- Essence
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Kinds
- Treatment
- Complications
Obesity can be caused by a variety of reasons.
Depending on the factors that provoked the gain of excess body weight, the disease is divided into several types. In particular, it can be alimentary (from the Latin word “alimentarius”, which translates as “food”). This means that it developed as a result of poor nutrition. In different sources it can be found under other names: primary, alimentary-constitutional, exogenous-constitutional. It's time to figure out what it is and how you can get rid of it quickly and easily.
What is nutritional obesity
The terminology of alimentary-constitutional genesis implies primary obesity, which is understood as a mental, physical disorder of normal food intake under the influence of negative factors (sedentary lifestyle, regular unhealthy eating in large quantities).
Once the first form of the disease is identified, it is quite easy to cure if all prescribed recommendations are followed. In the future, mandatory compliance with preventive measures is necessary.
Main reasons
Treatment of nutritional obesity largely depends on the correct identification of the causes of the disease, which are conventionally divided into 2 categories.
Exogenous factors:
- constant overeating;
- the presence in the daily diet of simple carbohydrates, fats (sweets, pasta, baked goods, fatty and meat dishes);
- improperly developed eating habits (eating at night, violation of the eating schedule);
- acquired type of nutrition (for example, established national traditions);
- physical inactivity (sedentary lifestyle).
Endogenous factors:
- diseases caused by metabolic disorders;
- hormonal imbalance due to lack or excess function of the gonads.
The main risk group is women during pregnancy and menopause, since stage 1 alimentary obesity is most often diagnosed in women.
Essence

In medicine, nutritional obesity is a disease associated with impaired metabolism. Along the way, pathologies can also be helped to develop by other harmful factors, most often external (lack of physical activity, for example), less often internal (diseases of organs and systems). Heredity and disorders of the brain and psyche are excluded from the causes. Everything else can contribute to the progression of the disease in one way or another.
It turns out that nutritional obesity is the fault of the person himself, who cannot organize and balance his own diet. If the body takes in more calories than it expends, this will invariably lead to excess body weight. And you can’t blame heredity and congenital neuropsychiatric diseases here.
However, there is one big advantage in this: if a person himself has brought his body to such a state, then he can also get rid of it himself by pulling himself together and going through the entire course of treatment from beginning to end under the supervision of specialists.
How to determine the degree of obesity and symptoms of the disease
In order to check the degree of obesity and calculate body fat mass, it is necessary to calculate BMI (body mass index) using the following formula:
I = m (weight in kg) / h2 (height in m).
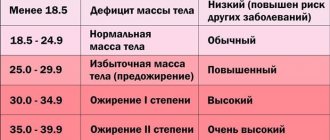
With a body mass index (BMI) of 30 kg/m2, a person is diagnosed with obesity, which requires clarification of the causes of its origin and the appointment of appropriate treatment. When pathology develops against the background of poor nutrition, it is of nutritional origin.
Clinical symptoms of such obesity:
- high BMI in comparison with the established norm;
- development of hypertension;
- the appearance of insulin resistance;
- disruption of internal organs;
- sweating and shortness of breath;
- increased amounts of food and constant overeating;
- internal complexes due to appearance (psychosomatics of obesity);
- development of type 2 diabetes mellitus;
- large increases in body weight;
- The waist size for women is more than 80 cm, and for men it is at least 94 cm.
If obesity is left untreated, negative symptoms will progress, which can lead to serious health problems and the development of psychological disorders.
Causes of obesity of alimentary-constitutional origin
In the birth of obesity, two components play a special role: a person has no control over the first, the second, especially in the first stages, is entirely in his hands. The first - constitutional - is a genetic given (here is not only the risk of developing metabolic disorders, but also the likelihood of excessive appetite and an inhibited satiety reaction). But conditions are needed for potency to enter the active phase. They are created by the second component - nutritional. Its essence follows from the name. We are talking about nutrition (“alimentum” translated from Latin means “food”) in the sense of both the quantity and quality of what is eaten. But that's not all. Another factor is the body's need for energy and nutrients. The more active your lifestyle, the higher it is.
As a result, we obtain a simple exchange formula: receipt minus expenditure. The higher the final value, the more worries the body has about what to do with the excess. Against the background of the corresponding genetic data, the body chooses a completely logical method - to save in reserve. Moreover, in difficult living conditions (in the past, and for some in the present), such a strategy was one of the conditions for survival.
One should not discount the factor of upbringing, or rather, the habits adopted in the family.
In psychosomatics, the topic of obesity is associated with the concepts of “protection” and “love”. Only a person acquires them at the wrong level. The same principle applies to increased appetite. Unsatisfied spiritual hunger (its “food” is conscious life experience) “descends” to the level of the body and finds its satisfaction in the absorption of material food.
Types of obesity
Nutritional obesity has varying degrees depending on BMI. Detailed information in the table below.
| BMI value | Obesity level |
| 25–29,9 | First |
| 30–34,9 | Second |
| 35–39,9 | Third |
| 40 and higher | Fourth |
First degree
Nutritional obesity of the first degree is already considered a disease, since body weight exceeds the norm, and a person begins to experience physical and aesthetic discomfort. At the same time, physical indicators increase (increased sweating, shortness of breath), but not so pronounced.
With proper treatment at this stage, complete recovery and maintenance of normal weight are possible.
Second degree
The second degree is clearly visualized and gives a person significant inconvenience (difficulty with walking, physical activity, breathing problems, inability to simply tie shoelaces). In most cases, obesity treatment begins at this stage.
Third degree
The third degree of obesity is difficult to treat, since the functioning of the organs of the whole body is disrupted (high blood pressure, pain in blood vessels, high blood sugar, the appearance of mental instability and depression).
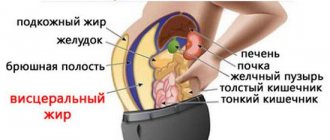
Depending on the location of adipose tissue, such obesity is divided into 3 types:
- android (male) obesity, when the fat layer is located in the abdomen, armpits, lower back and back;
- gynoid (female) obesity when the fat layer is located in the chest, buttocks, thighs and lower abdomen;
- Mixed obesity with even distribution of fat on the body.
At the fourth stage of obesity, severe symptoms are observed that are practically untreatable. Therefore, doctors recommend urgent treatment of this disease at earlier stages.
Stages of the disease
Fat begins to be deposited when the body is unable to completely use up the energy received from food. Doctors distinguish 4 stages of the disease:
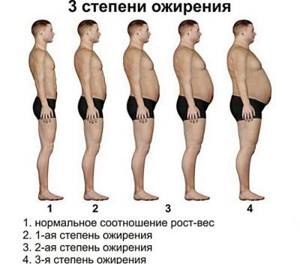
- In the first degree, the amount of fat exceeds the norm by 10-30%.
- In the second degree, the excess of lipids reaches 31-50%.
- With the third degree, body fat exceeds 50% and can reach up to 99%.
- At grade 4, the amount of fat reaches critical levels. They exceed the permissible limit by 100 percent or more.
Treatment method
The treatment method for nutritional obesity is based on turning to specialists, since it is impossible to treat such a disease on your own. The specialist will conduct all the necessary studies and prescribe the correct treatment regimen.
Recommendations for preventing the development of negative symptoms of the disease are discussed in more detail below.
Proper nutrition and diet
Treatment for obesity begins with providing the body with proper nutrition. However, express diets or long-term fasting will not give the desired result. Nutritionists advise following these recommendations:
- sufficient amount of protein and fiber in the daily diet;
- maximum salt restriction or use sea salt. In this case, it is best to salt dishes after cooking;
- exclusion of fried foods from the general diet;
- limiting the consumption of fats and spices of any origin;
- fractional meals (at least 6 times a day in small portions every 2–3 hours);
- the basis of the diet should consist mainly of vegetables and fruits;
- complete exclusion from the diet of trans fats, fast food, alcoholic and carbonated drinks;
- mandatory fasting days (3-4 times a month);
- breakfast should be hearty, and dinner, on the contrary, should be quite light and not exceed a diet of 100 calories;
- the daily calorie intake for women is 1200, and for men no more than 500;
- You need to have dinner no later than 3-4 hours before bedtime.
An approximate daily menu option when following a diet:
- 300 grams of chicken meat or cottage cheese;
- 700 grams of fruits, vegetables with the exception of bananas, grapes, potatoes and other starchy foods;
- no more than 10 grams of butter and sugar;
- from 50 to 100 grams of black or whole grain bread;
- 500 ml low-fat milk.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle
- morning exercises, running;
- compulsory gym sessions 3 times a week (aerobic exercises);
- Meals are best organized at the same time;
- ensuring adequate sleep at least 8 hours a day;
- regular walks in the fresh air;
- elimination of severe stress and emotional stress;
- prohibition of abuse of bad habits (alcohol, cigarettes);
- walking long distances and active physical activity during the day.

By following simple recommendations, excess weight begins to gradually disappear. The process is not fast, but the result obtained is well consolidated, and the general condition of the body is stabilized.
Physical exercise
As additional techniques, the nutritionist also prescribes active physical activity, presented in the list below:
- performing exercise therapy provided there are no contraindications;
- performing exercises involving a large range of motion to increase the load on the main muscle groups;
- the number of approaches is at least 20–30 times with maximum training intensity.
Regular exercise gives good results (elimination of up to 8 kg of excess weight). To treat nutritional obesity, you need hard work on yourself and constant control over your food intake.
Medications
Treatment of obesity with medications is carried out only as prescribed by the attending physician, provided there are no results in weight loss after following a diet and intense physical activity.
Exogenous constitutional disease is treated with special sibutramine-containing drugs, which are prohibited in many countries and are available only by prescription:
- Meridia;
- Slymia;
- Lindax;
- Sibutramine;
- Goldline;
- Reduxin.
The medications presented above have a certain effect on the hypothalamus (saturation center, thermogenesis). In parallel, such drugs are antidepressants in origin and regulate appetite levels.
Taking pills is prescribed only if there are appropriate indications:
- BMI is more than 30 kg/m2;
- the presence of a BMI of more than 27 kg/m2 and the parallel formation of type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia.
At the same time, drugs from this category have a considerable number of side effects:
- hypertension;
- hypothyroidism;
- the appearance of insomnia;
- dizziness and headaches;
- constipation, diarrhea, itchy skin;
- change in taste;
- the appearance of increased anxiety;
- dry mouth;
- nausea, vomiting;
- formation of tachycardia.
Sibutramines are banned because they can cause hallucinations and have narcotic properties. Therefore, such treatment requires mandatory consultation with the attending physician.
In cases of third degree obesity, plastic surgery, liposuction, and gastric resection can also be used.
Possible complications
Possible complications during the development of nutritional obesity cause irreversible changes in the body and lead to the development of serious diseases:
- the appearance of androgen deficiency;
- development of infertility;
- pain in muscles and bone tissue;
- hormonal imbalance;
- hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases;
- insulin resistance;
- hypertension (high blood pressure);
- metabolic syndrome (metabolic disorder);
- the appearance of shortness of breath;
- diagnosis of fatty liver and heart;
- oncological processes;
- decreased erection in men, decreased libido in women;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (ulcers, gastritis, pancreatitis);
- kidney and gallstones;
- psychoemotional disorder, depression;
- type 2 diabetes mellitus;
- apnea at night.
Alimentary obesity can be eliminated with the right approach to the problem (nutrition, diet, exercise, constant weight control). The progression of the pathology causes irreversible consequences that can cause death. In most cases, consultation with qualified specialists is necessary.
Symptoms of nutritional-constitutional obesity
Doctors have their own markers that help determine the degree of distress: body mass index, the thickness of the fat fold under the shoulder blade, on the thigh, abdomen, etc. But you can do without them: obesity in the literal sense of the word is obvious.
Other signs are already a consequence of stress, and over time, overload of the body's systems. This:
- dyspnea;
- high blood pressure;
- sweating;
- problems with the digestive system;
- joint pain;
- venous insufficiency;
- sleep disorders;
- fast fatiguability;
- apathy.
And... a strong feeling of hunger. This paradox is explained both by changes in metabolism during obesity (huge reserves become truly untouchable and are instantly replenished by blood glucose, the decrease of which causes hunger), as well as by disturbances in appetite regulation and a lack of satiety.
Reviews
Reviews about the treatment of nutritional obesity are generally positive, since this disease is subject to mandatory treatment and a number of therapeutic and preventive measures. In this case, not only appearance is important, but also the normal functioning of all internal organs.
Dear readers, was this article helpful? What do you think about the disease nutritional obesity? Leave feedback in the comments! Your opinion is important to us!

“After 30 years, my weight with a height of 160 cm began to go off scale over 100 kg and then I started thinking about losing weight. It was very difficult because my stomach was stretched and I was constantly hungry. At the same time, I increased my physical activity. As a result, minus 30 kg in 6 months. This is a significant result for me.”
Natalya, Kaluga
“Yes, excess weight is a serious health problem. I began to gain a lot of weight while still in school during adolescence and gradually gained 130 kg. The figure is simply huge and it is physically very difficult to move. So they prescribed treatment, and now I plan to lose up to 40 kg in at least 1 year.”
Elena Vasilievna, Simferopol
Post Views: 628
Symptoms
Manifestations of obesity depend on the severity. Main symptoms:
- constant overeating, increasing the amount of food consumed over time;
- weight gain and corresponding appearance;
- hypertension;
- skin rashes caused by increased sebum secretion;
- hyperhidrosis;
- dyspnea;
- apnea, sleep disorder;
- crepitus and joint pain due to increased load;
- increased concentration of glucose in the blood, which can result in the development of diabetes mellitus - there is even an expression: “full of sugar”;
- deterioration in the performance of internal organs;
- allergic reactions due to the fact that the liver cannot cope with its work;
- deterioration of immunity;
- psycho-emotional instability, development of complexes.
In children at an early age, motor skills are formed late, constipation, allergies, and a tendency to constant colds appear. By adolescence, metabolic syndrome develops (impaired all types of metabolism), insulin resistance (inadequate body response to insulin - both its own and those coming from outside), hyperlipidemia (high concentration of cholesterol and triglycerides), dismetabolic nephropathy (impaired kidney function and structural changes ).