In the 21st century, the problem of obesity has affected everyone - regardless of social status, age, gender and place of residence.
According to the World Health Organization, about 1.7 billion people in the world are overweight.
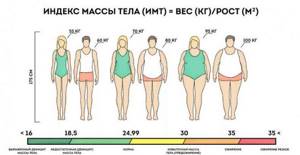
WHO predicts that by 2025, 40% of men and 50% of women will be obese. To diagnose obesity and determine its degree, the body mass index (BMI) is used, which is obtained by dividing the patient’s body weight (in kilograms) by his height (in meters), squared. Normal body weight corresponds to a BMI of 18.5–24.5. A BMI of 25.0–29.9 indicates overweight, and a BMI of more than 30 indicates that the patient is obese.
Diagnosis of obesity
:
- Class I obesity is diagnosed with a BMI of 30.0 - 34.9
- obesity II degree - with a BMI of 35.0 - 39.9
- III degree obesity (or morbid) - with a BMI over 40
It must be remembered that the BMI indicator is not reliable for children, pregnant women, as well as athletes and people with very developed muscles. For these categories of patients, the presence of obesity and its degree are determined differently.
Causes and consequences of obesity
A person can “earn” obesity on his own or “inherit it.” A common cause of obesity is regular overeating and low physical activity, i.e. burning insufficient energy when consuming high-calorie foods. Simply put, a person consumes too much and “spends” too little.
Obesity can also be caused by various malfunctions in the body. In particular, genetic and endocrine disorders can lead to obesity. True, this type of obesity is much less common than the first.
Obesity can cause a person not only moral discomfort and reduce his level of self-esteem, but also cause serious health problems, including the development of deadly diseases of the heart and gastrointestinal tract. Obese people are less productive and tire more quickly, and their life expectancy is shortened. Therefore, it is important that a person’s weight does not exceed the recommended norm and does not create additional stress on the body’s life support systems. Regular physical activity and a proper diet plan help you stay in shape. A therapist can help you form it.
Examination and diagnosis
A bariatric doctor may order a variety of tests to check for factors associated with being overweight or obese, such as:
- diabetes tests such as fasting blood glucose and hemoglobin A1C;
- lipid and cholesterol levels;
- thyroid-stimulating hormone level;
- liver blood tests;
- blood test for kidney function;
- vitamin D level;
- electrocardiogram to assess heart rhythm;
- exercise test to measure heart performance during exercise;
- Measuring your metabolic rate to see how many calories you burn at rest;
- other tests and tests, depending on individual medical needs.
How to calculate body mass index
Body Mass Index (BMI)
is a “marker” that makes it possible to assess how much a person’s weight corresponds to his height, i.e. whether current body weight is normal or outside the minimum or maximum threshold values. BMI is calculated using a simple formula: body weight in kilograms must be divided by height in meters squared.
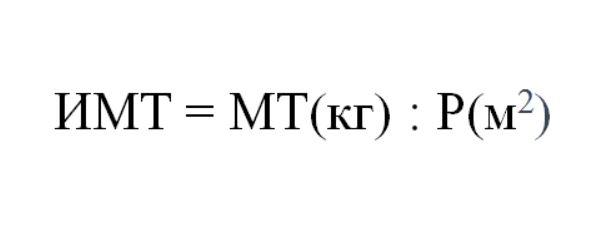
1.7 meters tall
weight
80 kilograms
, then the BMI will be
27.7
, this is an indicator
of excess body weight
.
The World Health Organization offers the following interpretation of BMI indicators:
Body mass index
- a conditional value, it does not take into account a person’s physique or the ratio of fat and muscle mass, so BMI is usually not calculated for professional athletes and pregnant women. However, if your body mass index does not fall within the “normal weight” range, then this is a reason to see a general practitioner. He may order additional tests to rule out the possibility of developing diseases that could contribute to weight gain.
The patient may also be classified as a “risk group”, or the so-called “overweight” group. They include people who cannot yet be diagnosed as obese, but excess body weight can trigger the development of serious concomitant diseases. Doctors usually recommend changing lifestyle and diet for such patients.
How is a person's body composition analyzed?
Calculating body mass index is not the only and far from the most accurate way to diagnose obesity. There are special devices that can be used to perform bioimpedance measurements
, i.e. analyze body composition. This diagnostic method is based on human anthropometric data and the ability of different types of tissue to conduct electricity differently.
The point is that the device can additionally evaluate tissue, distinguish muscle tissue from fat, determine skeletal muscle mass and fluid mass in the body. Using this analysis, we can say exactly how true the hypothesis is that a person has “heavy bones.” Knowledge of body composition helps doctors assess the risks of developing various diseases.
Who diagnoses obesity
A person can monitor their body weight independently, including by periodically calculating their body mass index and comparing it with the threshold values established by WHO. However, only a doctor can make a diagnosis of obesity. Typically a therapist.
If there is a suspicion of the development of diseases caused by obesity, the general practitioner can write a referral to the patient for consultations with other doctors. This is necessary to clarify the diagnosis and prescribe treatment. Obesity can also be treated with drug therapy, but the decision to prescribe it can only be made by a doctor if there are necessary medical indications.
Methods to combat obesity
If obesity is symptomatic, then treatment of the underlying disease will first be required. In most cases, this is a disease of alimentary-constitutional type, in which it is necessary to adjust the lifestyle by changing eating habits and introducing regular physical activity into the schedule.
Diet
An individual nutrition plan will be drawn up by a nutritionist. The main principle of the diet is to reduce the calorie intake to 1200-1600 kcal for women and to 1500-1900 kcal for men. The menu includes foods high in protein and fiber, and minimizes fats and simple carbohydrates. It is important to consume carbohydrates with a low glycemic index, as they reduce appetite and have a positive effect on blood sugar levels. It is recommended to keep a food diary to track any changes.
Physical exercise

An approximate set of exercises for obesity.
Physical activity is increased in accordance with the general condition of the patient and his level of physical fitness. With a high degree of obesity, a gradual increase in loads is required. It is better to start by increasing the duration of walking, then move on to gymnastics and swimming, and then you can start visiting fitness rooms, jogging and other more intense sports.
Yoga can be a good option, as it allows you to choose the appropriate direction for different health conditions. For example, for patients with severe obesity, yoga with a correct approach to the spine, slow and smooth, without inversions and other difficult poses, is suitable. Breathing practices will also be useful, as some of them help burn visceral fat.
Drug treatment
Medicines are prescribed only for high obesity, when the diet has proven ineffective and the patient has complications that do not allow increasing physical activity. In this case, therapy is carried out aimed at slowing down the processes of absorption and breakdown of fats and increasing the activity of serotonin and adrenaline receptors (to accelerate saturation and suppress appetite). HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, fibrates and ACE inhibitors are used in treatment.
In cases of severe obesity and in the absence of contraindications, bariatric surgery is permissible. Good results in the treatment of obesity are shown by such procedures as formation of a small stomach, gastric bypass and resection of part of the intestine.
Who treats the consequences of obesity?
Obesity
is a complex disease that can contribute to the development of other diseases. Therefore, a patient diagnosed with obesity may need consultation or assistance from other specialists.
Endocrinologist
will help identify the endocrine causes of obesity. To do this, the patient will need to undergo a test to determine the level of glucose and a number of hormones in the blood plasma, an oral glucose tolerance test and other recommended tests. If a doctor discovers an endocrine disease in a patient, he will prescribe the necessary drug treatment.
Excess weight in women can cause problems with pregnancy and the development of polycystic ovary syndrome. This should be determined by an obstetrician-gynecologist.
during the inspection. PCOS can be treated with medication or surgery. For effective treatment, it is necessary to take measures to normalize the patient’s weight. Recommendations for weight loss are given by your doctor.
Excess weight also affects the cardiovascular system. Obese people are at risk of developing hypertension, atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease and other dangerous diseases. For diagnosis and treatment, the general practitioner refers the patient to a cardiologist
.
If a general practitioner suspects that an obese patient has problems with the gastrointestinal tract, he will refer the patient to a doctor
-
gastroenterologist
. The hypothesis can be confirmed or refuted during the diagnostic process.
An obese man may experience decreased sexual function. A urologist will help solve this problem
. He will prescribe treatment based on the diagnostic results, but to restore sexual function the patient will have to work on normalizing his weight.
Sometimes excess weight can be a consequence of psychosomatic disorders. A neurologist helps to detect and eliminate the cause of these disorders.
or
a psychiatrist
. The general practitioner also refers the patient to him for an appointment. To treat depression, the patient may be prescribed antidepressants.
Excess weight can cause disturbances in static movement, a person can develop osteochondrosis, joint deformation occurs, and pain in the limbs occurs. An orthopedic traumatologist helps solve these problems.
.
In some cases, a patient diagnosed with obesity needs to visit several doctors at once in order to formulate a set of treatment measures. This will include recommendations on physical activity, dietary adjustments and the use of multi-target drugs. A number of medical institutions provide group classes to combat excess weight for obese patients.
Symptoms
The leading clinical manifestation of the pathology is excess weight. The patient's appearance changes characteristically - pseudogynecomastia, a fatty "apron" on the abdomen and a double chin may appear.
Against the background of obesity, hernias often develop - inguinal and umbilical, which is due to muscle weakness combined with an increased load on it.
In grades I and II, patients may not present any complaints other than the appearance of an aesthetic defect.
Against the background of III-IV degrees, the respiratory, cardiovascular and digestive systems suffer.
As the disease progresses, the following symptoms appear:
- hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating);
- peripheral edema (especially of the lower extremities);
- dyspnea;
- headache;
- dyspeptic disorders (heartburn, nausea);
- chronic constipation;
- arthralgia (joint pain);
- general weakness;
- daytime sleepiness;
- nervousness;
- increased irritability.
How to eat if you are obese
To treat and prevent obesity, doctors recommend switching to a healthy diet. This will be useful for everyone, even people with normal weight.
Doctors and nutritionists recommend taking food in small portions, but more often. It would be optimal to eat 4-5 times a day, avoiding overeating. The diet should be balanced and varied; you should definitely try to eat fresh fruits and vegetables all year round, and not just in season. It will be useful to switch to whole grain products. It is better to replace fatty meat with poultry; in rare cases, eating lean meat is allowed, but you will have to forget about meat and sausage products. You can consume milk and dairy products, but preference should be given to low-fat ones. Vegetable oils will be useful, but in moderation. The same goes for fish, nuts and legumes; it is recommended to include them in your diet at least 1-2 times a week. It is better to cook by steaming, avoiding frying.
Food should be chewed thoroughly and sufficient time should be given to eating. The last meal should be light; it is better to limit yourself to a glass of kefir or fruit. You should not eat immediately before bed; this will force the body to work again and will not give it the opportunity to prepare for rest. You need to leave at least a couple of hours for “unloading” before going to bed.
Physical activity if you are overweight
Physical activity is one of the methods to combat excess weight. According to WHO recommendations, people who want to lose excess weight need to move more. Physical activity should be regular, a total of at least 2.5 hours per week
. But not only the volume of training is important, but also the energy balance. Golden rule: “You need to spend more than you receive.” Simple math. Food provides a person with the energy that he must spend so as not to gain a couple more extra pounds. Aerobic types of physical activity are considered the most useful: swimming, dancing, Nordic walking, etc.
The load recommended for the patient must be determined by the doctor. It will largely depend on the condition of the body and the presence of concomitant diseases. Therefore, before choosing a physical activity regimen, you need to consult with your doctor.
Symptoms of obesity of internal organs
The first pathological symptom of the pathology is an enlarged abdomen against the background of thin lower extremities. The figure of such people is very similar to an apple. However, not in all cases internal obesity can be diagnosed by external signs.
You should pay attention to your health status if:
- the appearance of shortness of breath when performing even minor physical exertion;
- frequent disorders of the functioning of the digestive tract;
- the appearance of a feeling of fatigue that is present on an ongoing basis;
- menstrual irregularities;
- development of depression;
- decreased sexual desire and activity.
The clinical picture of obesity will depend on the degree of damage to internal organs.
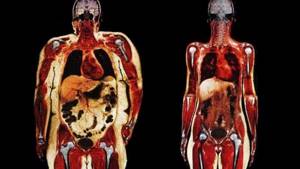
At the initial stages of formation, the pathology does not manifest itself in any way.
In the future, an increase in the amount of fat deposits leads to disruption of the functioning of one or another organ, and as a result, corresponding symptoms will appear.











