Obesity has become a serious problem nowadays. According to WHO statistics, every fourth inhabitant of the planet exhibits this dangerous disease to a certain extent. And every ninth person in the world is diagnosed with severe obesity. This phenomenon is very dangerous, and we are not just talking about aesthetic changes in appearance.
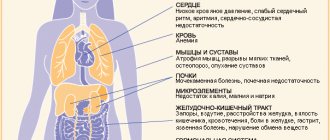
With obesity, all systems and organs are seriously affected: the stomach, intestines, reproductive, vascular and nervous systems, and especially the heart. But to clearly understand what exactly threatens excess fat on these organs, let’s first look at the heart.
Obesity of the heart, which is also called fatty degeneration of the myocardium, appears when there is a pathological accumulation of lipid tissue in the heart area or when muscle fibers are transformed into fat. This disease affects obese people and the fair sex after menopause. The process causes breathing problems, weakness and chronic heart failure, despite the fact that it has no specific symptoms.
Obesity of the heart - symptoms, main causes, methods of combating the disease
Obesity has become a serious problem nowadays. According to WHO statistics, every fourth inhabitant of the planet exhibits this dangerous disease to a certain extent. And every ninth person in the world is diagnosed with severe obesity. This phenomenon is very dangerous, and we are not just talking about aesthetic changes in appearance.
With obesity, all systems and organs are seriously affected: the stomach, intestines, reproductive, vascular and nervous systems, and especially the heart. But to clearly understand what exactly threatens excess fat on these organs, let’s first look at the heart.
Obesity of the heart, which is also called fatty degeneration of the myocardium, appears when there is a pathological accumulation of lipid tissue in the heart area or when muscle fibers are transformed into fat.
This disease affects obese people and the fair sex after menopause.
The process causes breathing problems, weakness and chronic heart failure, despite the fact that it has no specific symptoms.
Obesity Heart Risk Level
If a patient's obesity has reached the third stage, serious, sometimes irreversible changes appear in the structure of the heart. The fat accumulation, which is located in the myocardium, is actively increasing its volume. Fat particles gradually break into the tissue of the heart muscles, leading to weakening of this organ and dystrophy.
Excess weight affects the functioning of the heart extremely negatively, because the total amount of blood in the body increases significantly, which increases the load on the myocardium. This causes inevitable hypertrophy or degeneration of the organ - it becomes deformed and increases in size.
The implication is that the load on the heart muscles can be compensated, but in reality this does not happen.
In the future, with the active development of obesity, the enlarged myocardium ceases to adequately perform its main function, and stagnation forms in both circles of the blood supply.
The excess layer of fat tissue in the abdominal area prevents the heart from functioning as well as it used to. In this case, the diaphragm vibrates with low amplitude, squeezing all other organs. Thus, an additional pathogenic effect is exerted on a weak heart on the verge of dystrophy.
Why does fatty heart occur?
Heart obesity is a consequence of metabolic disorders in the body, which in turn is associated with excess intake of high-calorie foods. Junk food does not have time to be digested and absorbed fully, and as a result, residual fat begins to form layers of adipose tissue on the myocardium.
In fatty hearts, lipid cells accumulate near the heart sac. This process causes a phenomenon in which the contractile function of the cardiac myocardium decreases.
Its consequence may be the development of cardiac dystrophy, atherosclerosis of coronary vessels, ischemia and even functional heart failure.
Let's look at the factors that cause fatty heart disease:
- Excess weight. This is the main reason for the development of pathology. After all, all excess fat accumulates not only on the external parts of the body, but also on the organs inside.
- Disturbed energy balance of food. When the body constantly takes in more food than it can use, obesity develops.
- Alcohol. Excessive alcohol consumption can also lead to the development of this dangerous disease. In this case, beer is much more harmful than vodka and dry wine, since this drink contains significantly more carbohydrates. Alcohol itself oxidizes in the body and also releases energy, inhibiting fat metabolism.
- Genetic factor. The problem of storing excess fat can be caused by heredity. Such people often do not have external signs of excess weight, but at the same time, an excess amount of fat is deposited inside their organs, which does not allow the body to function normally.
Symptoms
Symptoms of dangerously fatty heart include:
- The main symptom that is typical for overweight people is shortness of breath. With third-degree obesity, this phenomenon makes itself felt even at rest.
- Heart pain. Due to the degeneration of the tissues of the muscles of the heart organ and their displacement by fat accumulations, a heart rhythm disturbance occurs. All this leads to weakening and decreased performance of the myocardium.
- Interruptions in heart rhythm cause tachycardia, high blood pressure and more dangerous pathologies in the heart muscle.
Treatment methods
As stated above, the main risk factor for the disease is excessive body weight. In this regard, the basis for the treatment of cardiac obesity is the normalization of body weight under the supervision of a nutritionist.
It is important to observe the factors that led to the pathological condition from the very beginning. Weight loss is ensured by an individually tailored diet, physical activity, and work with a psychologist.
When choosing a suitable diet, not only the number of calories in food is taken into account, but also what the diet was like before. It must contain all the required and important elements.
Another important treatment for obesity is exercise. It is recommended to start with low-intensity exercise, for example, walking. Doctors advise taking a relaxing swim.
If we are talking about severe obesity, doctors in some cases prescribe medications that reduce appetite. In rare situations, surgery may be necessary.
Preventive measures
All measures aimed at combating excess body weight and obesity of the heart should be reduced to reducing calories and the amount of food consumed, accelerating its digestion and absorption by the body.
In this case, a rational choice of diet is of great importance. After all, the body has already suffered without this, so it does not need additional stress.
Under no circumstances should you limit the amount of protein, otherwise such a diet will lead to dangerous consequences.
It is recommended to consume fatty, floury foods, sweets as little as possible, not sleep in the afternoon, and be sure to go for daily walks. Long-term walks in wooded and mountainous areas, physical activity in the fresh air, exercises and gymnastics in the morning, and physical education during sedentary work are also useful.
Loading…
Source: https://dlja-pohudenija.ru/serdcze/chto-sposobstvuet-ozhireniyu-serdcza-kakimi-simptomami-ono-soprovozhdaetsya-kak-izbavitsya-ot-bolezni
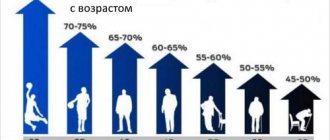
Why does a person gain weight after 30?
When a person is young, he can eat a lot and with pleasure - food is easily digested, the energy obtained from it is quickly spent, and practically no body weight is gained. But somewhere in the period after 25-35 years, the human body’s need for calories changes, and physical activity sharply decreases
.
“Initially, nature set the human life expectancy at 35-40 years,” says Boytsov. “During this time, he was guaranteed to have time to produce offspring, and this is quite enough within the entire population.” Therefore, we can say that after 30 years, nature does not need a person
.
And organizing conditions for maintaining health in the future is the result of independent efforts. Despite the age-related slowdown of metabolic processes, eating behavior
usually remains the same - he eats as in his youth. As a result, additional fat deposits are formed.
How obesity affects the heart, and how to lose weight for heart patients
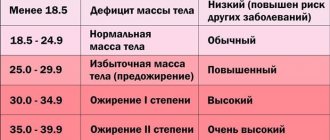
People who have a body mass index (BMI) above 30 are considered obese. The term "obesity" is used by doctors to describe the health of a person whose body weight is significantly higher than ideal values.
Almost 70% of Russians are overweight and obese, which means they are at risk for cardiovascular disease, stroke, hypertension, diabetes and many other diseases. This means that they need to start treating obesity to avoid these terrible consequences.
Motivation to maintain a healthy weight
All people, including children, need motivation in order to be motivated to do something, in our case, maintain a normal weight. The main motivation for adults to lose weight is the realization that losing even a few kilograms can relieve the stress on the heart and extend a comfortable life for several years. After all, when a person’s weight does not exceed BMI, then:
- blood circulates better through the blood vessels;
- the body can more easily control fluid levels;
- The risk of heart disease, stroke, diabetes, some cancers and sleep apnea is dramatically reduced.
What does obesity lead to?
The human body consists of water, fat, proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals. When a person is obese, meaning they have more than normal body fat (especially around the waist), they should not be surprised to have:
- Increased levels of total and bad cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood.
- Reduced levels of good cholesterol.
- High blood pressure.
- Diabetes.
- Heart attack.
- Atherosclerosis.
- As well as respiratory tract diseases, cholelithiasis, osteoarthritis, etc.
Obesity and coronary heart disease
Obesity causes a waxy substance to accumulate in the blood vessels of an ill person, which prevents the arteries from supplying the heart with enough blood.
Gradually, this vascular condition causes chronic heart failure and will definitely lead to angina pectoris or a heart attack.
Obesity and hypertension
When, due to the waxy substance, blood is unable to pass freely into the heart, it begins to put pressure on the walls of the arteries. This pressure gradually increases and one day is diagnosed as hypertension.
The more overweight you are, the more likely you are to develop persistent hypertension and one day experience a hypertensive crisis.
Obesity and stroke
Atherosclerotic plaques deposited in the arteries of an obese person can rupture, and the blood will carry a clot through the vessels, which, once in the blood vessels of the brain, will cause an ischemic stroke.
Metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease
The term "metabolic syndrome" refers to a condition in a person who is at risk for cardiovascular disease, diabetes and stroke. Clearly, where there is obesity, there is also metabolic syndrome. In addition, if a person has at least three of the following symptoms, we can talk about the presence of metabolic syndrome:
- The waist is poorly defined.
- High triglyeride levels.
- Bad cholesterol is high and good cholesterol is low.
- Frequent increases in blood pressure.
- There is an increase in blood sugar.
Forms of obesity
Each specific case of obesity occurs with a predominance of one or another form. The success of treatment depends on how accurately the doctor determines the cause of a person’s obesity.
Scientists identify three forms of obesity
Hyperphagic form
Gluttons suffer from this form of obesity. That is, people do not eat more than what their friends with normal weight eat, but they eat more than their body needs. Naturally, the extra pounds don’t take long to appear.
Gluttons, in turn, are divided into categories:
- Gluttons are gourmets . These “comrades” perceive food as a celebration of life. Therefore, they eat everything that is delicious, sweet, and high in calories.
- Gluttons by circumstance . These are employees of restaurants, canteens, etc., as well as those who constantly have to participate in business lunches. Such people realize that they constantly overeat only when their weight begins to increase.
- Know-Nothing Gluttons . People eat “whatever they have,” and, at some point, high-calorie foods begin to predominate in their food. This is the most mobile category, and it is much easier for those who are included in it to lose weight.
- Hypodynamic form
This form of obesity affects representatives of sedentary professions who do not know how to relax actively, but spend their free hours pleasantly with a book on the sofa or in a chair watching TV. True, representatives of this form of obesity do not eat too much, and their food intake does not depend on a bad mood.
Therefore, to lose weight, lazy people do not need cruel diets - a little more walking, dancing and any other physical activity can start the process of losing excess weight. And if such people also limit their consumption of sausages and oils, then getting into shape will not be difficult for them.
You just shouldn’t forget that the unloading of the diet should be gradual and at the final stage should not exceed 30%.
Psychogenic form of excess weight
This form of excess weight is the most common. People suffering from this type of obesity first eat up their problems as they arise, and when excess weight is added to all the troubles, it becomes a source of constant stress and the person begins to overeat always and everywhere.
A psychotherapist should participate in the process of losing weight for representatives of the psychogenic form of obesity. It happens that, working only with this specialist, the patient calms down, begins to eat less and loses weight.
There is another form of obesity - genetic predisposition to excess weight .
This type of obesity is the most difficult, not only because obesity is, as it were, “in the blood” of a person, but also because a child, who has been accustomed to overeating since childhood and constantly saw fat people around him, gets used to being fat, and excess weight begins to bother him only when it becomes life-threatening.
It is most difficult for people who are overweight from birth to lose weight - in order to achieve significant results, they need to increase physical activity, constantly monitor their diet and meet with a psychologist.
What exercise should people with heart disease do?
As mentioned above, people suffering from any form of obesity, in addition to being under the supervision of a psychologist and establishing proper nutrition, also need to increase physical activity. However, when it comes to cores, this can be very problematic. But there is a way out, because even the weakest hearts will not be harmed by yoga.
Yoga for weight loss (video)
by Alla-Maria
Source: https://RusMeds.com/kak-vliyaet-ozhirenie-na-serdca-i-kakim-obrazom-hudet-serdechnikam
Heart obesity: causes, symptoms, treatment, microscopic specimen, myocardium
Heart obesity develops as a result of the accumulation of lipids in the tissues of the organ. In medicine, the disease is called fatty degeneration of the myocardium. The pathology is accompanied by the replacement of muscle fibers with fat. This leads to disruption of the organ.
The likelihood of developing coronary disease and heart failure increases. Myocardial dystrophy does not always appear in overweight people. The disease can be triggered by hereditary disposition or prolonged stress on the body.
The treatment is carried out by a cardiologist.
Causes of Fatty Heart
In most cases, obesity of the heart is caused by an unhealthy lifestyle. The main predisposing factor is excess weight. The heart wall consists of three layers. The outer one is connective tissue with a small inclusion of fat. This layer is called the epicardium.
In the middle are muscle fibers. This layer is called the myocardium. The endocardium is located on the inside of the heart. It contains endothelial cells.
If a person leads a healthy lifestyle, a hereditary factor will not be able to provoke the development of myocardial dystrophy.
With myocardial dystrophy, adipose tissue penetrates into the middle layer, contributing to its deformation. As the disease progresses, healthy cells are replaced by fat.
The reasons for the development of pathology include:
- long-term exposure to ionizing radiation;
- hormonal imbalance;
- exceeding daily calorie intake;
- lack of oxygen to heart cells as a result of poor circulation or anemia;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- excessive physical activity;
- exposure to toxic substances;
- alcoholism.
Symptoms of a fatty heart
In the initial stages, there are no symptoms of cardiac obesity. They become apparent only at the stage of replacing more than 20% of healthy cells with fat. It is extremely important to consult a doctor when the first signs of pathology appear. Ignoring the problem can cost a person his life.
Characteristic symptoms of the disease include:
- increased blood pressure;
- swelling of the lower extremities and internal organs;
- increased fatigue;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- shortness of breath;
- sharp pain in the left side of the chest.
Swelling is considered a specific sign of the disease. When it occurs, thoughts about myocardial dystrophy arise last.
When you press on the skin surface, a dimple is formed on the limb, which does not disappear immediately.
Heart rhythm disorders are divided into the following types:
- extrasystole;
- bradycardia;
- ventricular block.
An increase in pressure is observed in the last stage of the disease. This occurs due to impaired circulatory function in the heart area. Shortness of breath occurs mainly during physical activity. But in advanced cases it becomes chronic.
Degrees and types of fatty liver
Myocardial dystrophy is classified depending on the nature of its origin and the degree of neglect.
According to the reasons for its occurrence, obesity of the heart is divided into the following types:
- toxic;
- ischemic;
- fat;
- focal;
- dishormonal.
Diagnosis of fatty heart
If myocardial obesity is suspected, the doctor interviews the patient. The reason for additional examination are complaints of chest pain and shortness of breath. At the initial stage, standard diagnostic procedures do not detect pathology.
In this case, an electrocardiogram is performed. It helps to identify the degree of deviation of the cardiac axis and a decrease in electrical conductivity.
Based on the results of the study, the disease is assigned a certain stage.
In order to analyze the contractility of the myocardial muscles, an ultrasound examination is performed. It also evaluates the size of the organ and the thickness of the heart chambers. To determine the degree of advanced disease, magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed.
To find the cause of obesity, the patient is referred for general clinical blood tests. Additionally, the thyroid gland and adrenal glands are examined.
Who to contact?
A cardiologist treats obesity of the heart. To see him, you must get a referral from a therapist. For general obesity, you can contact a nutritionist or endocrinologist.
Medications
For heart obesity, taking medications that normalize heart rate and vitamins is recommended. In some cases, hormone therapy is required. The treatment regimen is selected purely individually. If edema is present, diuretics are selected.
Furosemide is most often prescribed. It relieves the body of excess moisture, relieving the load on the heart muscles. The drug is available for use by people suffering from kidney diseases.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ql0XY0slGw8
To reduce pressure on the heart muscles, take Enalapril. It has an inhibitory effect on the enzymatic activity of the hormone synthesis catalyst formed by the kidneys.
As a result of taking Enalapril, the wall of blood vessels relaxes and blood pressure decreases. The drug can provoke negative reactions from the nervous system and skin surface.
If the above medications cannot be used for some reason, drugs that block kidney hormone receptors are prescribed. They act in the same way as ngiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors.
The main representative of this group of drugs is Valsacor. It reduces swelling, normalizes respiratory function and has a beneficial effect on heart rate.
In order to dilate blood vessels and eliminate spasms that cause pain, Nitroglycerin is prescribed. It is taken directly during a painful attack, since the effect of the drug is short-term.
The effect of drug therapy is observed a month after its start. The patient’s well-being is stabilized: heart rate and blood pressure levels are restored.
To consolidate the effectiveness of drug therapy, the following types of physiotherapeutic procedures are used:
- balneotherapy;
- ozone therapy;
- mud therapy;
- cardiac stimulation;
- exposure to electric current.
The drugs are taken strictly in accordance with the prescribed dosage.
Surgery
Surgery is required if drug therapy does not cope with the disease. The operation is performed if valve replacement is necessary.
After surgery, the patient must be under the supervision of doctors and follow their recommendations.
Exercise stress
Excessive stress on the body negatively affects the heart. Therefore, during treatment it is advisable to completely exclude them.
During the recovery period after drug treatment, sports activities are resumed. The intensity and nature of the loads are discussed with the attending physician. You should return to your normal life gradually.
Traditional treatment
Traditional medicine cannot be used as the main method of treating myocardial dystrophy. It complements drug therapy, increasing its effectiveness.
The following traditional medicines will help improve the functioning of the heart muscle:
- a decoction of goldenrod herbs, viburnum bark, motherwort and valerian;
- black elderberry flowers combined with rosemary and arnica flowers;
- infusion of hop cones, lemon balm, yarrow and valerian root;
- drink based on rosemary, lavender flowers, adonis and beaver.
To prepare a medicinal drink, the ingredients are poured into a small container and poured with a glass of boiling water. It is necessary to cover the infusion with a lid and leave for a couple of hours.
The resulting product is taken chilled, 50 ml per day. The minimum duration of treatment is 1 month.
Diet for fatty heart
The main cause of a fatty heart is poor diet. Therefore, during the treatment of pathology, it is extremely necessary to follow a diet. It is recommended to double the intake of vitamins and minerals involved in metabolic processes.
You should also improve your drinking regime. This will avoid swelling. To get rid of excess fat, it is advisable to limit your daily calorie intake.
The following products must be present in the diet of a person suffering from myocardial dystrophy:
- soups with vegetable or meat broth;
- sources of coenzyme Q10 (cauliflower, carrots, spinach and broccoli);
- cereals;
- dairy products;
- eggs;
- easily digestible meats.
It is necessary to exclude fatty and fried foods from the diet. You also need to give up smoked meats, coffee, fatty meats and spicy foods. The maximum daily salt intake is 3g. Sweets can only be eaten in the first half of the day in strictly limited quantities.
The daily calorie intake is determined individually, depending on the patient’s body weight and height.
Prevention
Considering the pathogenesis of the disease, it can be prevented by following the principles of prevention. The main rule concerns maintaining a healthy lifestyle. This means quitting smoking and drinking alcohol.
It is also important to keep the body in good shape by playing sports. Visiting the pool and walking in the fresh air are encouraged.
People who are prone to obesity need to maintain daily caloric intake. It is recommended to exclude high-calorie foods from the diet.
Any treatment actions must be agreed with a doctor.
The basis of the diet should be protein foods, vegetables and fruits. It is advisable to limit the consumption of desserts, baked goods and fast food products.
It is equally important to ensure proper rest. The optimal duration of continuous sleep is 7 hours. With its deficiency, metabolic processes slow down, which increases the risk of developing myocardial dystrophy.
Complications of obesity
The need for immediate treatment of obesity is due to the high risk of complications. First of all, they relate to cardiac activity.
If the patient does not take any measures, the following problems arise:
- At stages 3 and 4 of the disease, the structure of the heart may change, which will affect its functioning.
- Myocardial contractility is inhibited over time.
- Against the background of blood stagnation, heart failure develops. It manifests itself in shortness of breath, physical weakness and irregular heartbeat.
- In advanced cases, the likelihood of developing coronary artery disease increases.
- There is a deterioration in respiratory function. There is a lack of air and constant shortness of breath. Lack of oxygen affects human performance.
- The risk of sudden death due to cardiac arrest increases.
Forecast
Provided the treatment regimen is followed, the prognosis is favorable. Early diagnosis of the disease ensures rapid recovery. If the disease is detected in the final stages, the treatment process may take longer.
It should be remembered that medication prevents the appearance of new foci of fatty deposits. But medications have no effect on existing pathological areas.
Obesity of the heart is a disease that requires a responsible attitude on the part of the patient. The basis of the treatment process is nutritional adjustments and medications.
During therapy, the patient should be observed by a cardiologist. Constant monitoring will help to detect and eliminate a recurring disease in time.
Source: https://holesterin.guru/ozhirenie/ozhirenie-serdtsa/
Forecast
Provided the treatment regimen is followed, the prognosis is favorable. Early diagnosis of the disease ensures rapid recovery. If the disease is detected in the final stages, the treatment process may take longer.
It should be remembered that medication prevents the appearance of new foci of fatty deposits. But medications have no effect on existing pathological areas.
Obesity of the heart is a disease that requires a responsible attitude on the part of the patient. The basis of the treatment process is nutritional adjustments and medications.
During therapy, the patient should be observed by a cardiologist. Constant monitoring will help to detect and eliminate a recurring disease in time.
Obesity of the heart: its symptoms, causes, treatment and prevention. How does obesity affect the heart?
In recent decades, in many countries, doctors are increasingly faced with the phenomenon of obesity of the heart muscle. Such phenomena at first glance seem strange - after all, the myocardium consists almost entirely of muscle tissue.
Fatty degeneration of the myocardium or, more simply, obesity of the heart is a consequence of abnormal deposition of fatty substances in this organ or the result of fatty degeneration of myocardial muscle fibers.
An important factor that can lead to fatty heart disease is genetic predisposition.
What is the essence of pathology?
Many of our contemporaries are overweight, although even more people who are completely normal in terms of weight, under the influence of unreasonable fashion, stubbornly consider themselves too fat.
Doctors will diagnose “obesity” only when a person’s weight is 20% higher than normal.
By eye, normal weight can be determined by the formula: “weight = height – 100,” but a doctor can name it more accurately.
Obesity is a consequence of a disturbance in the body's metabolic processes associated with the excessive intake of high-calorie food into the body, which does not have time to be completely broken down, and as a result, the remaining fat begins to form adipose tissue.
If you look at a photo of an obese heart, it becomes noticeable that fat is deposited near the heart sac.
Because of this, the contractility of the myocardium is reduced, which in turn leads to the development of atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels, ischemic phenomena and the appearance of heart failure.
Overweight
The phenomenon of obesity of the heart can have quite a variety of causes. But the main one is that a person is overweight. After all, excess fat is deposited not only in visible places under the skin (belly, thighs, etc.), but also in internal organs, the functioning of which is disrupted by this.
The main cause of obesity is a persistent significant excess of nutrients entering the body over their expenditure.
Since the body always first uses the energy of more easily broken down carbohydrates, it begins to break down fats only in case of a lack of energy.
And if there is plenty of it, then the fats that enter the body turn out to be unclaimed. As a result, excess energy in the form of undigested fats is stored in fat cells.
Alcohol
Alcohol abuse also contributes to the development of obesity.
In this regard, beer turns out to be much more harmful than wine and even vodka, since it contains much more carbohydrates (daily dose in 5-6 glasses of foamy drink).
Ethanol itself easily oxidizes and releases its energy, slowing down the process of metabolism of fats circulating in the body. In addition, frequent drinkers lead a sedentary lifestyle and experience physical and mental lethargy.
Heredity
A hereditary predisposition factor can also lead to heart obesity. Such people may not look very plump outwardly, however, excess fat may be deposited in their internal organs (heart, liver, etc.), which begins to interfere with their work.
This is also a common problem in women after menopause.
- Shortness of breath becomes the first noticeable symptom in obese people. If cardiac obesity has reached a severe form, shortness of breath does not go away even in a calm state. Such patients are not only unable to engage in physical exercise, but they cannot even climb to the second floor.
- Heart pain is an important symptom of a fatty heart. When the myocardial muscles degenerate and grow into fatty tissues, the organ weakens.
- Arrhythmia. In an obese heart, the rhythm of its work fails, which is expressed in the appearance of tachycardia and the development of other serious pathologies.
- Very often, with obesity, blood pressure increases, and to very high values. Hypertension itself causes secondary pathological processes that damage other organs and systems, for example, the central nervous system.
Sometimes people complain that some point above their heart hurts in one place and believe that it is the heart that hurts. But in reality, this may turn out to be a sign of problems in a completely different system: from the digestive to the genitourinary. If a person feels any discomfort, he should immediately consult a doctor who will prescribe the necessary tests.
How does obesity affect the heart?
If you want to know how obesity affects the heart and still hope that there is nothing pathologically wrong with this condition, then you are sadly mistaken. Obesity is always bad.
- Patients with fatty heart disease often have hypertension, which further increases the risk of strokes or heart attacks.
- In a massive body, the volume of circulating blood increases significantly, which the heart has difficulty pumping. As a result, myocardial hypertrophy begins - its walls thicken, and the volumes of the chambers increase, although this still cannot compensate for the load on the heart. If obesity continues to progress, heart failure will begin and blood stagnation will occur in both circulation circles.
- If a person has grade III-IV obesity, then serious changes in the structure of the heart begin. The adipose tissue located in the epicardium grows significantly.
- Sometimes fatty degeneration of the heart is observed - the appearance of islands of adipose tissue among the striated muscles of the myocardium. This phenomenon significantly weakens the heart muscle, reducing its ability to contract. However, it should be recognized that fatty degeneration is much less likely to be a consequence of general human obesity; it is much more often caused by severe forms of inflammatory diseases.
- There is an impact of obesity on the heart and breathing, which can lead to serious problems.
- Excess fat tissue present in the abdominal cavity also interferes with the functioning of the heart. The amplitude of vibrations of the diaphragm decreases as the chest is compressed. Therefore, the body also experiences a secondary indirect pathological effect.
Treatment of obesity of the heart muscle
The heart of an obese person is treatable, that is, the changes that occur in it are reversible. The patient only needs to take control of his weight and get rid of the causes of obesity - and gradually the body and heart will return to normal.
In the process of losing weight, not only the externally visible folds of fat on the body will disappear, but also the fatty tissue in the heart and other internal organs will gradually dissolve, and their work will stabilize. Gradually, the person’s general well-being will noticeably improve.
But not only obesity itself can be dangerous, but also the wrong weight loss tactics. Therefore, you need to lose weight under strict medical supervision.
If an obese patient also has diabetes, angina pectoris or other ailments, then sudden weight loss is contraindicated for him. If the approach is too zealous, a person’s heart may not be able to withstand it - an arrhythmia will appear, which can easily end in sudden death.
If there is cardiac obesity, treatment should be carried out by a nutritionist who will choose the right diet for the patient. At the same time, he will take into account the general condition of the patient, the results of tests and a complete examination.
In addition to the diet, dosed physical activity will be prescribed to strengthen the myocardium. After all, when a patient quickly loses weight, his heart, tuned to pumping more blood, will begin to hurt.
Physical exercises should begin with light loads. Most often these are walking. Swimming also has a very beneficial effect.
In case of severe obesity, the doctor will add special medications to the treatment program that suppress appetite. Sometimes surgery is even recommended.
It is imperative to remember that if a person has signs of cardiac obesity, then long-term diets and any mono-diets are contraindicated for him. Changing the diet should be revised towards a more balanced, but nutritious diet, which must be accompanied by physical activity.
Features in children
The development of fatty degeneration at an early age is associated with general obesity. It has a more favorable course, since if the cause is timely eliminated, the process stops, and the young body compensates for the pathology.
Three reasons dominate:
- nutritional (passion for fast food, soda, sweets);
- endocrine (diseases of the endocrine glands have become “younger” in recent years);
- heredity.
The first two reasons are easily correctable. Sometimes it is enough to normalize nutrition or change food preferences, and the child becomes healthy.
The disease manifests itself more clearly, which also contributes to early diagnosis. Children are not prone to fatigue and shortness of breath at the slightest exertion, so these symptoms immediately alert parents and bring them to the doctor. Pain or swelling is much less common at a young age.