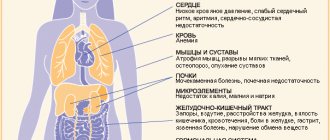
Testosterone is the main male sex hormone. It is produced primarily in the testes by Leydig cells. In small quantities - in the adrenal cortex.
Testosterone influences the development of male genital organs, regulates spermatogenesis and sexual behavior, and also participates in some parts of metabolism. Low testosterone in men leads to decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and mental disorders.
Causes of low testosterone
There are several main reasons under the influence of which low testosterone levels can be observed in a man’s body:
1. Age-related changes. It should be noted that after 30 years, the level of testosterone in a man’s body begins to decline and this is normal. Hormonal treatment may only be prescribed if abnormally low testosterone levels are observed.
2. Stress. Frequent emotional overload can lead to hormonal imbalance, and as a result, a decrease in testosterone synthesis in the body.
3. Poor nutrition. Lack of vitamins and microelements in the diet that are necessary for the normal functioning of the body can lead to testosterone deficiency.
4. Lack or excess of physical activity. Both conditions are dangerous for the male body. Testosterone levels can decrease both with physical inactivity and with regular physical overexertion.
5. Bad habits. Tobacco smoking, alcohol abuse, and drugs definitely cause a decrease in testosterone levels in the body. A similar effect can occur when taking certain medications.
6. Obesity. In this case, low testosterone in men is observed due to the body’s increased production of female hormones – estrogens, which causes serious disruptions in the functioning of the entire body.
Etiology
The most common predisposing factors that can reduce testosterone in males are:
- age category over forty years - it is after this period that a physiological decrease in such a substance occurs. This is due to the aging of the body and it is not possible to reverse this process;
- poor nutrition - if the body does not receive enough vitamins and micronutrients, then the production of such a sex hormone will be insufficient;
- The presence of excess body weight in a person is one of the most dangerous causes of this condition. Obesity not only leads to a decrease in the concentration of male sex hormones, but also affects the activation of the production of estrogens - female hormones;
- excessive addiction to drinking alcohol, smoking tobacco and drugs;
- insufficient physical activity of a person - a moderately active lifestyle helps prevent the appearance of such a symptom and helps to increase testosterone. It is noteworthy that excessive physical activity can also serve as a source of development of such a disorder;
- abuse of certain drugs;
- genetic predisposition;
- injury to the testicles and other organs of the male reproductive system;
- carrying a mobile phone in trouser pockets;
- Klinefelter's syndrome.
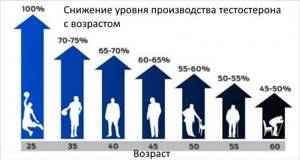
Decline in testosterone production as men age
Despite the fact that testosterone is a male sex hormone, it is also present in the body of female representatives. It is produced by the adrenal glands and is found in small quantities.
Reasons for decreased testosterone in women:
- Down syndrome;
- entry into menopause;
- menopause;
- acute adrenal insufficiency, against the background of which the glands cannot secrete the required amount of this substance;
- anorexia and bulimia;
- indiscriminate use of certain medications;
- surgical excision of one or a section of two ovaries;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- severe physical or emotional stress;
- prolonged exposure to stressful situations.
It follows from this that a decrease in testosterone levels in representatives of both sexes is often caused by physiological factors, but sometimes it can indicate the course of a particular disease that requires medical intervention.
Low testosterone: symptoms
Signs of low testosterone can vary and largely depend on age. For example, if the fetus lacks this hormone during intrauterine development, this can lead to congenital abnormalities of the genital organs (for example, underdevelopment of the penis or scrotum).
A lack of testosterone during puberty can lead to impaired development of secondary sexual characteristics (lack of voice change, decreased hairiness, underdevelopment of muscle tissue, and so on).
Signs of low testosterone in adulthood:
- decreased libido;
- hair loss;
- increase in body fat due to decreased muscle mass;
- decline in physical activity;
- development of impotence and infertility;
- depression;
- osteoporosis.
Low testosterone does not pose a threat to the patient's life, but significantly reduces its quality. A decrease in energy causes the development of chronic fatigue syndrome, muscle atrophy leads to loss of physical strength and the development of obesity, erectile dysfunction leads to depression, and with osteoporosis, bones become fragile and brittle.
Low testosterone levels in men - signs
Common Signs and Symptoms of Low Testosterone in Men
Erection problems
Testosterone stimulates penile tissue to produce nitric oxide, which leads to an erection. If hormone levels are too low, a man will not be able to achieve an erection.
Factors that may cause erectile dysfunction:
- smoking;
- problems with the thyroid gland;
- high cholesterol.
Hair loss
Many men experience hair loss as a natural part of aging.
Decreased bone mass
Testosterone helps produce bone tissue and maintain bone volume. Low testosterone can cause this volume to decrease, which can make bones brittle and susceptible to fractures.
Reduction in testicular size
A man with low testosterone levels may notice a decrease in the size of his testicles. The scrotum may become softer than usual.
Decreased sperm count
Semen is the fluid that contains most male ejaculates. This type of fluid helps the sperm move towards the egg. Testosterone stimulates sperm production, and a decrease in sperm count may indicate decreased testosterone levels.
Sleep problems
Many men with low testosterone have sleep apnea. This serious disorder temporarily stops breathing, which can disrupt sleep.
Decreased sexual desire
Men with low testosterone often experience decreased sex drive. A decrease in sex drive occurs naturally as we age, but it may be due to low testosterone levels.
Decreased muscle mass
Testosterone plays a role in muscle development, and decreased levels of the hormone can lead to significant muscle loss.
Tides
While many women attribute hot flashes to estrogen levels that fluctuate during menopause, low testosterone levels can also cause this symptom.
Decreased energy levels
Low testosterone levels can lead to low energy levels and fatigue. A person may feel tired even after resting, or may have decreased interest in exercise or movement.
Increased body fat
Decreased testosterone levels can lead to increased body fat. In some cases, men with hormone deficiency develop gynecomastia, which causes breast enlargement.
Mood swings
Some evidence suggests that people with low testosterone experience lack of attention, irritability and depression.
Diagnosis of low testosterone
Typically, a man consults a doctor only when he feels a strong decrease in his sexual performance. All other symptoms are either ignored or unexpressed.
To determine the level of testosterone in a man’s body, a special table has been developed, which contains a number of clarifying questions with which you can find out the real state of hormonal levels.
The following symptoms indicate that the level of male hormones is low:
- erectile dysfunction, ejaculation;
- decreased libido;
- orgasm disorder;
- decreased reproductive function;
- somatic disorders (obesity, decreased physical strength, feeling of constant fatigue, urination problems);
- psycho-emotional disorders (sleep problems, increased irritability, decreased concentration and memory, depression).
In addition, laboratory methods are used to determine the level of testosterone in the blood (it is important to exclude other endocrine diseases).
Symptoms
Signs of a decrease in the level of this sex hormone in men and women will be slightly different. Thus, the basis of the clinical picture of such a disorder in representatives of the stronger half of humanity is the following symptoms:
- lack of sexual attraction to the opposite sex;
- increased sweating;
- decreased bone density, which makes a person susceptible to frequent injuries or fractures;
- increase in body weight and volume of mammary glands;
- sparse hair on the face, pubic area and armpits;
- muscle and joint pain;
- decreased performance;
- frequent mood swings and depression;
- constant fatigue and weakness;
- sleep disorders;
- dry skin;
- formation of wrinkles;
- premature ejaculation;
- decrease in testicular volume;
- erectile dysfunction.
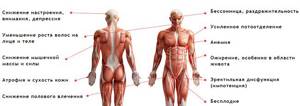
Symptoms of testosterone deficiency in men
The decrease in testosterone in women is clinically less pronounced than in men. This is explained by the fact that such a hormone is not the main one for females.
In such cases, the lack of such a substance is expressed in the following symptoms:
- decreased or absent sexual desire;
- inability to get pleasure during sexual intercourse;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle;
- frequent hot flashes;
- dry skin;
- increased fragility of hair and nail plates;
- causeless fatigue and constant weakness;
- decreased physical strength;
- problems with concentration;
- accumulation of fat in the abdomen, arms and neck;
- change in voice timbre;
- apathy and irritability;
- bone fragility;
- drowsiness during the day and lack of sleep at night.
If the cause of low testosterone is any pathology, then the symptoms will be supplemented by the clinical manifestations of a particular disease.
Treatment for low testosterone
The therapy is complex and largely depends on the reasons that caused the decrease in the level of the main male hormone in the body. Treatment of low testosterone in men involves a number of mandatory measures:
- treatment of concomitant diseases;
- review of treatment if medications prescribed by a doctor negatively affect the level of testosterone in the body;
- diet;
- hormonal therapy.
In addition, it is necessary to have regular sex life, give up bad habits, and play sports.
Legumes, sweets, and meat products increase testosterone.
Low testosterone can occur when consuming the following foods:
- energy drinks, strong coffee and tea;
- beer – it contains a lot of phytoestrogens;
- salty, fried, fatty foods;
- strong alcohol.
This does not mean that the use of the above products is completely prohibited, but it is necessary to observe the measure and prevent abuse.
If low testosterone is not a consequence of age-related changes, but a pathological defect and is not relieved only by lifestyle changes and diet, then drug treatment is indicated. For this purpose, hormone replacement therapy or stimulating therapy may be prescribed, the effect of which is aimed at increasing the production of testosterone by the body itself.
In almost all cases, when replacement therapy is prescribed, improvement occurs, and the level of male hormones in the body increases.
In our online store we offer you the following remedies for the treatment of low testosterone, which can be used as part of complex therapy for this pathology:
- L-Arginine;
- IGF-1;
- Secretagogue;
- TestoJack 200;
- DHEA cream with DHEA.
Before using any drug, you should consult your doctor.
Treatment methods
Non-drug methods for increasing testosterone in men:
- Normalization of sleep. Restoration of the body occurs in the deep sleep phase. Shallow and intermittent sleep interferes with the adequate functioning of internal organs and the production of sex hormones. It is recommended to sleep 7-8 hours a day. The criterion for a normal night's sleep is to feel well after waking up.
- Balanced diet. Testosterone production is promoted by foods rich in zinc, selenium and magnesium. Food should be balanced in essential nutrients.
- Taking vitamins. The hormonal background is stabilized by vitamins B, C, D, E. Taking omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids will benefit you.
- Drinking regime. It is recommended to drink at least 1.5 liters of water per day. During intense physical activity, fluid volume increases.
- Rejection of bad habits. It is recommended to quit smoking. You should reduce the amount of alcoholic beverages or stop drinking alcohol. Drug use is excluded.
- Normalization of weight. A decrease in the proportion of adipose tissue leads to a decrease in the proportion of estrogen and an increase in testosterone levels.
- Physical activity. Training in the gym, including weight training, increases testosterone. Training should be regular. Walking and sprinting will also be beneficial. It is important to avoid overload - physical exhaustion negatively affects the hormonal balance of the body.
- Sexual activity. Flirting and intimacy lead to increased testosterone.
- Limiting stressful situations. With prolonged or repeated stress, cortisol production increases, which leads to a decrease in testosterone. A good mood helps increase testosterone production.
- Sunbathing. Exposure to the sun increases vitamin D synthesis and helps increase testosterone levels.
- Hardening. Pouring water leads to a short-term increase in testosterone and has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the body.
Drug therapy involves taking hormonal drugs that can compensate for the lack of testosterone . Injectable, oral and transdermal forms of drugs are used. The dosage and duration of administration are determined by the course of the pathology.
Hormone replacement therapy is prescribed only by an andrologist after a complete examination and establishment of an accurate diagnosis. Uncontrolled use of hormonal drugs threatens to disrupt the production of your own testosterone and develop dangerous complications.
Prevention of low testosterone
Low testosterone, the symptoms and treatments for which are described above, is preventable. In order to reduce the likelihood of developing this pathology to a minimum, the following recommendations must be followed:
- to refuse from bad habits;
- lead an active lifestyle, walk more often, play sports;
- avoid stress if possible;
- eat right, do not abuse fast food and other unhealthy foods;
- have regular sex life with a regular partner;
- monitor your weight;
- do not exhaust yourself with diets and intense physical activity;
- avoid physical inactivity;
- When working in hazardous industries, observe the necessary safety measures;
- treat concomitant diseases in a timely manner, preventing them from becoming chronic;
- When you reach an age when testosterone levels begin to decline (35-40 years), monitor your condition and, if suspicious symptoms appear, consult a doctor for diagnosis and possible treatment of this condition.
Health to you!
Diagnostics
Despite the fact that a lack of male sex hormones is often a completely normal physiological process, sometimes it can be a consequence of some illness, which means that patients need to undergo a comprehensive examination, which includes:
- a clinician studying the medical history and collecting an anamnesis of the patient’s life;
- conducting a detailed interview with the patient to identify the time of onset of symptoms;
- conducting an objective examination;
- laboratory studies of the level of hormones in the blood - will show a direct decrease in this hormone, and will also indicate a possible pathological reason for the sharp decrease in testosterone levels in men and women;
- Ultrasound of the genital organs.
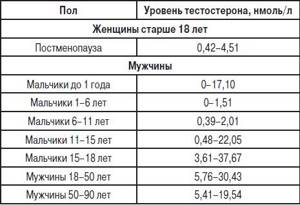
Testosterone levels in men and women
Depending on individual indicators, additional laboratory and instrumental examination methods may be prescribed.
Treatment
Testosterone deficiency is compensated using the following conservative methods:
- taking medications;
- compliance with diet therapy;
- psychotherapy;
- normalization of wakefulness and rest.
Drug therapy is intended only for men and consists of performing hormonal replacement treatment, which will help achieve:
- normalization of male libido;
- normalizing erection;
- resumption of hair growth in the pubic area and armpits;
- increasing bone density;
- normalization of muscle strength.
The basis of therapy for reducing testosterone levels in women is diet therapy, which is also important for males, but is of a secondary nature. The therapeutic diet involves enriching the menu with products that increase the content of this sex hormone. These ingredients include:
- seafood;
- cabbage and beets;
- green grapes and mango;
- melon and carrots;
- raisins and pineapple;
- oranges and pear;
- prunes and pomegranate;
- zucchini and bell pepper;
- black currants and plums;
- any greens;
- pearl barley, buckwheat and wheat porridge;
- curry and turmeric;
- cardamom and garlic.

Testosterone Boosting Foods