage, it is important to avoid hot, spicy foods, store-bought sauces, smoked meats, and canned foods.
We recommend reading the article about MRI of the pancreas. From it you will learn about the indications for MRI of the pancreas, restrictions on its use, when it is prescribed with contrast, and what the examination can reveal.
And here is more information about the hormone somatotropin.
Obesity of the pancreas occurs when there is an excess intake of fat from food, increased body weight, and metabolic disorders. In the early stages, fatty infiltration is asymptomatic. With significant lipid deposition, insufficient secretion of enzymes and hormones occurs. Patients have an increased risk of pancreatic necrosis and cancer.
To make a diagnosis, blood tests, ultrasound and tomography are prescribed. Treatment involves diet therapy and medication.
Auxiliary treatment
Folk remedies are used as additional therapy. These are infusions and decoctions of herbal preparations. They are used only with the permission of the attending physician.
The most common decoction is based on valerian, nettle, calendula, St. John's wort. All herbs are mixed together in equal proportions - 10 g per glass of boiling water. Drink the infusion in equal parts seven times a day.
Decoctions of mint, rose hips, chamomile, immortelle, and wormwood are also used.
They also turn to physiotherapy, hirudotherapy (the use of leeches), spa therapy, and the use of mineral waters.
Useful video
Watch the video about the connection between pancreatic cancer and obesity:
Similar articles
- MRI of the pancreas: preparation...
MRI of the pancreas is prescribed if it is impossible to accurately identify the problem on ultrasound. A little preparation for the examination is required. Indications: suspected diffuse changes, cancer, cysts. MRI with contrast will help identify the smallest sizes of formations. Which is better - CT or MRI? Read more - Ultrasound of the pancreas: how to prepare, normal...
If certain diseases are suspected (cancer, pancreatitis, tumor, lump, cyst), an ultrasound scan of the pancreas is prescribed for diabetes. This accessible method allows you to find signs of diffuse changes and problems, and establish the normal size for an adult. How to prepare? Why is echogenicity needed? Read more
- Cholecystitis and diabetes: causes of development, nutrition, than...
If a patient has cholecystitis and diabetes at the same time, then he will have to reconsider his diet if the first disease has just developed. The reasons for its appearance lie in increased insulin, alcoholism and others. If acute calculous cholecystitis develops against the background of diabetes mellitus, surgery may be required. Read more
- What does excess pancreatic hormone cause?
The somatostatin hormone is mainly responsible for growth, but the main functions of synthetic analogues are also used for other serious diseases. What happens if there is an excess of pancreatic hormone? Read more
- Ultrasound of the pancreas for a child: preparation...
In some cases, an ultrasound scan of the child's pancreas is performed. It is important for a qualitative study to carry out preliminary preparation. What are the norms and deviations? Read more
What's under the stomach?
The pancreas is the same one that is located under the stomach, which is why it gets its name - an organ that is very important for the normal functioning of our body. What can I say, is there anything useless in our body?
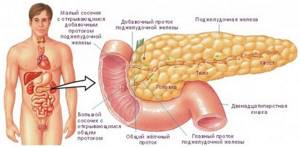
Mother Nature got it all right, but not all the cogs always function as they should. Sometimes it even happens that it seems to us that everything is normal. But in fact, as in the case we are talking about today, you may not know for a long time that a failure has occurred somewhere. The failure is serious and can lead to irreversible consequences.
Unnoticed worker
After all, this body is in charge of such incredibly important processes as
- secretion of most digestive enzymes - it helps digestion and absorption of nutrients
- the production of hormones, which makes it an important participant in the process of regulating carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism, in other words, metabolism.
- production of insulin, the lack of which provokes diabetes.

To avoid going to the doctor later
As we know, it is better to prevent any disease than to treat it later. What to do in this case? What preventive measures exist to prevent pancreatic obesity?
- Do not abuse alcohol and do not smoke.
- Control your weight. Don’t miss the sneaking first degree of obesity, which is often mistaken for a harmless extra fold on the stomach.
- Do not overeat fatty foods.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle: spend more time outdoors, get enough sleep, avoid stress, eat right and provide your body with suitable physical activity.

It will also be very useful to read a good book in which the principles of proper nutrition are laid out on the shelves. For example, the book by Svetlana Bronnikova, the first and so far only conscious nutrition trainer in Russia, psychologist and psychotherapist, specialist in the field of digestive problems, “Intuitive Nutrition. How to stop worrying about food and lose weight."
In it, Svetlana talks in a simple and understandable language to the widest range of readers about how to improve your diet in an ordinary, non-dietary way. As a result, reduce weight and thereby avoid problems associated with obesity.