Obesity-related diseases have been spreading rapidly in recent years due to affluent lifestyles, poor eating habits and technological advancements that are disabling people from physical activity. Empirically proven cases of alarming health consequences from all this include obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. The number of cases of such pathologies is growing around the world at an alarming rate.
Along with the emergence of “lifestyle diseases,” the prevalence of metabolic syndrome—a range of metabolic disorders associated with insulin resistance, inflammation, and blood lipid disorders—is increasing.
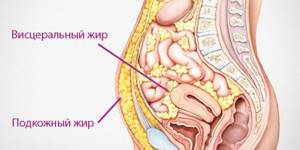
The diagnostic marker of this syndrome is abdominal or visceral obesity, characterized by excess visceral or intra-abdominal adipose tissue. It should be noted that metabolic syndrome is not necessarily characterized by the classic risk factors for obesity and diabetes, such as LDL cholesterol, but rather hypertriglyceridemia, HDL cholesterol, and high blood pressure are more common factors.
High blood pressure
People with visceral obesity experience physiological imbalances, particularly altered adipokines, endothelial function, insulin resistance, and a proatherogenic state. In addition, people with abdominal obesity have a relatively high risk of cardiovascular and cardiometabolic diseases, especially when they also suffer from hypertension or dyslipidemia.
Abdominal obesity: causes
The cause of this disease is an imbalance between the calories entering the body from food and their expenditure. The energy intake into the body exceeds its expenditure, and the excess begins to be stored in the form of fat. Well, what contributes to this? There are several reasons and, as a rule, they appear in combination and do not “go” alone: - disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract, which lead to a constant feeling of hunger and systematic overeating; - passive lifestyle, little movement, both at work and during rest; — disruption of metabolic processes in the body; - psychological factors (stress and depression), which are caused by insufficient levels of serotonin. The development of abdominal obesity due to dysfunction of the hypothalamus, and a decrease in the perception of the satiety hormone - leptin. People with this disease have normal leptin levels, but the body does not respond to it. Abdominal obesity is not easy to treat due to the psychological reasons on which this disease depends. But it is precisely stressful conditions that “force” a person to absorb food in huge quantities.
Signs and symptoms
Abdominal - internal - fat necessarily surrounds all internal organs in the human body - liver, pancreas, heart. The largest amount of fat is located on the anterior abdominal wall. Fat protects internal organs (intestines, stomach, spleen) from mechanical stress. In adults with normal body weight, the weight of the “protective pad” is 3-3.5 kg, the internal organs function normally, and the appearance does not change.
With visceral obesity, the amount of fat increases - its total weight can exceed 10-20 kg, the abdominal wall begins to bulge, and the functions of internal organs are impaired.
A person's body mass index may remain within the normal range, but a diagnosis of abdominal obesity may still be made. For a woman, the critical waist size is more than 80 cm, for a man - more than 94 cm.
Additional symptoms of the condition:
- arterial hypertension – blood pressure often increases;
- diabetes mellitus type 2;
- violation of metabolic processes in general; in particular - slow intestinal metabolism, impaired bile secretion, uric acid deposition, causing arthrosis.
Visceral fat, when accumulated in large quantities, takes on a hormonal function and begins to stimulate the adrenal glands, which synthesize cortisol, the stress hormone. Under the influence of cortisol, the body is in chronic tension, internal organs work “to wear out”, as if under stress.
The production of another hormone, interleukin-6, also increases. It stimulates the mobilization of energy in adipose tissue and muscles, which leads to an increase in the patient’s temperature. Constant low-grade fever and a general condition on the verge of inflammation exhaust the body and contribute to a decrease in immune status.
Weight gain has a particularly negative effect on men. Their production of female sex hormones increases, libido decreases, and sexual function is impaired. Women are luckier - the condition affects the sexual sphere only at a severe stage of obesity (when body weight exceeds normal by 40%).
Patients with severe visceral obesity necessarily require treatment; the most severe manifestation is sleep apnea. A person can suffocate in their sleep.
Abdominal obesity: complications
This disease is dangerous not because of the extra pounds, but because of the complications it causes. First of all, abdominal obesity affects the normal functioning of the cardiovascular system, causing heart and vascular diseases: - myocardial infarction; - vascular atherosclerosis; - arterial hypertension; - enlargement of the left cardiac ventricle; - stroke; - coronary heart disease; - deterioration of blood clotting. Among other things, it is the cause of such serious diseases as diabetes and metabolic syndrome. In women, abdominal obesity causes increased production of male sex hormones, resulting in menstrual irregularities and hirsutism.
Calculation of normal body weight. Obesity levels
To find out what weight is normal, use a simple formula: Height (cm) – 100 = normal weight. Example: 189cm-100=89, that is, with a height of 189 cm, the weight should ideally be 89 kg. The permissible error is 8-10 units. Based on this formula, 4 degrees of obesity are distinguished:
1st degree. Excess body weight is 8-10 kg. The disease does not cause any inconvenience for humans. During physical activity, shortness of breath appears, which quickly goes away with rest.
2nd degree. Weight exceeds the norm by 10-15 kg. Shortness of breath and sweating appear even with minor physical activity. My legs get tired quickly and swell in the evening. The human figure undergoes changes, visible fat deposits appear on the stomach and arms.
3rd degree. Excess body weight is 50% or more of normal weight. Increased load on the heart and lower limbs negatively affects a person’s mobility. Physical activity is reduced to a minimum.
4th degree. Very rare. A person's excess weight exceeds normal weight by 4-5 times. The patient practically does not move and cannot care for himself. The load on the heart, liver, kidneys and other organs is catastrophic. Without medical care, a person dies.
Abdominal obesity: treatment
Treatment for this disease depends on the individual, i.e. Full control over this process rests with him. On the one hand, it is good when the treatment is under the complete control of the patient, but on the other hand, this requires a certain amount of willpower. The first thing that includes the treatment of abdominal obesity is diet. It is low-calorie with limited consumption of fats (primarily animal fats), since they have a high cholesterol content. The diet is prepared by a specialist taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient: his weight, degree of obesity, gender, food preferences. Secondly, this is the correction of physical activity and its regularity. If abdominal obesity occurs against the background of any disease, then an appropriate method of treating the underlying disease is used. The difficulty in treating abdominal obesity is that during this therapy it is necessary to raise the patient’s immune status and correct the immune system if obesity has caused complications in the form of heart, liver or kidney diseases. Dysfunction of the immune system is the main cause of all diseases, incl. and abdominal obesity, and without eliminating its malfunctions, nothing can be cured. It is for this reason that Transfer Factor is used in the complex treatment of abdominal obesity and related diseases. It supports and strengthens the human immune system, subsequently preventing a “rollback” to previous positions after completion of therapy. The basis of this drug is made up of immune molecules of the same name, which, when entering the body: - eliminate failures of the endocrine and immune systems; - being information particles (of the same nature as DNA), transfer factors “record and store” all information about foreign agents - causative agents of various diseases that (agents) invade the body, and when they invade again, “transmit” this information to the immune system a system that neutralizes these antigens; — eliminate side effects that are caused by the use of other medications. There is a whole line of this immunomodulator, from which Transfer Factor Advance and Transfer Factor Glucouch are used in the Endocrine System program for the prevention and complex treatment of endocrine and immune diseases and complications, including abdominal obesity .
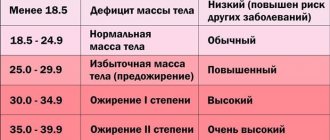
Table of the main criteria that determine the parameters of obesity
| BMI, kg/m2 | Waist circumference, cm | |
| Normal weight | < 25 | ≤ 102 |
| Initial overweight | 25 — 29,9 | ≤ 102 |
| Obesity 1st degree | 30 — 34,9 | ≤ 102 |
| Obesity 2 degrees | 35 — 39,9 | ≤ 102 |
| Obesity 3 degrees | > 40 | ≥ 102 |
Types of obesity
Medicine knows 3 types:
- Visceral is the deposition of fat on the internal organs of a person.
- Gynoid - fat is deposited mainly on the thighs, buttocks and below the navel.
- Abdominal - excess weight due to excessive fat deposits in the waist and abdomen.
The latter type is becoming increasingly common. If earlier doctors noted a higher percentage of morbidity in men, now women have become just as actively exposed to this disease.
How to deal with abdominal obesity?
The main goal of combating obesity is to eliminate visceral fat from the body.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a comprehensive examination, carefully collects anamnesis, and, if necessary, refers you to other specialists for consultation.
If there are problems with the hormonal function of the body, it is necessary to do an ultrasound of the thyroid gland. Based on the results of the analysis, hormonal medications are prescribed.
An increase in blood sugar is an alarming sign of the onset of a disease such as diabetes. Complex treatment includes drugs that reduce blood glucose. In such cases, it is necessary to fight the cause (disease), and not the consequence (excess weight).
If obesity is hereditary, treatment methods are developed together with an endocrinologist and immunologist.
Obesity treatment
The pharmaceutical industry offers a wide range of medications for weight loss. They differ in effectiveness and method of application:
- to reduce appetite;
- causing a feeling of satiety;
- increasing energy consumption;
- promoting the rapid breakdown of fats in the body.
Medicines are taken only as prescribed by a doctor. You can choose only tea for weight loss on your own.
Liposuction
This is a surgical operation during which fat is pumped out from problem areas of the body. Indicated in severe cases (stage 3-4 obesity). The operation is simple and takes place under general anesthesia. Up to 6 kg of fat is pumped out in one session. Working capacity is restored within a day. To achieve the best effect, it is advisable to wear special underwear for 3 months.
If serious violations of organs and systems are not observed, a comprehensive weight loss program is developed. It includes therapeutic nutrition, physical exercise, and consultation with a psychotherapist.
Medical nutrition
First of all, it is necessary to reduce the consumption of high-calorie foods.
Excluded from the diet:
- cakes;
- pies;
- candies;
- cookie;
- baking;
- confectionery;
- canned food;
- smoked meats;
- pickled vegetables;
- salty fish;
- fatty meats;
- potatoes, pasta;
- sparkling water;
- spicy snacks.
The daily diet should include:
- vegetables fruits;
- black bread;
- honey (as a sugar substitute);
- dairy products;
- lean meat;
- fish;
- greenery;
- eggs;
- the vinaigrette.
A nutritionist will help you create a menu for each day. You need to eat often (5-6 times a day), in small portions (serving no more than 250 grams). At night, be sure to drink a glass of kefir or low-fat yogurt.
Fasting days (apple, cottage cheese, meat, rice, fruit, dairy) are required once a week.
However, without physical activity, the results of treatment will be insignificant.
Therapeutic exercise for abdominal obesity
To reduce excess weight, it is necessary that the energy supplied from food is not only completely wasted, but also that its deficiency is felt. In such cases, physical education comes to the rescue.
Correctly selected set of exercises:
- helps to completely waste energy;
- trains the heart;
- strengthens and builds muscle mass;
- promotes fat burning and weight loss;
- improves the functioning of the pulmonary system;
- increases a person’s performance and vital activity.
The set of exercises is compiled according to the principle “from easy to difficult”:
- The initial stage includes more exercises for warming up, stretching, developing joints, and bending in different directions.
- Subsequently, exercises are added: walking, easy running, squats, jumping in place.
- And only then can you do abdominal pumping, push-ups, sprinting, and so on.
- To consolidate the results, it is useful to take up swimming, cycling, tennis, and Nordic walking.
Ways to remove visceral fat from the abdomen
To remove visceral fat in men and women, a comprehensive approach is required. The key to effectively getting rid of internal fat is a set of the following measures:
- cleansing the intestines and liver;
- balanced diet;
- physical exercise;
- massage;
- taking medications;
- traditional methods.