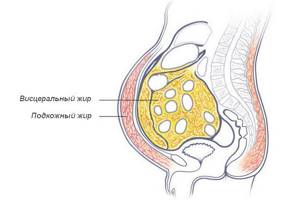
Visceral obesity is the deposition of excess fat in the cells of internal organs.
Excess weight, as well as too much body weight, always has consequences for a person in the following pathologies:
- Disturbances in the functioning of endocrine organs;
- Pathology diabetes mellitus;
- Pathologies of the vascular system;
- Diseases of the heart organ;
- The work of human joints and supporting apparatus.
Failure to comply with the daily routine and nutritional culture always threatens visceral obesity with the development of serious pathologies.
Pathogenesis
Visceral obesity is the growth of subcutaneous fat around vital internal organs, impairing the performance of functional duties, which leads to their failure.
A decrease in working life can lead to a complete stop in the functionality of the organ.
Normally, any person has the necessary fat reserves inside the body, which perform the following functions:
- Fat is a shock absorber for organs when a person falls or moves;
- An internal reserve energy supply is created to support organs in non-standard and extreme situations;
- Protects organ cells from the influence of negative side factors.
Visceral obesity is diagnosed not only in obese people, but also in people of thin build.
The type of visceral obesity can only be identified by a diagnostic method and it is impossible to visually determine how large the volume of fat mass is on the internal organs.
Most often, fat is localized in the following areas of the body:
- On the stomach and thighs in women;
- In the abdominal area and on the back in men.
In male and female bodies, even without excess weight, obesity can occur of the visceral type (beer belly).
A bulging belly, with a slender figure, is caused precisely by this type of build-up of internal fat on the organs.
What diets will help you get rid of internal fat (visceral obesity)
Visceral (internal) fat is a type of deposit that is located around the internal organs.
This type of deposits is the most dangerous to health. But in small amounts, visceral fat is necessary for the body to function normally. It serves for shock absorption and also nutrition of internal organs. There are several types of fat in the human body:
- Retroperitoneal.
- Subcutaneous abdominal.
- Internal visceral.
All these types are different from each other. The difference between them is not only the place of formation, but also their significance for the body. For example, subcutaneous fat does not negatively affect the human body.
But an excess of visceral fat can cause harm to the body such as:
- shortness of breath;
- heart attack;
- phlebeurysm;
- fast fatiguability;
- diabetes;
- heart and vascular disease;
- diseases of the digestive system.
And this is not the entire list of the negative effects of excess fat deposits on health.
Classification
There is a certain classification of visceral obesity:
| description of the pathology of obesity | BMI unit of measurement kg/m2 | degree of visceral obesity | the risk of developing concomitant pathologies with waist circumference is measured in centimeters | |
| in women - 80.0 - 88.0; | in women, the waist is greater than 88.0 cm; | |||
| for men - 94.0 - 102.0 | in men, more than 102.0 cm. | |||
| overweight | 25,0 — 29,90 | excess weight | increased risk | high enough |
| average obesity | 30,0 — 34,90 | first degree | high risk of development | highest possible |
| moderate type obesity | 35,0 — 39,90 | second degree | high enough | highest possible |
| severe obesity | more than 40.0 | third degree | highest possible | highest possible |
Also, the visceral type of fat accumulation is divided according to the nature of the pathology:
- Stable flow - the weight does not fluctuate in any direction for a long time;
- Progressive accumulation of fat - rapid weight gain;
- Residual in nature , in which even after losing weight, fat remains on the internal organs.
Visceral fat accumulation is also classified according to its location:
- Heart organ - fat inside the heart sac leads to failure;
- Liver cells - pathology fatty hepatosis;
- Kidney organ - leads to disruption of the urinary system and urinary organs;
- The pancreas is a digestive malfunction.

Visceral fat
How to lose visceral fat with pharmacological treatment

In recent years, major discoveries have contributed to the identification of some of the most important molecular pathways involved in the regulation of energy metabolism. It is worth noting that several of these molecular targets are transcription factors that play a central role in both energy homeostasis and inflammation. It is clear that these discoveries have contributed to the development of new drugs of potential interest. Glitazones are a class of drugs that activate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-γ, a transcription factor that regulates glucose homeostasis and has anti-inflammatory activity as well as potentially anti-atherosclerotic properties. Equally important is the observation that glitazones increase subcutaneous fat deposition and thereby prevent the accumulation of harmful intra-abdominal fat, perhaps a phenomenon that explains how this class of drugs improves insulin sensitivity. Although glitazones have been associated with reductions in all-cause mortality and composite cardiovascular endpoints in some clinical trials, recent meta-analyses have highlighted that glitazones may cause heart failure in some patients. In one meta-analysis, rosiglitazone was associated with excess cardiovascular mortality. The question of whether the two molecules of this class, rosiglitazone and pioglitazone, have marked differences in their metabolic properties remains unresolved and is being discussed at this stage.
A large proportion of obese individuals are insulin resistant and suffer from hypertension. Because hypertension, hyperinsulinemia, and visceral adipose tissue are linked by complex, reciprocal molecular interactions, it is logical to expect that blocking an interconnected pathway could provide benefits on multiple scales. In this regard, blocking RAS, a key pathway regulating adipocyte differentiation, using ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers may offer promising avenues. Although not designed for this purpose, clinical trials have shown that RAS blockers significantly reduce the risk of diabetes. On the other hand, studies have emphasized that with regard to cardiovascular events, there appear to be no significant differences between different classes of antihypertensive drugs. Despite these findings, it should be emphasized that many recent intervention trials comparing different antihypertensive drugs were not specifically designed to address obesity-related hypertension. Therefore, in light of the devastating consequences of type 2 diabetes, future studies specifically examining the role of RAS blockers in hypertensive, glucose intolerant, and obese patients may provide important insights.
Causes of visceral obesity
Factors provoking visceral obesity:
- Inherited genetic predisposition to accumulate fat in the body;
- Hormonal imbalances in women during menopause and menopause;
- Failure in the hormonal sphere in the female body during the period when a woman is carrying a child and feeding the baby with mother’s milk;
- Nervous tension - situations of constant stress;
- Psycho-emotional causes - panic attacks, as well as depression and psychosis;
- Abuse of alcoholic beverages, especially beer in men, when there is a hormonal imbalance and replacement of the male hormone testosterone with female hormones that do not take part in the breakdown of fat molecules;
- Physical inactivity is a complete lack of physical activity on the body, no activity or walking;
- Disturbance in the functioning of the brain organ - the hypothalamus;
- Poor nutrition - the diet is dominated by fatty foods and foods containing a maximum of carbohydrates;
- The process of overeating;
- Negative effects on the body of certain groups of medications - a group of hormonal drugs, antidepressants, and tranquilizers;
- Failure in the endocrine system;
- Pathology of the thyroid gland - hypothyroidism;
- Cushing's syndrome - Itsenko;
- The pathology of a decrease in the level of the hormone serotonin, which makes a person understand that he is already full of food.
If the visceral type of obesity occurs due to poor nutrition and physical inactivity, then this is the most favorable course of the disease, which can be cured by adjusting nutrition (diet) and increasing stress on the body and playing sports.
If fat accumulates in the abdominal area due to endocrine disruption and other pathologies, then this type of visceral obesity will occur in a chronic stage.
Fat accumulates in the abdomen due to endocrine disruption
Methods to combat visceral fat
Although this type of deposits is the most dangerous for the body, it is the easiest to deal with. Unlike other types.
It is very important to adjust your diet. And it won’t do without physical activity.
But this does not mean that you need to go on a strict diet. The best option would be to gradually review your diet. This applies to people with large body weight. Because a sharp restriction in food can harm the body.
To organize a diet to get rid of visceral fat, you must first:
- exclude fatty, fried foods, as well as smoked foods;
- eat 5 times a day in small portions;
- reduce the consumption of fats and carbohydrates;
- drink 2 liters of water per day;
- exclude sweets and flour;
- It is prohibited to drink carbonated drinks.
It is necessary to include more fruits, vegetables, and greens in your diet.
Products that help fight fat deposits:
- broccoli and cauliflower;
- greenery;
- cucumbers;
- apples;
- dried fruits;
- berries;
- citruses;
- dairy products (low fat);
- eggs;
- all types of legumes.
Don't forget about physical exercise. This is important in the fight against fat deposits. Aerobic exercises and cardio exercises help well. But people weighing more than 85 kilograms should treat them with caution. You can start with brisk walking. To avoid unnecessary stress on the heart.
Changing your lifestyle is hard work on yourself. But do not forget that visceral fat can pose a threat to health.
Calculation formula
The visceral type of obesity may not appear visually for a long period of time and may be located inside the human body.
You can visually suspect fat accumulation only when body weight begins to increase, but there are no signs of excess fat in the abdominal area.
For this reason, every person, especially those with a predisposition to the development of systemic pathologies and diseases of the heart organ, needs to constantly monitor their weight index and prevent it from deviating from the norm.
In order to calculate the required normal weight, there is a calculation formula:
Indicator I (BMI) is equal to weight in kilograms (M) / per person’s height in meters squared (H2). If the BMI index shows a deviation from the norm higher than 30, then urgent measures must be taken.
Hormone production disorders

In the internal organs there are fat cells in which a hormone-like substance is synthesized - adiponectin. Thanks to it, glucose production in the liver is reduced and muscle fibers become more sensitive to insulin. Also, with sufficient concentration, the blood thins and the processes of blood clot formation are inhibited.
When visceral fat begins to form in large quantities, these protective mechanisms can no longer work as before. This is due to the fact that special substances are released in adipose tissue that disrupt the functioning of these hormones.
Metabolism in fat cells is regulated by the hormone leptin. Initially, its amount in the blood depends on the amount of fat deposits in the internal cavity and it is undesirable to allow its strong fluctuations. Thanks to it, cells are protected from the toxic effects of triglyceride breakdown products. With obesity, the content of this hormone in the blood drops sharply.
In the vessels with this disease there is almost always calcium in large quantities, to which cholesterol is added. In such patients, atherosclerotic plaques are diagnosed.
Visceral adipose tissue also produces a hormone that disrupts the functioning of blood vessels and promotes their narrowing. All this leads to the fact that the detoxification system in the body can no longer function fully. For this reason, a large amount of harmful substances builds up in the blood. This condition leads to an imbalance in the alkaline balance and the development of acidosis.
Symptoms of pathology
Excess body weight is not the only sign of visceral obesity; there are also other symptoms:
- The pathology of a high blood pressure index is arterial hypertension;
- Diabetes mellitus type 2;
- Shortness of breath when walking and resting;
- Swelling in the limbs and face;
- Libido in women and potency in men decreases;
- The functionality of the genital organs is impaired, which can lead to impotence and frigidity, as well as infertility, both for men and women;
- Diseases of the heart organ - rapid heartbeat - tachycardia, slow heartbeat - bradycardia, as well as lack of oxygen in the myocardium, which provokes cardiac ischemia:
- Pathologies of the liver organ - frequent nausea and pain in the right side of the body;
- Lethargy of the body and increased weakness;
- Increased fatigue of the body;
- State of depression and stress;
- An appetite that a person cannot control, leading to overeating.
To check yourself whether there is a pathology of visceral obesity, then you need to be weighed on scales that have a body fat analyzer.
Such scales can be purchased at pharmacy kiosks. Patients with heart pathologies and vascular diseases need to have such scales.

Scales with fat analyzer
Abdominal obesity of the apple type
Abdominal obesity is also known as visceral obesity or apple obesity. In this type of obesity, adipose tissue is mainly deposited in the abdominal cavity. We are talking about visceral obesity when a woman’s waist circumference is at least 80 cm, and a man’s is at least 94 cm. Abdominal obesity is more common in men.
Abdominal obesity is one of the components of the so-called metabolic syndrome. Extra pounds and increased abdominal fat are often accompanied by other health problems:
elevated blood triglyceride levels (>150 mg/dL);
arterial hypertension ;
elevated fasting glucose (>100 mg/dL);
low HDL cholesterol (called good cholesterol), <40 mg/dL in men and <50 mg/dL in women.
Treatment methods
Therapy for visceral obesity is divided into weight loss and maintaining this weight. This entire process can take time - about one year.
Visceral obesity is treated by an endocrinologist, who can involve a cardiologist and surgeon in treatment.
Treatment of excess weight is comprehensive and the main method is diet and an active lifestyle. The diet also accompanies the drug course of therapy.
Nutrition
The main focus of the diet is to reduce excess weight by reducing fat volume.
Diet principles:
- Reduce daily caloric intake by 30.0%;
- Reduce fat and carbohydrate intake;
- Changes in the nutrition process should be carried out gradually;
- 1 time per week - fasting days;
- The diet must comply with the approved products provided by the endocrinologist;
- Minimum salt and sugar;
- You need to eat up to 6 times a day in small portions;
- You can use the services of nutritionists, or use diet table No. 8 according to Pevzner.
In combination with a diet, use sports, or exercise in a fitness club, and be sure to walk or ride a bike.

The diet must correspond to permitted products
Drugs
If dietary nutrition does not help reduce weight in visceral obesity, then the doctor prescribes drug therapy with the following drugs:
- Medicine Orlistat . The course of therapy is from 90 days to 4 years;
- The drug Metroformin is used for diabetes mellitus , which reduces the percentage of fat absorption from the intestines;
- Analogues of the glucagon-like peptide substance , which give the patient a feeling of fullness in the stomach.
It is also necessary to take into account that the use of diuretics in the treatment of visceral obesity is prohibited and it is impossible to use any drugs on your own.
The effectiveness of the medications occurs within 12 months.
If the process of losing weight has been successful, then re-diagnosis of the patient’s body is necessary in order to identify new parameters of the body and possible risk factors for the development of visceral fat gain.
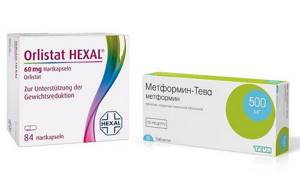
The drugs Orlistat and Metformin used in the treatment of visceral obesity
Operations
If drug treatment for visceral obesity is ineffective, the patient is offered surgical intervention.
The surgical techniques are:
- Installation of a balloon inside the stomach cavity, which absorbs a certain part of the food;
- Shunting in the small intestine area;
- Reduced gastric capacity.
Also, after surgery, it is necessary to go through a rather difficult period of rehabilitation process, which lasts more than one month. At the same time take iron supplements, calcium salt minerals and multivitamins.
Liposuction is performed after stabilization of body weight, and during this period, abdominal plastic surgery can be performed.
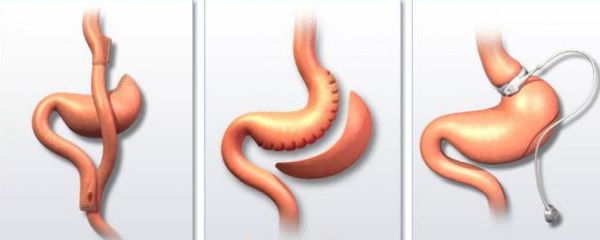
Bypass surgery and gastrectomy
Abdominal obesity – how to treat?
Abdominal obesity is a health problem and therefore requires consultation with a doctor. First of all, it is necessary to determine whether we are dealing with simple obesity or with secondary obesity resulting from another disease.
To do this, the doctor will perform a thorough history and physical examination and may expand the diagnosis to include additional tests (such as hormonal tests). If we are dealing with secondary obesity, treatment of the underlying disease is important.
If you are simply obese, your first step should be to change your diet and lifestyle. It is recommended to consult with a nutritionist and together develop a rational diet. Nutritionists and doctors will create an individual nutrition plan. You can also try one of the weight loss diets on your own - the low-calorie diet, the South Beach diet and another that speeds up fat burning.
In addition, physical activity is necessary, which should be planned depending on the current capabilities of the body. Sometimes, despite trying to change your lifestyle, you cannot achieve sufficient weight loss. Pharmacological treatment should then be considered.
In Russia, the drug orlistat is used to treat abdominal obesity. Other drugs that limit the absorption of fats from food, such as chitosan, may be used. It works by binding lipids and therefore inhibiting their absorption.
About
Complications
Complications of the development of visceral obesity affect many body systems and almost all internal organs.
Fat compresses the myocardium, which does not pump the required amount of blood through the circulatory system, which leads to the following pathologies:
- Severe migraine pain;
- Hypoxia of internal organs and brain cells;
- Blood pressure index is too high;
- Ischemia of the cardiac organ;
- Myocardial infarction;
- Ischemic type stroke;
- Slowing down the lymph flow.
Visceral obesity also causes the development of serious pathologies:
- Metabolic syndrome in diabetics, when the body becomes intolerant to glucose;
- Diabetes mellitus, both insulin-dependent and non-insulin-dependent;
- Development of atherosclerosis;
- Disorders of the menstrual cycle in women;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- Oncological neoplasms;
- Pathology of fatty hepatosis, which can lead to stoppage of liver function;
- Phlebeurysm.
These complications are quite dangerous for the body, and they must be treated together with the pathology of visceral fat deposition.
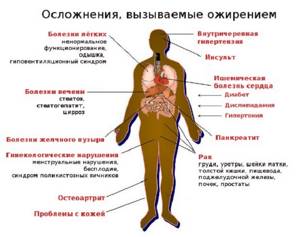
Complications caused by obesity
Why is it dangerous?
The effect of excess accumulation of fatty tissue negatively affects blood pressure. Fat envelops the heart, puts pressure on the blood vessels, which causes severe headaches, the development of ischemia, atherosclerosis and heart attack. Since the movement of lymph and blood throughout the body slows down, this leads to a deficiency of oxygen in the tissues. Visceral obesity is dangerous because it can hide inside the body for a long time, disrupting the functioning of organs, and is difficult to treat. However, with an integrated approach to the problem, pathology can be defeated. Otherwise, there is a risk of developing:
- Alzheimer's disease;
- varicose veins;
- oncology;
- diabetes mellitus;
- fatty hepatosis;
- hirsutism, menstrual irregularities;
- metabolic syndrome (when the body becomes tolerant to glucose);
- formation of cholesterol plaques.
Prevention
Prevention of visceral obesity must be addressed long before it begins to manifest itself visually.
Prevention measures:
- Proper nutrition with limited carbohydrates and fats;
- Active lifestyle and sports;
- Quitting nicotine addiction;
- Refusal of alcohol, especially beer;
- Avoid overstraining the nervous system, which can cause disruption of the endocrine organs.
How to get rid of it
If you carefully study the reasons for its appearance, you can identify the following methods of control:

- Review your diet , introduce foods high in coarse fiber into your diet. Consume large amounts of complex carbohydrates and replace animal fats with vegetable ones.
- Introduce physical activity, walking, and swimming into your daily lifestyle .
- Drink plenty of water , because... In most cases, the metabolism in the body slows down precisely because of the lack of water. Restoration of metabolism in general.
- Correct daily routine : good sleep at least 9-10 hours a day.
- Medicines - in some cases, their use is necessary when a person cannot cope with his problem on his own; medications are administered aimed at cleansing the body of toxins, suppressing appetite and accelerating digestion due to rapid metabolism.
- Massage is an auxiliary method of struggle that has a positive effect in combination with the listed methods and is aimed at tightening the abdominal muscles and draining lymph.