Excess weight is one of the common problems of our time. It not only makes the appearance aesthetically unattractive, but also has a negative impact on health. The disease occurs in several stages, each of which has distinctive features. Second-degree obesity develops immediately after the primary stage of the disease. From 30 to 50% of the total body weight in this case is occupied by fat deposits. At this stage, a person’s well-being deteriorates significantly. Shortness of breath, increased sweating, joint pain and tachycardia appear.
What does stage 2 obesity mean?
Obesity 2 (moderate) degree (ICD code 10 - E66) is a serious disease that occurs as a result of excess weight and after the first stage of obesity. It occurs as a result of leading an incorrect and sedentary lifestyle, due to various diseases, taking certain medications, and ignoring treatment for stage 1 obesity.
This pathology is an increase in the thickness and volume of internal and subcutaneous fat. A large amount of fat that forms around the internal organs and compresses them, causes disruption of their structure and function (visceral obesity), which entails a dangerous condition for human life and health, as it subsequently leads to the development of various complications.
Adults and older people, as well as teenagers and children, are equally susceptible to this condition. You can learn more about childhood obesity from this article.
The main indicator characterizing this condition is BMI in the range of 35-39.9 kg/m2. Body mass index is calculated using the formula:
I = m/h2
Where weight in kg is divided by height squared (height is measured in meters).
How to calculate body mass index
In young women, stage 2 obesity occurs as a result of overeating and a sedentary lifestyle. After 35 years, a slow metabolism can provoke this condition. But, as a rule, the main reason is hormonal imbalance. The disease develops according to the gynoid type, the figure is pear-shaped.
In men, this pathology is less often diagnosed due to the fact that the male body does not have the same tendency to accumulate as the female body. The main factors for gaining excess body weight are the consumption of fatty foods, physical inactivity, and excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, especially beer. The disease develops according to the abdominal type, in which the figure is like an apple.
In children under 1.5 years of age, obesity develops due to hereditary factors or the fault of their parents. The main reasons are excessive use of formula milk and incorrect introduction of complementary foods. One of the most dangerous stages is puberty, during which the body reacts inadequately to changing hormonal levels. Pathology develops according to a mixed type.
In children
Pediatricians are sounding the alarm: stage 1 obesity is no longer a rarity among their young patients and is becoming more common every year.
Of course, based on body weight alone, it is impossible to diagnose a child as obese. Gender, age, body type – all this affects the child’s weight. Obesity in children can be diagnosed only when body weight exceeds the average (for a certain age) by at least 20 percent:
- for one-year-old babies – over 12 kilograms;
- for children three years old - over 18 kilograms;
- for children five years old - more than 25 kilograms;
- for seven-year-old children – starting from 32 kilograms;
- for children of ten years of age - from 45 kilograms;
- for teenagers fifteen to sixteen years old - over 85 kilograms.
Doctors say that the main causes of obesity in childhood are a sedentary lifestyle and abuse of fast food, sweets and carbonated drinks. In fact, more than 92 percent of childhood obesity cases have no known cause. Hormonal and genetic factors account for less than 8 percent of cases. Moreover, this is, as a rule, either hypothyroidism or growth hormone deficiency, while cases of syndromic obesity are negligible.
Genetic predisposition also plays an important role. Statistics show that the majority of children whose parents or grandparents were overweight also have a body weight that is far from normal.
The matter, however, is not only about genetics or nutritional errors. A certain proportion of cases of grade 1 obesity occur due to pituitary and hypothalamic disorders. Thus, during puberty, this disease may indicate pubertal dyspituitarism - a violation of metabolic processes in the body and the hormonal balance of the HPA axis. In this case, fat deposits are localized in the area of the shoulders, chest, buttocks and thighs - that is, of a mixed type. In these same places, signs of strip-like skin atrophy (atrophoderma) may appear.
Types of obesity
Experts distinguish between primary and secondary forms of obesity. Primary obesity (nutritional, exogenous-constitutional) occurs as a result of a sedentary lifestyle and overeating. Secondary obesity (endocrine, hypothalamic) is caused by disturbances in the functioning of various parts of the brain, adrenal glands and endocrine organs.
Primary obesity is the most common form of pathology. According to statistics, the appearance of excess and excess body weight is associated with:
- poor nutrition - consumption of large amounts of alcohol, carbonated drinks, sweet, spicy and salty foods, as well as foods with a lot of fats and carbohydrates;
- low physical activity - ignoring sports, sedentary work, spending weekends watching TV and computer.
Secondary obesity is associated with improper functioning of the endocrine system and hypothalamus. But the quality of nutrition also plays an important role in the appearance of excess weight, so it will not be superfluous to adhere to the principles of proper nutrition.
Obesity - principles of treatment
Obesity
is a chronic, lifelong, multifactorial, genetically determined, life-threatening disease caused by the accumulation of excess fat in the body, leading to serious medical, psychosocial, physical and economic consequences.
The role of obesity in the development of cancer of the mammary glands, uterus, prostate, and colon is known. Obesity is accompanied by a decrease in physical and mental performance up to complete disability, deprives patients of the opportunity to lead a normal lifestyle, leads to social disadaptation and the development of depressive states in them.
E66.0. Obesity caused by excess supply of energy resources. E66.1. Drug-induced obesity. E66.2. Extreme obesity accompanied by alveolar hypoventilation. E66.8. Other forms of obesity. E66.9. Obesity, unspecified.
Obesity surgery, or bariatric surgery
(from the Greek baros - heavy, obese, weighty) - a relatively young field of surgical gastroenterology, the subject of which is
morbid
(morbid) obesity, i.e. clinically expressed forms of the disease.
Causes
The main reason for the development of stage 2 obesity is the neglect of the first stage of the disease.
Provoking external and internal factors include:
- hormonal disorders;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- various viruses and infections;
- iodine deficiency;
- consequences of poisoning;
- complications after TBI;
- low physical activity;
- chronic lack of sleep;
- use of psychotropic medications;
- frequent stress and nervous tension;
- unbalanced diet;
- lack of thyroid hormones;
- genetic predisposition to obesity.

If the cause of the disease is infrequent physical activity, stress and poor nutrition, then coping with this problem will be quite simple. It is much more difficult to fight pathology if it is caused by various diseases. First you will have to undergo a course of treatment, but therapy is not always effective.
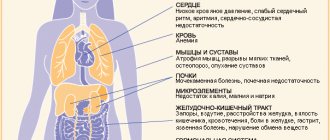
Obesity-related diseases
Obesity is the most important cause of the development of arterial hypertension, sleep apnea syndrome, type 2 diabetes mellitus, diseases of the joints, spine, veins of the lower extremities, digestive tract, sexual disorders, infertility, as well as a complex of metabolic disorders, united by the concept of “metabolic syndrome”
(syndrome). -X, insulin resistance syndrome).
The development of the metabolic syndrome, described in 1988 by G. Riven, is based on abdominal obesity and the state of insulin resistance developing against this background, which in turn determines the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, atherogenic dyslipidemia, coagulopathies, urinary metabolic disorders acids, etc. The inevitable consequence of this complex and interconnected set of disorders is the development of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases (the main cause of mortality).
Signs
Signs of second degree obesity are:
- the occurrence of shortness of breath at rest;
- deterioration of health;
- visible unsightly fullness;
- body mass index more than 35;
- decreased performance, physical activity;
- weakness for no reason;
- the formation of swelling in the arms and legs in the summer;
- increased heart rate during physical activity;
- increased sweating.
Each of these signs cannot indicate the presence of stage 2 obesity. But together they form a clinical picture of the pathology. The final diagnosis can only be made by a specialist based on examination.
Based on the location of fat deposits, pathology is divided into 5 types:
- gynoid - buttocks and thighs;
- abdominal - belly;
- mixed - whole body;
- Cushingoid - the whole body, with the exception of the limbs;
- visceral - internal organs.
Body mass indices
Obesity of the second degree is diagnosed by simple calculations. The main indicator for classifying the disease is body mass index (BMI). To identify it, total body weight (kg) should be divided by height (m) squared.
The diagnosis is also made based on a person’s appearance. Fat may be distributed evenly throughout the body or concentrated in certain areas. It depends on your body type. There are three main varieties: pear, apple and hourglass.
In the first case, the bulk of the fat is localized on the buttocks. The apple body type is characterized by the accumulation of fat on the stomach and waist. With an hourglass figure, the weight gained is distributed throughout the body.
Photo of 2nd degree obesity

Photos of 2nd degree obesity in women

Photos of stage 2 obesity in men
Photos of type 2 obesity in children
Epidemiology
At the end of the 20th century, WHO described obesity as a non-communicable epidemic.
In industrialized countries, morbid obesity affects from 2 to 6% of the population, which is 1,700,000 people on the planet; Two-thirds of the US population is overweight, with every fifth adult and every seventh teenager morbidly obese. Obesity is the cause of death for more than 700,000 people in the United States and 1,000,000 people in Europe each year. In the structure of mortality in Europeans, 13% of cases are associated with obesity.
Over the past 20 years, the incidence of obesity in Europe has tripled, and currently approximately half of adults and one in five children are overweight. Compared to the situation in 1970, the incidence of obesity among children has increased 10 times.
Treatment
Treatment of the second stage of obesity involves taking certain medications and surgery. The statement that taking pills will allow you to lose up to 20 kg in a month is just an opinion, since doctors themselves doubt the effectiveness of such drugs. However, without these medications, the weight loss process will take longer.
What pills help you lose weight correctly in stage 2 obesity? These are anorectics and fat and carbohydrate blockers, let's look at each of them in more detail.
Anorexics
This group of drugs has a direct effect on the human brain, namely on the saturation center in the hypothalamus. They help reduce hunger and make it easier to tolerate food restrictions.
In the Russian Federation, it is allowed to take tablets with sibutramine, which are prohibited in some countries:
- Reduxin;
- Lindax;
- Meridia;
- Goldline;
- Slimia.
Drugs containing amfepramone (Fepranone) or phenylpropanolamine (Dietrin) may also be prescribed.
Fat and carbohydrate blockers
Such drugs prevent the absorption of fats and carbohydrates in the intestines, which cause weight gain. In combination with diet and sports activities for stage 2 obesity, such drugs show decent results.
Most often, drugs containing orlistat as the main active ingredient are prescribed:
- Xenical;
- Listata;
- Orsoten;
- Glucobay.
At the same time, various dietary supplements, for example, Chitosan, show worse results.
If obesity is in an advanced stage, therapy is not limited to just taking pills; surgical intervention is also necessary. In cases where other methods of weight loss have not produced any results, and obesity threatens serious complications, including death, experts prescribe bariatrics (gastric bypass, also known as banding). Liposuction is not advisable, since the procedure provides only a temporary effect.
It is acceptable to use traditional medicine (diuretics and fat-burning herbs). But only after the permission of the attending physician.
Contraindications
Drug therapy for type 2 obesity is prohibited in the following situations:
- age under 16 and over 65 years;
- breast-feeding;
- pregnancy.
In addition, each medicine has its own list of contraindications, which must be studied first.

Nutrition (diet) for type 2 obesity
Treatment of obesity 1st degree
First-degree obesity is treated with diet and exercise. In some cases, the specialist additionally prescribes Charcot showers and water aerobics classes.

At first you will find it difficult to exercise. But don’t despair, pull yourself together and remember, only you can improve your health. If your health allows you, you can start with short runs in the morning. When returning from work or shopping, take the stairs and forget about the elevator. Take tips on how to get your body in order at home.
If none of this works, try finding simple video courses with sports exercises. If you do them regularly, you will notice improvements in your figure and mood in a short time.
Diet
Since an unbalanced diet is a common cause of obesity, therapy will be ineffective without diet correction. Many experts are inclined to believe that the main method of combating type 2 obesity is diet therapy, which is why it is classified as a therapeutic measure.
There is no universal diet that would help all overweight people cope with their problem. In some cases, you have to go on several diets to find the one that would be effective in a particular case. It can be noted that the wine diet is definitely not suitable for obesity, since it belongs to the strict category and involves the consumption of alcoholic beverages.
When choosing a suitable diet, you should adhere to certain requirements:
- Dishes should be simple, yet have sufficient nutritional value. The body of someone losing weight must be supplied with vitamins, microelements and important amino acids.
- Eating a lot of fiber helps cleanse the intestines, so that excess weight will quickly disappear.
- An important condition for all dishes is their low calorie content. In this case, we recommend that you try the 1500 calorie diet.
- During the diet, carbonated drinks should be completely excluded from the diet, replacing them with mineral water and natural berry and fruit compotes. Also prohibited are honey, smoked meats, sausages, sweets, pickles, flour products, alcohol, spicy seasonings and sauces, and ice cream. It is necessary to minimize the consumption of granulated sugar and salt, oil and fats. You can only eat black and gray bread, mainly bran.
- The consumption of dairy products is allowed, but with a minimum fat content, preferably low-fat. Fruits can also be eaten, but they must contain a minimal amount of sugar, no grapes or bananas!
- While losing weight, you should reduce the size of portions and eat smaller meals (6 times a day).
- It is useful to include unsweetened fruits, fresh vegetables and herbs in your diet. You can eat apples, but only green ones.
- Be sure to have a fasting day at least once a week. It helps cleanse the body of harmful substances that prevent excess weight loss. At this time, you can only eat certain dishes, for example, apples or cottage cheese (preferably low-fat). It is permissible to eat only vegetables other than potatoes on a fasting day.
- The importance of drinking regime has long been proven when losing weight. You need to drink at least 2 liters of clean water per day if there are no problems with swelling. The principle of the diet for the lazy is based on the drinking regime. It is also useful to know how much water to drink to lose weight.
The calorie content of daily diet foods should be lower than before losing weight. But the figure should not be less than 1200 kcal.
Below is a sample menu for stage 2 obesity. Remember, portions should be reduced and the frequency of their intake increased.
Menu:
- first breakfast - unsweetened coffee with milk, boiled meat, sauerkraut;
- second breakfast - unsweetened green tea, low-fat cottage cheese;
- lunch - unsweetened fruit and berry compote, borscht cooked in vegetable broth without meat, boiled chicken, baked vegetables;
- afternoon snack - green apple;
- first dinner - baked potatoes, boiled lean fish;
- second dinner (before bedtime) - a glass of low-fat kefir.
Diet for type 2 obesity should be varied and low in calories. If desired, borscht can be replaced with vegetable stew or soup, baked potatoes with a salad of boiled beets and low-fat sour cream or baked carrots.
It is necessary to eat as many fresh vegetables and unsweetened fruits as possible, and gradually include porridge from cereals rich in fiber into the diet. In this case, you will be interested to know about the most useful cereals for weight loss.
The most important thing with stage 2 obesity is the desire to lose weight and become healthier. This means you will need to be patient to achieve your goal.

Exercising for type 2 obesity
Drugs
You need to understand that stage 1 obesity is not so much excess weight and a changed appearance, but rather a chronic disease of the endocrine system, in which metabolic processes in the body are disrupted. To cope with it, diet or exercise alone is not enough. In this case, complex treatment is required, which also includes medications.
Their composition, effectiveness and effect on the nervous system have caused and still cause a lot of controversy. Is it advisable to take them, what results should you expect, how not to harm yourself by starting to take a dangerous drug - all this needs to be discussed in advance with your doctor and, of course, study all the available information on the Internet.
We bring to your attention a list of the safest drugs used for stage 1 obesity:
- Orlistat (Xenical) is a drug that inhibits the action of a pancreatic enzyme. Thanks to it, the amount of fat absorbed in the intestine decreases. If the diet contains a large amount of fatty foods, taking Orlistat will be accompanied by frequent bowel movements with the release of fatty particles - steatorrhea. There is no need to be afraid of this phenomenon: it is enough to minimize the consumption of fats so that the unpleasant symptoms immediately disappear.
- Rimonabant (Acomplia) - promotes weight loss, helps prevent or completely eliminate the consequences of obesity such as hyperlipidemia or insulin resistance.
- Liraglutide (Saxenda, Victoza) – helps enhance the action of the hormone responsible for satiety.
- Lorcaserin (Belviq) is an effective appetite suppressant.
- Naltrexone helps suppress cravings for richly flavored foods (especially sweets).
The names of anti-obesity pills are in parentheses, with the active ingredient listed first.
Physical activity
Excess weight will not go away on its own if you only follow a diet and sit on the couch or at the computer the rest of the time. Movement is life, so behavioral therapy plays a huge role when losing weight.
If you want to get rid of excess weight, you will have to change your lifestyle. For this:
- Try to move more. If you are at home, turn on some rhythmic music and start cleaning. Take the stairs, forget about an elevator, and take walks in the fresh air.
- Practice all methods of complex therapy for obesity.
- Be less nervous and worry. Enjoy life!
- Find motivation to lose weight and do everything to achieve what you want.
- Give up bad habits, forget about alcohol and high-calorie foods.
- If you have mental health problems, take a course of antidepressants.
- Exercise regularly. Do exercises in the morning, go to the pool at lunch, and go cycling in the evenings. All these activities form the basis of exercise therapy (physical therapy), which can be prescribed by a specialist.
- Get enough sleep. Sleep at least 8 hours a day.
- Strictly follow all recommendations of your doctor.
Follow these rules, as well as follow the recommended diet therapy, and in a short time you will be able to achieve amazing results.
How to get rid of obesity?
An endocrinologist or nutritionist can enlighten you on how to combat obesity. The basis of therapy is adjusting nutrition and increasing physical activity.
If the desired result cannot be achieved, drug treatment and herbal medicine are used. In rare cases, surgery is performed.
Diet for 2nd degree obesity
With type 2 obesity, there is an urgent need for weight loss. For these purposes, the doctor prescribes the patient to follow an individual diet. It should be remembered that losing weight should not be too fast. Therefore, it is not recommended to use therapeutic fasting.
The basic principles of a diet for obesity include:
- inclusion of fiber-rich foods in the menu;
- increasing food intake up to 5-6 times a day;
- reduction in portion size;
- refusal of sweets, flour products and carbonated drinks;
- limiting fats of natural origin;
- compliance with the daily calorie intake;
- reducing salt to a minimum;
- Regular consumption of the required amount of water.
It is recommended to eat complex carbohydrates in the first half of the day. The best option would be cereals, fruits and dairy products.
At lunchtime, preference should be given to soups with low-fat broth. In the afternoon you need to eat protein foods. For its absorption, it is important to consume the required amount of fiber.
Exercise for Obesity
Active physical activity helps to lose weight if you are obese. With their help, the calories entering the body are consumed much faster. The optimal frequency of classes is 3 times a week.
After visiting the gym, there should be time for the body to recover. To begin with, it is enough to do gymnastics in the morning and practice walking in the fresh air before going to bed. In the future, you can increase the load.
With regular swimming, the functioning of the respiratory system improves and the figure tightens. Yoga and fitness classes are also welcome. Exercise on exercise equipment is permitted only under the supervision of an instructor.
Herbal medicine for obesity
If you are obese, you need to learn how to properly lose weight with the help of herbal medicine. Each product has a specific dosage regimen. Herbal medicine helps to increase the effectiveness of the main treatment. Without following a diet, it does not bring the desired result.
The most common herbal remedies include:
- When used correctly, vesicular ficus has a stimulating effect on the thyroid gland, ensuring the restoration of metabolism. 1 tsp dried and crushed ficus pour 2 tbsp. hot water. The drink is infused and then filtered. The resulting volume is taken several times a day.
- Parsley in the amount of 1 tbsp. pour a glass of boiling water. The resulting infusion is taken 150 ml 2 times a day. The benefits of parsley include its high content of fiber, vitamins and macronutrients.
- Herbal collection No. 6. The composition includes yarrow, corn silk, juniper fruits and alder buckthorn bark. 2 tbsp. The mixture should be poured into a thermos and filled with 500 ml of hot water. Leave the infusion overnight. In the morning it should be strained thoroughly. The medication is taken 100 ml 3 times a day.
- Collection No. 3. 100 g of cystoseira, 50 g of anise and 50 g of licorice are mixed in a small container. 1 tbsp. the herbal mixture is poured with a glass of boiling water. After an hour, the infusion is ready for use. The drink is taken 1 glass up to 3 times a day.
- A decoction of flax seeds reduces appetite and has a laxative effect on the body. In addition, it is rich in fiber and vitamins, which is extremely important when losing weight. Before preparing the decoction, the seeds are thoroughly washed. 50 g of raw material should be poured into 1.5 liters of water and placed on the stove. After boiling, you need to remove the foam. After 1 minute, the medicinal product is removed from the stove and comes to readiness under the lid. It should be taken 1 tbsp. before every meal.
Obesity and the army
Many parents and boys are interested in the question of whether people with the second degree of obesity are accepted into the army. We have already described above how to calculate body mass index, now we will look at what criteria a specialist uses to determine whether an overweight guy is fit for service.
The categories of citizens who determine the degree of suitability of a conscript for military service are described below::
- Category “A” - full suitability for military service.
- Category “B” - suitability for combat service with some restrictions. When undergoing a medical examination, the presence of minor pathologies is confirmed, for example, slightly impaired vision.
- Category “B” - assignment of the status of limited fitness. This category exempts you from serving in peacetime, but during martial law, the conscript is enrolled in the 2nd line.
- Category “G” - assignment of the status of “temporarily unsuitable”. It means that the conscript has some pathologies that can be treated, for example, fractures or obesity. In such a case, a deferment of six months is provided, which can be extended in the future if necessary.
- Category “D” - complete exemption from military service due to unfitness.
Based on this, it should be noted that a conscript with stage 2 obesity can be drafted into the army only after correcting his weight and undergoing the necessary therapy.
Operation
Diet, exercise and drug therapy did not give the desired effect? In this case, bariatric surgery will come to the rescue.
This treatment is used only for serious indications. If you just have a few extra pounds that you want to get rid of quickly, this method is not for you. The indication for surgery is a body mass index exceeding 40. However, in some cases, surgery may be prescribed for a body mass index of 35 or more, but only when the patient has serious health problems:
- hypertension;
- varicose veins;
- non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus;
- diseases of the joints of the lower extremities.
The operation may consist of:
- gastric bypass - dividing the organ into two unequal compartments, with normal functions remaining in the smaller part;
- insertion of a special balloon into the stomach, thereby reducing the volume of this organ;
- banding of the upper part of the stomach, which promotes saturation with smaller portions of food compared to the usual volume;
- sleeve gastrectomy to significantly reduce the volume of the organ and affect ghrelin - the so-called “hunger hormone”.
Surgical intervention has a number of contraindications, so doctors prescribe it only for vital indications.
Obesity is a serious illness that is easier to avoid than to later get rid of numerous consequences. Keeping your weight under control is the key to your health.
Complications
Due to the fact that visceral fat puts pressure on most internal organs, their functioning is disrupted and slowed down.
In the absence of treatment and control by specialists, stage 2 obesity becomes the cause of the following diseases:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract - pancreatitis with complications;
- gallbladder diseases (more common in women);
- haemorrhoids;
- hypertension;
- type 2 diabetes;
- fatty hepatosis;
- cardiac ischemia;
- phlebeurysm;
- myocardial infarction;
- ailments of the musculoskeletal system;
- labored breathing;
- impotence, infertility.
If treatment is ignored, pregnancy may not occur. Such a diagnosis is dangerous during pregnancy, since in this case the risk of developing various complications in the early stages of pregnancy, and anemia and respiratory ailments in the later stages increases.
Obesity of the 2nd degree is not a death sentence and is not as dangerous as the last stage of the disease. But at the same time, it carries more serious consequences than the initial stage of obesity. Therefore, it is important to seek help from specialists rather than wait for the problem to go away on its own.
E66 Obesity
Obesity is a condition in which excess fat deposits accumulate in the human body.
A person is considered to have this disease if their weight exceeds the maximum allowable for their height by at least 20 percent. Obesity occurs when the energy value of food entering the body exceeds the body's needs. Predisposition to obesity can be inherited either as a result of established eating habits or due to a genetic factor. In rare cases, obesity can be a symptom of a hormonal disorder such as hypothyroidism. Some medications, especially corticosteroids, can also cause obesity.
The risk of developing the disease increases with age. Women are more often affected. Sometimes a predisposition to obesity is inherited. The main risk factors are intemperance in eating and a sedentary lifestyle.
Obesity can cause a variety of health problems because it puts extra stress on the organs and joints of the human body. For example, the most common such problems include shortness of breath, pain in the back, hip and knee joints. Obesity increases the risk of developing some common, potentially life-threatening diseases, such as arteritis, stroke and high blood pressure.
If obesity develops, you should consult a doctor. To exclude concomitant diseases, the patient will have a blood test taken for sugar (to rule out diabetes mellitus) and cholesterol. Additionally, blood tests may be taken to detect other hormonal disorders. At the appointment, most likely, the patient’s weight and height will be measured, and an individual diet will be developed. In addition, physical activity of a certain intensity will be recommended.
Non- drug treatments
Obesity is most often treated with a weight-loss diet and increased exercise. Typically, daily calorie intake is reduced by 500–1000 from the amount recommended for people of the same height, gender and age as the patient. An individual diet is designed in such a way as to ensure slow, gentle weight loss. The diet can be selected by a doctor or nutritionist, although the patient may additionally join a self-help group. Regular moderate-intensity exercise is absolutely essential for weight loss.
Appetite suppressant medications may be effective. Sibutramine regulates appetite by affecting neurotransmitters in the brain. In addition, medications such as orlistat, which reduce the ability of the digestive tract to absorb nutrients, may be helpful. In rare cases, obesity can be treated with surgery. For example, the stomach may be stapled to reduce its size.
Complete medical reference book / Transl. from English E. Makhiyanova and I. Dreval. - M.: AST, Astrel, 2006. - 1104 p.
Surgery
Surgical interventions on the digestive tract for obesity have been known since the early 50s of the 20th century.
In order to reduce body weight in 1953, V. Henriksson (Sweden) performed resection of a significant portion of the small intestine
.
Due to the irreversible nature of changes in the intestinal tract, this operation has not become widespread. In the 1960s and 1970s, jejunoileobypass surgery
. Due to a sharp decrease in the absorptive surface of the small intestine after surgery, significant sustained loss of body weight was observed, and effective correction of hypercholesterolemia was also noted. At the same time, the study of long-term results showed that they were achieved at the cost of severe disturbances in water-electrolyte balance, hypoproteinemia, liver failure, nephrolithiasis and polyarthralgia due to anaerobic bypass enteritis in the small intestine excluded from passage. Currently, jejunoileal shunting is used extremely rarely.
As a historical stage, various modifications of horizontal gastroplasty
, which were popular in the 1980s. Their essence boiled down to transverse (horizontal) suturing of the stomach using a stapler, leaving a narrow exit from its small part to the larger one. Due to the insufficient and unstable effect, as well as the relatively high incidence of late complications and reoperations, the number of supporters of vertical gastroplasty and non-adjustable gastric banding has significantly decreased over time.
Obesity classification
Table 70-1. Classification and principles of treatment of obesity
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | Characteristics of the condition | Treatment |
| 18-25 | Normal body weight | Not required |
| 25-30 | Excess body weight | Self-restraint in food, increase in physical activity |
| 30-35 | Obesity I degree (initial) | Conservative treatment, including medication, if ineffective - installation of an intragastric balloon |
| 35-40 | Obesity II degree (severe) | Conservative treatment, installation of a balloon, in the presence of concomitant diseases - surgical intervention |
| 40-50 | Obesity III degree (morbid) | If conservative measures are ineffective, surgical intervention is performed. |
| Over 50 | Obesity IV degree (superobesity) | Surgery; a significant proportion of patients require preoperative preparation |