Bariatric surgery is a field of medicine that combines manipulations and surgical interventions that are performed to reduce total body weight, treat obesity, as well as prevent and treat obesity-related diseases. Surgical weight loss is a scientifically proven method of combating excess weight, the effectiveness and safety of which has been proven by many years of practice and the results of hundreds of clinical trials.
Surgical weight loss: principles, results and benefits
Bariatric surgery offers several alternative surgical treatments for obesity and related conditions. Some methods are based on slowing down the evacuation of food and prolonging the feeling of satiety without disrupting the physiology of digestion. Radical treatments modify the anatomy and function of the digestive tract, resulting in decreased absorption of nutrients, fats, carbohydrates, and food calories.
Regardless of the method used, surgical weight loss leads to guaranteed weight loss - patients manage to get rid of 40-90% of excess weight. When using radical methods, lifelong results are achieved.
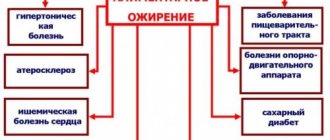
The most important result of the operation is the prevention or reversal of severe chronic diseases that increase the risk of premature death. Among the diseases associated with obesity are not only diabetes mellitus, but also atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension, coronary heart disease, and degenerative diseases of the spine and joints.
Bariatric surgery normalizes body weight and metabolic processes, reduces the risk of premature death, and increases life expectancy. Maintaining a normal body weight does not require strict dieting, but following the basic principles of proper nutrition will further improve your health and improve your quality of life.
Surgical methods of losing weight: types of operations
Modern bariatric surgery uses various methods to solve the problem of obesity and chronic diseases associated with excess body weight. The choice of surgical method of weight loss is made on the basis of a detailed analysis of the clinical case after comprehensive laboratory diagnostics.
Basic surgical methods of weight loss (types of operations):
- Gastric banding.
- Gastric ballooning.
- Longitudinal gastrectomy.
- Gastroplication (suturing of the stomach).
- Gastric bypass surgery.
- Biliopancreatic bypass.
You can obtain detailed information about modern methods of surgical treatment of obesity at the Weight Loss Center (Moscow) during an individual consultation. Consultations are conducted by a surgeon of the highest category, Dmitry Vladimirovich Gladyshev. This publication discusses the main surgical methods of weight loss with a brief description of the principles of each surgical intervention, its features and advantages.
Prevention of complications
- To monitor the condition of the sutures, leave a drainage tube in the abdomen for a while;
- To prevent ulcer formation and reflux - esophagitis in the first three months after surgery, drugs that reduce the acidity of gastric juice are prescribed;
- To prevent the formation of gallstones, the gallbladder is removed;
- For gastric bypass and biliopancreatic bypass, lifelong intake of B vitamins, iron, calcium and vitamin D is prescribed. For other types of operations - for the duration of weight loss;
- To prevent constipation, it is recommended to drink fluids between meals and, if necessary, take laxatives.
- Some complications can be avoided by changing your eating habits.
Gastric banding
Gastric banding is a surgical method of losing weight, the principle of which is based on slowing down the evacuation of food by narrowing the stomach at the border of its upper and middle third.
Principle of the method.
During surgery, a ring is placed on the outer wall of the stomach, which narrows the lumen of the organ and slows down the evacuation of food from the stomach into the small intestine. The total volume of the stomach does not decrease. The operation is performed under anesthesia under the control of endoscopic equipment (laparoscopic method).
The bandage (ring) slows down the movement of food through the upper digestive tract. Lingering in the upper third of the stomach, the food bolus affects the baroreceptors of the mucous membrane, which prolongs the activation of satiety centers in the brain. After banding, patients do not feel hungry for a long time and are satisfied with small portions of food.
Advantages.
Gastric banding surgery is performed without compromising the integrity of the organ. The physiology of the digestive process and the natural path of food through the gastrointestinal tract are preserved. After surgery, the absorption of essential nutrients, including vitamins and minerals, is not impaired.
Effect
. Gastric banding allows you to get rid of 30-40% of excess weight and promotes the formation of correct eating habits. The result is achieved by reducing food consumption and reducing the overall calorie intake.
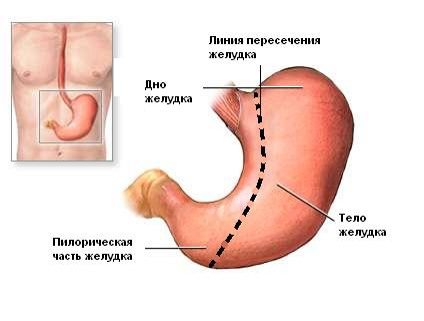
Sleeve gastrectomy
Reducing the size of the stomach during this operation is carried out by removing most of the stomach. A narrow tube is created from the stomach, which makes it difficult for solid food to pass through the narrow long sleeve and it remains in the stomach longer, creating a lasting satiety effect. In addition, appetite decreases, as the section of the stomach in which the hormone ghrelin (hunger hormone) is produced is removed. The operation is performed laparoscopically. The duration of the surgical intervention is about an hour.
Advantages of the operation:
sleeve gastrectomyWeight reduction reaches 60% of excess weight;
- Preservation of the muscles of the inlet and outlet sections of the stomach (sphincters) contributes to the normal movement of food from the stomach to the intestines;
- After the operation, blood sugar normalizes;
- The operation is performed at any age, starting from adolescence;
- Disturbances in the metabolism of proteins, fats, vitamins, and calcium are not so pronounced, since the intestinal stage of food digestion is preserved;
- There is no need to take vitamins and minerals throughout your life;
- The gallbladder is not removed.
When is it done?
- With a body weight of 35 to 45 kg/m2 and the risk of performing more complex operations;
- As the first stage for subsequent bypass operations;
- If gastric banding is ineffective.
Video: laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy
Gastric ballooning
Gastric ballooning is a surgical method of weight loss based on reducing the effective volume of the stomach by installing a silicone balloon filled with saline into the organ cavity.
Operating principle
. Formally, gastric ballooning does not apply to surgical methods of weight loss. This is not an operation, but a simple manipulation that takes about 30 minutes and does not require general anesthesia. The procedure is carried out using an endoscope, which is inserted into the stomach cavity through the esophagus, as during a diagnostic gastroscopy.
Installing a balloon reduces the usable volume of the stomach, which speeds up saturation, reduces food consumption and reduces the energy value of the diet.
Advantages.
Ballooning is a non-surgical method of losing weight, which is used in cases where anesthesia is contraindicated for the patient for health reasons. Another advantage of this method of losing weight is the preservation of normal digestive physiology. Essential nutrients are absorbed in full. The result of the operation is reversible, which leaves the possibility for the subsequent use of other surgical methods for treating obesity.
Peculiarities.
The silicone balloon is gradually destroyed by the aggressive environment of the stomach (hydrochloric acid and digestive enzymes); it must be removed after six months. For this reason, ballooning is often used as a preparatory step before radical surgery.
Longitudinal gastrectomy
Longitudinal gastrectomy is a surgical method of weight loss based on the actual reduction of the total volume of the stomach due to resection of the lateral part of the organ. Other names of the technique: longitudinal gastrectomy (gastric bypass), sleeve resection (Sleeve).
Operating principle
. Sleeve resection is performed under anesthesia. During the operation, the surgeon removes the side part of the gastric wall, the volume of the organ is reduced to 100 milliliters. The valve system is preserved, which ensures normal motility and physiological functioning of the digestive tract after surgery.
The surgical method of weight loss gives excellent results due to a decrease in the total volume of the stomach. The excellent effect is explained not only by a sharp decrease in food consumption, but also by a decrease in the secretion of ghrelin - the “hunger hormone”, which was produced in the removed fragment of the gastric wall before the operation.
Reference
. Ghrelin is a hormone that is produced in the stomach and acts on the hunger centers in the brain, causing and increasing appetite.
Advantages.
After longitudinal resection of the stomach, no foreign objects remain in the abdominal cavity. The motility of the digestive tract is not affected, the physiology of digestion is not disturbed. Essential vitamins, amino acids and microelements are absorbed in full. The absorption of drugs is not impaired.
Effect.
Sleeve resection normalizes the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and promotes the formation of correct eating behavior. After surgery, patients manage to lose 65% of excess weight. This surgical method of weight loss provides long-term stable results.
Vertical gastroplasty - indications and contraindications
The method of surgical treatment of obesity under consideration has several names.
During the manipulation, the surgeon performs a longitudinal resection of the stomach , resulting in the formation of the so-called. “sleeve”, the diameter of which is about 10 mm.
In this regard, in medical sources this operation is also called sleeve or longitudinal gastrectomy . The unofficial name of this procedure is SLIV , which translated from English (Sleev) means sleeve.
During the operation, important components of the stomach are not affected: the operator eliminates its lateral area. Therefore, the stomach remains fully functional.
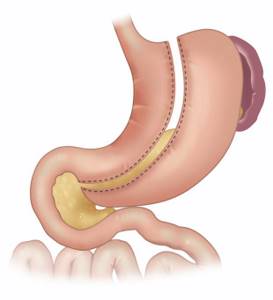
Vertical gastroplasty is resorted to if the patient’s body mass index fluctuates between 35-50 kg/m2.
And also in cases where obesity was caused by:
- Arterial hypertension.
- Diabetes mellitus type II.
- Osteoarthritis.
- Sleep apnea syndrome.
- Some other pathologies.
This operation is also indicated in situations where...
- Non-invasive weight loss techniques have proven ineffective.
- The patient has a pronounced adhesive process in the small intestine, which makes bypass surgery impossible.
- Body mass index exceeds 60. Surgical treatment of such conditions takes place in two stages, the first of which is sleeve gastroplasty.
Contraindications to the gastric reduction procedure under consideration:
- Serious disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract in the active stage of development: gastritis, duodenal ulcer/stomach, inflammation of the pancreas/gallbladder.
- Surgical procedures performed on the stomach in the past that negatively affected its lumen.
- Severe diseases of the liver, heart, kidneys, respiratory system.
- Patients treated with immunosuppressive drugs.
- Infection of the body.
- Defects in the functioning of the central nervous system.
- Pathologies associated with blood clotting.
- Bad habits: alcoholism, drug addiction.
- The period of bearing a child.
In the absence of compelling evidence, the doctor has the right to refuse surgery to persons under 18 years of age, as well as persons over 65.
Gastroplication (Sleeve 2)
Gastroplication is a modification of the previously discussed surgical technique. Unlike sleeve resection, gastropplication surgery does not remove part of the organ. Reducing the working volume of the stomach is achieved by applying a longitudinal suture to its side wall.
Operating principle.
The gastric suturing operation is performed under general anesthesia. During the operation, the surgeon places a longitudinal suture on the side wall of the organ, which reduces the effective volume to 100 milliliters.
Advantages
. This surgical method of losing weight does not violate the integrity of the organ. The motility of the digestive tract and the physiology of digestion are not impaired. Medicines and essential nutrients are fully absorbed. The result of the operation is reversible, which leaves ample opportunity for the subsequent use of other methods of surgical treatment of obesity.
Gastric bypass
Gastric bypass is a radical surgical treatment for obesity and related diseases, in which the surgeon reduces the volume of the stomach and creates an anastomosis between the stomach and the small intestine.
Reference
. Gastrobypass surgery is historically the first surgical method for treating obesity. The first operation was performed in 1966. Since the method gave excellent results, it became the starting point for the creation of a new branch of medicine, known today as bariatrics, or metabolic surgery.
Operating principle
. During restrictive bypass surgery, the upper part of the stomach is isolated, resulting in a significant reduction in the effective volume of the organ. The second stage of the operation is the creation of a gastrointestinal anastomosis, that is, suturing the small intestine to a previously isolated reduced part of the stomach.
The high effectiveness of this surgical method of weight loss is explained by a radical change in the digestion process. The volume of the stomach is reduced, which leads to a decrease in food intake. After creating the anastomosis, the bolus of food is directed from the upper stomach to the small intestine, bypassing part of the stomach, duodenum and part of the small intestine.
Advantages.
Since the creation of the method to this day, gastric bypass surgery has been considered the gold standard of bariatrics. Patients get rid of 80% of excess weight without strictly restricting caloric intake. The result is stable, body weight remains normal even in the very long term.
Peculiarities
. Gastric bypass surgery disrupts the natural pathway of nutrients through the digestive system. Because of this, the absorption of not only energy sources is reduced (which gives a positive result), but also essential nutrients. After gastric bypass, patients must constantly take vitamin and mineral complexes prescribed by their doctor.
Complications after gastric reduction surgery
All complications can be divided into complications:
- Related directly to the operation
- Delayed complications
Complications directly related to the operation
Considering the special population of patients: morbid obesity and associated concomitant diseases, there is a possible risk of severe (lethal) complications), as with any other operation on the abdominal organs.
Complications are possible in the form of rupture of sutures on the intestines and stomach with the development of peritonitis; bleeding in the abdominal cavity; wound infections; cardiovascular and pulmonary complications.
During laparoscopic operations, the stomach, esophagus, and spleen may be injured, which will make it necessary to continue the operation using the “open” method.
Delayed complications
- Formation of a stomach ulcer at the junction (anastomosis) of the stomach and small intestine;
- Violation of the tightness (insolvency) of the anastomosis sutures;
- Conditions that develop due to malabsorption of fat-soluble vitamins, calcium, iron: anemia due to iron deficiency, osteoporosis (destruction of the hard bone base) due to lack of calcium and vitamin D, night blindness develops due to lack of vitamin A;
- Often after surgery, patients are bothered by frequent loose stools (diarrhea) when eating sweet or fatty foods, or vice versa, by constipation, due to reduced portions of food intake and decreased contraction (peristalsis) of the intestines;
- Possible formation of gallstones;
- Inflammation of the esophageal mucosa due to the reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus (reflux - esophagitis);
- Dumping syndrome is a result of rapid passage of food from the stomach into the intestines. It develops after gastric bypass surgery and is associated with the rapid flow of food from the “little stomach” into the small intestine. Dumping manifests itself - a syndrome of hand tremors, weakness, dizziness, which goes away after 10-15 minutes. At this time, it is better to take a horizontal position. Some surgeons believe that this is not a complication, but an additional restriction for the patient after bypass surgery, preventing him from taking large amounts of liquid, high-calorie food;
- Temporary hair loss, the exact cause of which is unknown, may be due to hormonal changes in the body. The peak of prolapse occurs in the period from the third to the ninth month after surgery, and subsequently the prolapse stops;
- During gastric banding surgery, it is also possible to move (migrate) the band, erosion at the point of contact of the band with the wall of the stomach, vomiting, discomfort or pain in the abdomen after eating, dilatation of a small stomach;
- In addition, such a specific complication, characteristic only of weight loss operations, is failure to achieve the desired weight loss after surgery or weight gain again.
Biliopancreatic bypass
Biliopancreatic bypass is a surgical method of weight loss based on reducing the volume of the stomach and creating an anastomosis (shunt) between the stomach and the ileum.
Operating principle.
The general principle of operation does not differ from the previously discussed gastric bypass surgery. The difference is that most of the small intestine is isolated, requiring the appendix and gallbladder to be removed at the same time. Biliopancreatic bypass is the most radical operation, which is performed when there are direct indications.
Advantages
. This surgical method of weight loss is actively used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. After biliopancreatic bypass, patients can do without glucose-lowering drugs, including insulin, from the first days after surgery. Body weight is normalized, patients manage to get rid of 90% of excess weight. The result is stable in the long term.
Flaws
. Biliopancreatic shunting disrupts the physiology of the digestive process. After surgery, the absorption of essential nutrients deteriorates, which requires lifelong intake of vitamin and mineral complexes prescribed by a doctor.
Bariatric surgery: the whole truth about “weight loss surgery”
Bariatric surgery is a type of surgical procedure that can help people with severe obesity lose weight and indirectly reduce body fat. Such surgical interventions are performed on the stomach and small intestine: as a result, the amount of food intake or absorption of nutrients is reduced, which ultimately leads to weight loss. However, bariatric operations affect not only the function of the gastrointestinal tract - their effect is more global: almost all types of weight loss operations are aimed at restoring metabolism, that is, normalizing metabolism.

Bariatric surgery: should we expect miracles? 10887
However, despite the apparent simplicity of this method of treating obesity, bariatric surgery is overgrown with myths and misconceptions: weight loss surgery is either expected to provide a magical transformation, or, on the contrary, it is accused of terrible consequences. Let's find out the truth about bariatric surgery step by step.
How bariatric surgery works
Bariatric surgery promotes weight loss by limiting the amount of food that goes into the stomach (surgery reduces its volume) and by interfering with the small intestine, which impairs the absorption of nutrients (medically known as malabsorption). Sometimes a combination of these two principles may be used - reducing the volume of the stomach and restricting and removing part of the small intestine. One way or another, after surgical interventions of this kind, the patient’s body receives fewer calories, which leads to a systematic and long-term reduction in body weight. Bariatric surgery also often leads to hormonal changes, which after some time normalize metabolism - and in obese people it is impaired in almost 100% of cases. In addition, new “shapes” and sizes of the stomach or a decrease in the area of the walls of the small intestine indirectly form healthy eating habits in the patient: he begins to eat less and even changes the quality of his diet.
General information about “weight loss surgery” 10923
However, most importantly, changing the route of nutrient flow provokes positive changes in the activity of intestinal hormones, in particular ghrelin and leptin. These local hormones promote satiety (a feeling of fullness in the stomach), help suppress hunger, and also reverse one of the main mechanisms by which overweight and obesity induce the development of metabolic syndrome, and subsequently type 2 diabetes.
Types of bariatric surgery
The most common techniques used in bariatric surgery are gastric banding, gastric plication, gastric bypass with gastrojejunostomy, laparoscopic sleeve (gastrectomy) gastrectomy and biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal exclusion. Each type of bariatric surgery has its own advantages and disadvantages.
The “gold standard” of bariatric surgery is considered to be gastric bypass with gastrojejunostomy - this is the most studied and popular type of weight loss surgery. Today, gastric bypass is the most commonly performed bariatric surgery worldwide.
Benefits of Bariatric Surgery
- Bariatric surgery guarantees significant and long-term results - weight loss after such interventions can range from 60 to 80% of excess weight (depending on the type of surgery and the individual characteristics of the patient). So, in some cases, a person loses up to 50% of his total body weight.
- Today, most bariatric surgeries are performed using minimally invasive methods (laparoscopic techniques), and this, of course, should also be considered one of their advantages.
- Bariatric surgery not only limits the amount of food consumed, but by normalizing metabolism, it can create conditions in the patient's body that increase energy expenditure.
- They stimulate favorable changes in the activity of hormones in the intestines, which ultimately reduces appetite and ensures an earlier onset of a feeling of satiety.
Bariatric surgery is a method of treating morbid obesity 10773
Disadvantages of Bariatric Surgery
- These are technically more complex procedures that can potentially lead to higher risks of complications ranging from infections to severe gastrointestinal and metabolic disorders. Therefore, it is extremely important to take the choice of a surgeon and clinic for weight loss surgery seriously. By the way, conscientious specialists do not undertake to perform bariatric operations without indications. That is, if a person is diagnosed with obesity, he should choose alternative methods of losing weight: diet and exercise.
- The most common potential risks of bariatric surgery are vitamin and mineral deficiencies, in particular vitamin B12 deficiency. Also, in the long term, iron, calcium, and folic acid may be deficient. Vitamin and mineral deficiencies may not develop immediately, but after some time, so patients often do not notice such complications, exacerbating the lack of nutrients.
- The disadvantages of weight loss surgery include hospital stay; the length of hospitalization depends on the type of operation, and after surgery on the small intestine it is the longest.
- After such procedures, strict and lifelong adherence to fairly strict dietary recommendations and regular intake of vitamins and mineral supplements are required.
Bariatric surgery: myths and reality
Myth 1: Most people who have bariatric surgery regain their excess weight after some time. Is it true. According to statistics, up to 50% of patients who have undergone various types of bariatric surgery gain weight after a year or two, but this is a small figure (approximately 5% of total body weight). However, most of these patients are able to maintain their weight loss results over the long term and maintain an improvement in their quality of life. In any case, significant and sustained weight loss after “weight loss surgery” is in sharp contrast to the effect of most non-surgical treatments.
Myth 2: The risk of dying from metabolic disorders after bariatric surgery is higher than the risk of dying from the consequences of obesity. Is it true. As body weight increases, life expectancy decreases - these are medical statistics. Individuals with severe obesity suffer from many life-threatening conditions that significantly increase the risk of premature death. Among them are type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, etc. At the same time, despite the poor health of obese patients before surgery, the likelihood of dying after surgery is very low. The benefits of bariatric surgery far outweigh the risks. Associated with excess body weight.
Myth 3: “Weight loss surgery” is an excuse for the lazy: To lose weight and keep it off, severely obese people simply have to stick to a strict diet and follow an exercise program. Is it true . People who are severely obese tend to be resistant to the long-term weight loss that can be achieved through diet and exercise at a normal body weight. Bariatric surgery is much more effective at maintaining long-term weight loss, in part because it helps normalize metabolism, which is significantly impaired in obese people. Diets, as a rule, negatively affect metabolism (for example, for many o). It is worth remembering that here we are not talking about people with a normal BMI: “weight loss surgery” is indicated only for obesity.
The effectiveness of bariatric surgery 12541
Myth 4. Many patients become alcoholics after bariatric surgery. Is it true . In fact, some patients admit to having problems with alcohol after surgery - but not many. Most of them had abused alcohol at some time before surgery. At the same time, susceptibility to ethanol does increase after obesity surgery—especially if alcohol is consumed during a period of rapid weight loss. Therefore, such patients are recommended to avoid drinking alcoholic beverages, at least during rapid weight loss: during this period, even small doses of alcohol cause intoxication.
Surgical weight loss: results
Surgical weight loss is an effective method of treating obesity and obesity-associated diseases with a history of practical application of more than half a century. The variety of operations allows you to choose the optimal treatment strategy for each patient.
Reducing body weight helps normalize metabolism, prevent and reverse the development of serious diseases, including diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease, arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis, acute vascular events (heart attack and stroke).
Surgical weight loss gives excellent results that are stable in the long term. Patients manage to maintain normal body weight without diets or strict calorie restrictions.
You can get detailed information about surgical weight loss methods at a personal consultation with a surgeon at the Weight Loss Center (Moscow).
Gastric Bypass – Benefits and Side Effects
This procedure is also called gastric bypass.
Its essence is to create, through laparoscopy, a small stomach (no more than 30 ml) , which is connected to the rectum.
In rare cases, doctors resort to open surgery , which is not so difficult to perform, but is more traumatic.
Once gastric bypass is completed, food will go directly into the small stomach. The rest of the stomach is removed from the digestive process. However, the gastric juice and bile produced here take part in the digestion of food.
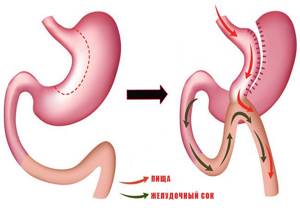
Gastric bypass, due to its many advantages, is today considered the gold standard in many developed countries of the world:
- Thanks to this technique, patients' body weight is reduced by 80-85%. In some cases this figure may be higher.
- Gastrobypass surgery is an excellent way to combat type 2 diabetes. Research has shown that many patients who have undergone this operation do not need to take medications that help lower blood sugar.
- This manipulation helps to minimize the risk of cardiovascular diseases. This is due to the effect it has on the composition of the blood.
- Manifestations of pathologies associated with obesity become less pronounced. These pathologies include arterial hypertension, bronchial asthma, defects in the musculoskeletal system, etc.
Like any other surgical intervention, gastric bypass has its side effects:
- The appearance of an ulcer at the junction of the small stomach and small intestine. Occurs in 5 cases out of 100, and more often in smokers.
- Nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, as a result of adhesions/strictures between the stomach and intestines.
- Regular constipation, which can lead to the formation of hernias and hemorrhoids. To avoid this phenomenon, patients need to focus on liquid foods after surgery, which contain a lot of fiber.
- An insufficient amount of proteins in the body can cause general weakness and hair loss. To eliminate this deficiency, in a hospital setting, the patient is given an intravenous infusion of all the necessary substances.
- Exacerbations associated with deficiency of microelements and vitamins.