Many people train a lot, often beyond what their body can handle. Strength training has become popular among many training programs and people, in order to quickly achieve the desired result, sometimes overdo themselves in the gym. When classes no longer bring the desired effect and it becomes almost impossible to perform even minimal loads, this indicates overtraining or overwork of the body.
If there are errors during the training process, as well as if there is a violation in their planning, with forced power loads using extreme stress during reduced performance of the body, a state of overfatigue and overtraining develops.
“Strength does not come from physical endurance. It comes from an unshakable will.” - Mahatma Gandhi
These two conditions are related to each other because fatigue is a reaction to overtraining.
What is overtraining?
If you believe that overwork does not threaten even an experienced bodybuilder, then this is a deep misconception. When playing sports from a hobby turns into real fanaticism, the consequence is overtraining.
Overtraining is a physical, emotional, as well as behavioral state of the body that occurs when the intensity and volume of training programs significantly exceeds a person’s recovery ability. Overtraining causes blocking of progress, as well as a decrease in body weight and strength indicators.
Overwork is the most common problem among bodybuilders, but other athletes, such as sprinters, are also susceptible to it. Overtraining of muscles in people who train frequently and in excess amounts ultimately leads to the inability to fully recover after intense physical exercise. This leads to the development of certain symptoms.

Low performance in sports, the inability to achieve the desired result is the first and important symptom of overtraining of the body. The state of overfatigue includes decreased motor coordination, changes in the immune and hormonal state, decreased performance, mood changes and sleep disturbances.
The appearance of overtraining is always preceded by a phase that subsequently leads to this state. This phase is called overvoltage. This condition is manifested by fatigue after training, a decrease in the power of the activities performed and can last up to 14 days.
The essence and consequences of overtraining syndrome
Overtraining is the body’s reaction to increased physical activity, which increases the body’s adaptation period. Progress in sports is unimaginable without increasing the intensity and volume of training. Competent progress should be based on correct training programs that provide for a smooth increase in sports performance. The nature of this syndrome is that as a result of intense training, the body does not have time to adapt, and this leads to microtraumas in the muscles, increasing the load on the heart and central nervous system.

Athlete overtraining syndrome can occur for several reasons:
- intensive work in the gym after a long break;
- a sharp increase in the volume of work during training, which exceeds the usual volume of training;
- frequent exercise and insufficient recovery period between trips to the gym;
- low protein content in food, lack of a balanced diet;
- disease training;
- the presence of obvious sources of stress in everyday life.
The consequences of the syndrome can subsequently affect the state of the human nervous system, cause cardiovascular diseases and provoke other unpleasant consequences.

Types of overtraining (overfatigue)
Overfatigue is usually divided into two types: aerobic and anaerobic.
Aerobic fatigue
Aerobic exercise promotes the rapid breakdown of fat, since with this type of training there is an increased consumption of oxygen by the body, and also, such exercises strengthen the cardiovascular system. Such workouts include running, swimming, playing basketball, cycling, and brisk walking.

If, while doing aerobic sports, you feel like you are unable to speak without additionally swallowing air, then the aerobic activity is too intense. In the future, this can lead to a slow reaction rate, depression and bradycardia (low heart rate).
Anaerobic fatigue
Anaerobic exercises include a type of physical activity in which movements of the muscular system are performed using energy obtained as a result of anaerobic glycolysis. That is, glucose in the body is oxidized in the absence of oxygen. Anaerobic exercises include arm wrestling, bodybuilding, and powerlifting. Anaerobic training is designed to increase muscle mass and improve overall endurance of the body.
Anaerobic muscle activity when working with heavy weights should last no more than 3-5 minutes, after which rest is required. If the training is too intense, then this entails the appearance of corresponding symptoms due to overtraining. Excitability, restless behavior, sleep disturbances, weight loss, and rapid heartbeat occur during rest after exercise.

Also, overtraining (overfatigue) is usually divided into three types, which are somehow related to each other.
Muscle fatigue
This type of overwork is characterized by muscle fatigue, which subsequently leads to pain throughout the body. This symptom can otherwise be described as “ache” in the muscles. Subsequently, this leads to decreased performance and the inability to perform even basic exercises.

Nervous fatigue
All movements of the body are directly related to the brain, therefore, the nervous system is actively involved in the training process. By training the muscular system, the central nervous system is also loaded.
Bodymaster.ru recommends Fitness Trainers:
If she is not prepared for physical activity and a given pace (this mainly applies to beginners), then there is a high probability of nervous overstrain, which in the future will lead to nervous overtraining. The athlete will experience mood swings, frequent dizziness, sleep disturbances, and decreased physical activity.
Psychological fatigue
If you do not pay attention to the symptoms of overwork and continue to engage in physical activity incorrectly, then the combination of muscle and nervous fatigue will ultimately lead to the third type of fatigue - psychological. By engaging in the same training program for a long time and intensively, the athlete begins to lose interest in sports due to the lack of desired results. Apathy, loss of motivation, and reluctance to move forward arise.
If you feel any of the symptoms listed above, then you should not turn a blind eye to it in order to avoid more unfavorable consequences. Before moving on to the reasons that predispose to overfatigue, it is advisable to become familiar with the pathogenesis or physiology of overfatigue, by what mechanisms this condition occurs.
How to identify symptoms of overtraining?
This condition does not develop in the body in just a couple of days; its appearance can be divided into 2 stages:
Overwork
You get a feeling of exhaustion after work or after studying, the body wants to rest, but you, overcoming fatigue, still rush to train, thereby increasing the ailment that has appeared and causing stress in the body. You won’t be able to do a full workout anymore, because you simply don’t have enough strength for it. After such training, the overall performance of the body decreases, and as a result, it will become more difficult for you to do even mental work.
How to deal with overwork?
This sign of overtraining is not difficult to overcome. Necessary: good sleep, eating more complex carbohydrates, adjusting your daily routine, taking vitamins, temporarily reducing the intensity and number of workouts, devoting enough time to relaxation and relaxation.
And try to avoid conflict situations at work and in the family - this also unnecessarily strains your nervous system. If you do not pay attention to overwork and continue skiing or biathlon, then this type of overwork develops into the next stage - overexertion.
Overvoltage
You begin to feel muscle pain almost constantly, your endurance and strength decrease, apathy occurs, and the desire to attend training under these conditions practically disappears.
At this stage, many fans of cyclic sports use powerful fat burners or pre-workout complexes. Wanting to quickly achieve maximum effect in the shortest possible time, they often exceed the manufacturer’s recommended dosage several times.
This method only aggravates the current situation: the body’s capabilities are already at the limit, and the athlete further pushes it by taking powerful stimulants. The body needs rest, but as a result it gets even more overstrained muscles and exhaustion of the nervous system.
The use of stimulants is a mistake of many athletes, including biathletes and cross-country skiers. Thus, they try to quickly eliminate the manifestations of overtraining instead of fighting its causes.
And then a real apocalypse begins for your body, after which it will be much more difficult to recover.
Unusual body reactions that may be symptoms of overtraining!
This happens in triathlon. The athlete quite suddenly feels that he has significantly lost muscle tone, strength, and has become less endurance. The load on his body is heavier than it was before. The athlete develops insomnia, anxiety, and loss of appetite.
Sometimes, on the contrary, the athlete is attracted to carbohydrate foods, or to unhealthy foods and alcohol. The consequence of this is weight gain due to excess fat, and muscle tissue continues to break down under the influence of the hormone cortisol.
Disruptions appear in the cardiovascular system, the immune system is affected, irritability appears, and the athlete becomes lethargic and overwhelmed.
This is a consequence of a decrease in the level of the hormone testosterone and an increase in the level of estrogen in his body.
Physiology of overfatigue (overtraining)
Increased growth in results in physical condition occurs during the recovery period after training. The process takes from two to several days. It takes up to 1 month to fully restore the muscular system after intense strength training. If there is an imbalance between the time for recovery and the volume of training, then the athlete’s athletic performance will decrease.
With a mild degree of overtraining, several days of rest or a reduction in physical activity of the training are necessary until the physical condition of the body is completely restored. If a more severe degree of overtraining occurs, the symptoms of fatigue will progress and the athlete’s condition will worsen. In this case, complete recovery will take several weeks or even months.
Overtraining occurs due to the following factors:
- poor nutrition,
- fatigue at work,
- disruption of the body's circadian rhythm,
- training sessions during the menstrual cycle.
Overtraining often occurs in bodybuilders who engage in training associated with high loads, especially during drying periods.
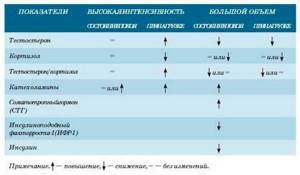
There are certain mechanisms of overtraining that arise in the body for various reasons:
- Microtrauma of muscle tissue exceeds the rate of their recovery.
- Low levels of amino acids in the body. This condition is also called protein malnutrition, where there is an imbalance of energy and proteins that adversely affects muscle tissue.
- During the period of fasting, nutritional deficiency can lead to the activation of catabolic reactions, resulting in the destruction of muscle tissue.
- With frequent stress and insufficient recovery after training, the level of the hormone cortisol increases, which, if elevated, can destroy muscles.
- Overload, the exhaustion of the central nervous system during strength training, also leads to overtraining.

Since overwork affects not only the physiology of the body, but also neurological and emotional aspects, it is necessary to understand the causes of overwork.
What is overtraining
The first description of the syndrome was made by McKenzie. According to him, this is primarily a depletion of the nervous system. Karkhman believed that this phenomenon was maladaptation, combined with a violation of the body’s regulatory abilities.
Simply put, overtraining can be defined as an imbalance between recovery and training. This is a state of the body in which it does not have time to fully recover after high loads. In this regard, many experts prefer to use the term underrecovery.
Causes of overwork
Overtraining is often typical for beginners who intensively subject an ill-prepared body to serious physical activity. Also, professionals whose progress is decreasing, and they are trying with all their might to correct the situation by increasing the strength load.
The main reason here is the increased desire to achieve the desired result. It is a misconception that the more a person trains, the greater the effect of the training will be. Fitness and bodybuilding require a careful approach, which should not go beyond the physiology of the athlete.
Before moving on to the symptoms of overtraining, it is necessary to take a closer look at its causes.
The phenomenon of sports addiction
This reason is mainly common among beginners. According to the theory of sports addiction, during and after training, the joy hormone (endorphin) is released into the blood in large quantities, which makes a person satisfied and brings a feeling of joy. Some athletes note a positive state after training, and its absence is observed by a drop in mood and a strong attraction to the gym.
A person tends to engage in training more often, which ultimately leads to overtraining.

Among professional level athletes, sports addiction manifests itself in the form of a desire to achieve greater results by increasing the intensity of training, reducing rest time between training approaches, increasing weight lifting and the frequency of training (more than once a day).
Frequent training to the point of exhaustion leads to a completely different result. Instead of the expected progress, in the form of increased endurance, increased muscle mass and increased athletic performance, everything happens differently. Endurance decreases, performance decreases, muscle tissue is destroyed, and athletic performance decreases.
Following the same program for a long time
When the body receives the same physical load, for example, a constant number of approaches and repetitions, working weights, this also leads to overtraining.
The training program should change every month or every two months. If you constantly follow the same program for a long time, this leads to “emotional burnout,” resulting in physical fatigue, which reduces performance and leads to muscle weakness, as well as myalgia (muscle pain).
Insufficient rest and sleep lead to fatigue
Adequate rest and sleep determine overall well-being and health in general. Even if you don’t devote a lot of time to sports or don’t do it at all, and for example, work up to 10 hours a day, you still need to devote at least 7-8 hours to sleep a day. And if you regularly engage in sports, and intensively, then sleep and rest need to be given even more importance.

On average, the process of muscle recovery takes from 24 hours to several days, and if strength training is excessively intense, then complete recovery may take a whole month. Therefore, it is imperative to give the body the necessary time to rest in order to prevent overwork.
Fatigue as a result of poor nutrition and deficiency of nutrients
The occurrence of overtraining is also characterized by a low caloric content of the daily diet and a deficiency of macro- and microelements. When the body does not receive enough nutritional components for normal functioning, the process of catabolism occurs, which prevails over anabolism. That is, the synthesis of nutrients decreases, and their destruction increases.

In this case, not only muscle tissue is damaged, but also the cardiovascular system. Therefore, a clear deficiency of proteins, carbohydrates and fats, as well as vitamins and minerals, can take you out of training for a long time, up to several months.
Stress at work and at home, decreased immunity
Frequent stressful situations and painful conditions also contribute to overtraining of the body. During periods of stress and reduced immunity, the level of cortisol (stress hormone) increases in the blood. It is this hormone that promotes catabolic processes in the body. Based on this, we can conclude:
- Unresolved problems at work or in the family constantly force the body into a state of catabolism, that is, destruction, which means the risk of overwork increases.
- In a sick state and a weakened immune system, there is also a high probability of overtraining the body.

During such periods, it is advisable to reduce the activity of training or take a break for 2-3 weeks to give the body a rest and get out of a state of stress. Such a pause in sports will not play a significant role on the result, but it can protect you from the adverse consequences of overtraining.
Knowing the causes of overwork, it is important to become familiar with the signs of this pathological condition.
How to Avoid Overtraining
Preventing overtraining is easier than treating it. Therefore, do not take your health lightly, especially if you exercise a lot. Prevention of overtraining is in many ways similar to its treatment:
- Adjust your training plan depending on how you feel, everyday problems and stress at work
- Don't do hard workouts when you're tired
- Sleep at least 7-8 hours a day, try to fall asleep and wake up at the same time every day
- Eat a varied diet without strict diets. If you are on a strict diet, reduce your workout load.
- Avoid stressful situations or try to change your attitude towards them
- Get a medical examination 1-2 times a year
- Train under the guidance of a trainer if possible.
- It's better to be underloaded than overloaded
Signs of overwork
Every athlete who regularly engages in active sports should be aware of the signs (symptoms) of overtraining:
- Fatigue and decreased physical strength even when performing basic physical exercises.
- Depression and loss of motivation, a feeling that achieving the desired result is becoming impossible.
- Irritability, frequent mood swings.
- Decreased appetite, even after intense training.
- Increased heart rate, both during and outside of exercise.
- Constant muscle pain, which prevents you from playing sports.
- Decreased immunity, frequent colds.
It must be remembered that it also happens when athletes do not experience any of the listed symptoms, although the pathological condition has already appeared. This is called an asymptomatic state, when the result of the training does not increase, but only worsens. If there are signs of fatigue, then measures must be taken to prevent this condition. It is advisable to consult a sports medicine doctor for more clear recommendations.

For a more in-depth explanation, it is worth noting that signs of overwork are divided into three types. This is physiological, neurological and psychological fatigue.
Physiological signs of fatigue
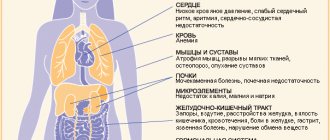
Physiological symptoms of overtraining include disturbances in the normal vitality of the body and all internal organs.
- Increased blood pressure, increased heart rate at rest.
- Decreased immunity and frequent colds.
- Decreased appetite after strength training.
- Hormonal imbalance, which leads to loss or sudden weight gain, as well as decreased libido in men and menstrual irregularities in women.
- Disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, which leads to bowel dysfunction (diarrhea or constipation).
- Constant pain in muscles (myalgia) and joints, dull or aching.
- Decreased performance, sudden loss of strength.

All these signs indicate physiological overtraining.
Neurological signs of fatigue
This group includes signs associated with dysfunction of the peripheral and central nervous systems. During training, not only muscle tissue, but also the nervous system is subjected to increased stress. The optimal load on the central nervous system cannot be predicted, since there are no clear boundaries. If the permitted volume of load on the central nervous system is exceeded, a state of neurological exhaustion occurs, which is characterized by certain symptoms:
- Headaches and dizziness.
- Disturbance of normal sleep: interrupted sleep, hypersensitive sleep state (waking up from any sound), insomnia. Nightmares are possible.
- The appearance of numbness and tingling in the limbs (often in the evening).
If such symptoms occur, it is possible that the nervous system is tired.
Psychological signs of overwork
This group of symptoms includes everything that relates to the psychological and emotional state of a person associated with the training process:
- A sharp decrease in motivation for sports.
- Mood swings.
- Depressive disorder and irritability.
- Unreasonable panic fear, apathetic attitude towards life.
- Reluctance to engage in physical exercise; I want the workout to end as soon as possible.
Knowing the mechanisms of overtraining, as well as its signs, it is also important to take into account the definition of overtraining criteria in order to understand the boundaries of its transition.
Symptoms of Overtraining
Overtraining is different from normal fatigue. In case of fatigue, it is enough to rest for 1-3 days, supercompensation will occur, the body will be ready to train and progress again. Overtraining is a protracted condition when results drop and the general condition of the body worsens. It has a cumulative effect, so it may not be noticed immediately.
Main symptoms of overtraining:
- Increased heart rate at rest. Normally, the resting pulse can fluctuate by ±5 beats; if the deviation is more than 10 beats, this is a bad sign
- High or low blood pressure
- Insomnia, frequent awakenings
- Poor appetite or constant hunger, digestive problems
- Irritability, depression, loss of motivation, anxiety, emotional instability
- Low performance and fatigue during training
- Fatigue immediately after waking up, feeling unwell throughout the day
- Sudden weight gain or loss
- Inexplicable drop in form, lack of progress and motivation. Even with regular training, your form only drops, your condition worsens, and a few days of rest do not improve the situation.
- Injuries due to light loads outside of training
- Menstrual irregularities
- Common ARVI diseases
At the first symptoms of overtraining, reconsider your training plan, reduce volumes and intensity. The hardest thing is to realize that this is overtraining. Often, athletes begin to train even more in an effort to “endure” this condition. Ignoring the symptoms can completely break the body, then recovery can take a year or more.
Methods for determining overtraining (overfatigue)
There are several strategies that can be used to determine whether an athlete is entering a state of overtraining.
Heart rate analysis
The athlete and coach should monitor their morning heart rate each day to determine whether the athlete is training at the appropriate level of physical activity. It is better to monitor heart rate in the morning, when the athlete comes to the gym rested and has not yet been exposed to the stress of the day.
If your resting heart rate is elevated for several days, this may be a sign of overtraining. In this case, the trainer needs to reduce the intensity of the training program, preferably add aerobic exercise, and, of course, carefully monitor the athlete’s heart rate for the next 48 hours.
Taking an orthostatic test
A continuation of the heart rate analysis is the orthostatic test, which is considered an important indicator of the stability of the cardiovascular system during physical activity. Measurements in the orthostatic test are carried out by standard heart rate measurement (at the wrist or carotid artery), and using heart rate monitors, which are already available in smart watches and applications on smartphones.
Normal heart rate is 60-80 beats/min. Changes in heart rate when changing body position (from horizontal to vertical) are assessed at the following levels:
- from 0 to +10 is considered an excellent result;
- from +11 to +16 – good;
- from +17 to +22 – normal;
- more than +22 – already unsatisfactory.
Deviations in the negative direction (that is, a decrease in heart rate during an orthostatic test) are also considered an unsatisfactory result and a reason to postpone or reduce training volumes.
Heart rate variability (HRV) monitoring
At a certain point, the state of the body is determined by the balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. An important point is the body's ability to change its own balance between the two nervous systems.
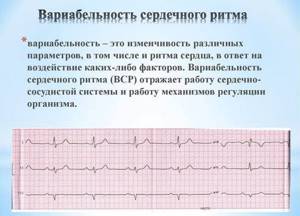
For example, if the next day you plan to train with a high level of load, then after sleep it is necessary for the body to be rested (dominance of the parasympathetic system).
On the other hand, the predominance of the sympathetic system increases the consumption of oxygen, which is so necessary for complete recovery. In this case, it is recommended to plan training with a lower level of load.
Today it is possible to use a heart rate variability monitor directly on your smartphone using the Welltory application.
The program analyzes many different indicators that affect a person’s physical and mental state. The value of the application lies in the fact that the user can measure heart rate variability using a smartphone camera or a chest heart rate monitor. The appropriate option can be selected in the application settings.
At the end of the diagnosis, the program provides an estimated result of the body’s condition and provides a list of all indicators that can be shown to the treating doctor or personal trainer.
Keeping a training log
Athletes often neglect this technique. It is easy to record the training time and the load received, but recording the threshold intensity of the load during training is often not recorded. Therefore, the coach needs to closely monitor the athlete and, of course, convey to the athlete the information that they need to train within their own physical capabilities.
It is advisable for the coach to keep a special journal, which will reflect the physiological impact of the training on the athlete. Also, in the journal you need to make notes about the athlete’s well-being after training, 2-3 hours after it and the next day.
Using a hand dynamometer
A handheld dynamometer is a pressure device that records pressure. This is a quick and effective way to objectively assess overtraining or daily fatigue. The dynamometer also allows you to assess the load on the central nervous system.
Before starting training, the athlete squeezes the device with each hand and records the result. If the result is constantly decreasing, this may mean that the central nervous system is tired and that the body needs recovery.
Ruffier's test for diagnosing fatigue
This technique is intended to measure the performance and prepare the heart muscle for physical activity. The method is based on assessing heart rate before and after physical activity during simple and intense exercise.
The advantages of the method include the ease of measuring the result. This does not require special equipment. The disadvantages include the inaccuracy of the result, due to the individual characteristics of each organism.
Formula for calculating the Rufier sample:
IR = ((P1+P2+P3)*4-200)/10, more details:
IR - individual calculation; P1 - pulse before the start of the load (30 squats in 45 seconds); P2 - pulse after the end of the load; P3 - pulse 60 seconds after exercise.
The calculation value comes out in a numerical range from 0 to 21. The lower the value, the more prepared the cardiovascular system is for physical activity.
Now that we have an idea of how and by what methods overtraining of the body is determined, we can talk about methods of treating overfatigue.
Ways to treat fatigue
Treatment of overfatigue consists of several stages, each of which is important and mandatory for the recovery of the body. All types of treatment are balanced and aimed at eliminating symptoms and ensuring normal human performance.
Adjust the training process in case of overwork
When a severe case of overtraining occurs, you should stop exercising for 2-3 weeks. If you experience symptoms of overtraining, it is strongly recommended to avoid going to the gym. For 2-3 weeks, you can practice yoga at home or do gymnastics in the morning. This should be the maximum load so that the body can fully recover.
If overtraining occurs in a moderate form, then you can go to the gym, but at the same time reduce the intensity of your training. A decrease in intensity includes:
- Reduce the number of workouts (no more than three times a week).
- Reduce the weight of working scales by 10-15%.
- Increase the rest period between sets.
- Avoid workouts that develop endurance (interval cardio training, CrossFit, etc.).
- Prioritize from basic exercises to isolated exercises.
- Warm up before training and stretch after finishing.
In mild and moderate forms of overtraining, it is important to follow the correct training process, and if the symptoms are severely developed, then completely eliminate physical exercise for a while until the body has fully recovered its strength.
Eating when overtired
Proper nutrition is an important part of playing any sport, and when overtraining occurs, the body especially needs to receive a balanced amount of nutritional components.
The following recommendations must be followed:
- Meals should be nutritious 4-6 times a day.
- Adequate protein content (for women 1.5 grams per 1 kg of body weight, for men 2 grams per 1 kg of body weight when training at moderate intensity three times a week).
- Mandatory content of fresh vegetables and fruits in the diet.
- Avoid coffee and medications containing caffeine.
- Take a complex of vitamins B, C, E and sports supplements (glutamine and amino acids).
Proper nutrition will help restore the body in case of overtraining and speed up the return to the usual training program.
Relaxation
With relaxation, both physical and emotional, the body is able to recover faster, muscle tissue and the nervous system quickly return to normal. Relaxation includes yoga and meditation, walks in the fresh air, healthy sleep, at least 8-9 hours a day.
Relaxation methods also need to be included in the mandatory program for the body after overtraining.
Relaxing (Swedish) massage for athletes
Massage has a positive effect on athletes, since not only muscle tissue relaxes, but also the nervous state of the body returns to normal.
The effect of massage promotes more relaxed breathing, expansion of the bronchi in the lungs, freeing them from phlegm. Increases blood circulation in all organs, lowers blood pressure. Improves the lymphatic system, which promotes better elimination of toxins and reduced swelling.
Also, a relaxing massage relieves muscle tension, strengthens muscle tissue and reduces muscle pain. Stimulates the supply of oxygen and nutritional components to all organs and tissues of the body.
Massage also has a positive effect on the human psyche, improving sleep, relieving stress and internal tension. Not only the body relaxes, but also the mind. A relaxing massage allows you to maintain body tone and keep your mind alert, and is also useful when the body is overtrained.
Exercises with a massage roller
Massage is indispensable in an athlete’s practice for muscle recovery, but there is not always free time to visit a massage room. Therefore, self-massage using a massage roller and a special application has become a very popular recovery method. You can download the program on any smartphone.
To perform the exercise, you need to choose a massage roller; they differ in size and degree of hardness. The choice depends on preferences, how much you need to stretch the muscles, and whether a roller is selected for beginners or professional athletes.
However, in order to avoid unpleasant symptoms and long absences from training, it is advisable to know about the prevention of fatigue, which is in many ways similar to its treatment.
Prevention of overwork
To avoid overtraining, you must follow the recommendations and advice of instructors in the gym. Often, overweight people strive to perform exercises constantly and with heavy loads in order to quickly achieve the desired result. But in the end, the weight does not decrease, and there is no strength or desire to move forward. This is already considered a sign of overtraining of the body.
Before starting training you must:
- do a bioimpedance analysis of your body composition and set a realistic fitness goal;
- determine the optimal heart rate during exercise to achieve a goal, for example, to burn fat;
- perform the Cooper functional test to determine your physical fitness.
Tips for Avoiding Overtraining
To avoid overtraining, it is important to monitor your condition. To get pleasure from training and the desired result, you need not to overexert yourself, eat right, pay great attention to rest after exercise and normal sleep.

If you notice signs of overtraining, it is recommended not to self-medicate, but to seek help from a trainer or sports medicine doctor.