What are fats, proteins and carbohydrates? Which products contain them in the greatest quantities? Nutrition tips. Practice shows that with proper organization of the diet, namely taking into account calories, the amount of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, it is easier to solve problems of any complexity. With proper nutrition management, you can fight excess weight, gain muscle mass, “get dry” and restore lost health.
The main problem of many people is simple laziness, which does not allow them to look at the table of protein, fat and carbohydrate content in foods, where all the information is available - the volume of each element per 100 grams and the total calorie content. The only question is what benefits does each of the nutritional components bring and how to correctly “read” the BZHU table. Let's look at these questions in more detail.
Basics of proper nutrition
Having an idea of the nutritional value and purpose of individual nutrients, you can influence the functioning of the body, the development of muscle mass, the elimination of fat (lipid) deposits, increasing performance and endurance through the preparation of diets with different purposes.
The basis for healthy eating are:
- completeness of the diet;
- control of the composition of BJU products;
- calorie control;
- portion distribution;
- drinking regime.
Before experimenting with various diets that involve certain restrictions, you should, first of all, ensure that your diet is complete.
Each food component has its own purpose. Proteins are directly involved in the construction of tissues and cells. Fats and carbohydrates provide energy and glycogen in the muscles and liver. Up to 80% of all daily food should be eaten before evening time. You can eat before bed, but preferably healthy, low-calorie foods in small quantities.
Recent nutritional research has found that strictly limiting the amount of time you eat during the day to 9 hours reduces your risk of diabetes, lowers your blood cholesterol levels, and makes you less likely to gain weight.
Proper nutrition largely depends on the ratio of food components. Their excess or deficiency can negatively affect the most important functions of the body, ability to work, emotional state, physical and mental development.
Balance of proteins, fats and carbohydrates
Fats, proteins and carbohydrates contained in food must be counted in order to consume them in the required quantities. Calculation is carried out using tables of calorie content and component content or information on packages.
Fats and carbohydrates in insufficient quantities reduce the possibility of mental and physical activity due to lack of energy, and in excess they lead to the formation of a fatty layer, which leads to the risk of diabetes.
Due to an imbalance in the protein-fat ratio in the diet, the amount of bad cholesterol in the blood increases. This is the cause of atherosclerosis and diseases of the cardiovascular system.
According to statistics, among people over 20 years old, 3 out of 4 consume a lot of fat, which puts them at risk.
Violation of the proportion of carbohydrates and proteins leads to disruption of metabolism and restoration of the body.
For a proper balanced diet, food components should be consumed in percentages of 25-30%, 50-60%, 10-15%, respectively.
The balance of the BZHU can be adjusted individually. For example, consider that increasing the amount of protein in the diet with high energy expenditure can have an adverse effect on the human body. The proportion of protein in the diet should become less:
- 4500-5500 kcal – 13%;
- 5500-6500 kcal – 12%;
- 6500-8000 kcal -11%.
Features of eating buckwheat on a diet

Buckwheat porridge is one of the most common products used in dietary nutrition. Buckwheat promotes weight loss due to its high content of dietary fiber, amino acids, antioxidants and carbohydrates.
Is it possible to lose weight on buckwheat?
When done correctly, the buckwheat diet promotes weight loss and also has a beneficial effect on the body as a whole.
Features of the buckwheat diet:
- carbohydrates are broken down slowly, and the body spends a lot of energy on their digestion;
- high calorie content gives a feeling of satiety and eliminates exhaustion;
- buckwheat cleanses the walls of the stomach, improves digestion and resolves visceral fat;
- speeds up metabolism, thanks to which a person loses excess weight:
- removes excess water and toxins.
There are various diets based on buckwheat:
- by duration: 3-day, weekly, 2-week;
- by product: chicken, vegetable, dairy, apple;
- on water and buckwheat (used as a fasting day);
- medicinal;
- strict;
- lightweight.
Most often, buckwheat is used during a mono-diet, but sometimes those who want to lose weight add vegetables and fermented milk products to their diet. Thanks to this method, it is possible to lose up to 10 kg in 2 weeks, provided that you perform physical activity and maintain water balance.
Recommendations for following the diet:
- drink water - approximately 30-40 ml per 1 kg of weight;
- do not eat 5 hours before bedtime;
- It is better to steam buckwheat - this way it retains more nutrients;
- If you feel very hungry, drink 1 tbsp. kefir or eat an apple;
- Instead of caffeine, which retains water in the body, drink herbal teas.
An approximate version of the buckwheat mono-diet:
- in the morning drink 1 tbsp. water;
- half an hour later, eat a portion of porridge steamed with boiling water;
- for lunch - steamed buckwheat with green vegetables;
- for dinner - a portion of buckwheat porridge;
- Drink water during breaks.
The maximum duration of a buckwheat diet is 2 weeks. The best option is 5-7 days once every 6 months. At the same time, engage in light sports, get enough sleep and drink more water.
Contraindications for the buckwheat diet
Despite the beneficial properties of the product, if the diet is not followed correctly, health problems may arise.
This option for losing weight has its disadvantages:
- decrease in pressure;
- headache;
- fast fatiguability;
- mood swings.
It is necessary to follow the diet with caution for people who:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- diabetes;
- oncology;
- metabolic problems;
- heart diseases;
- individual intolerance;
- kidney diseases.

What happens if you only eat buckwheat every day?
According to doctors and nutritionists, daily consumption of buckwheat will not cause harm if consumed with dairy products, vegetables, and fruits. Due to the high calorie content, the body will be provided with a sufficient amount of energy, and the feeling of hunger will occur less frequently.
This diet will provide the body with all the necessary minerals, amino acids, and antioxidants. To maintain health, it is recommended to alternate buckwheat with other porridges and cereals.
Important! The daily daily intake of buckwheat with proper nutrition is 150-200 g.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates in foods are the main source of energy. Their main task is to allow the brain and muscles to work normally and cope with the necessary loads and energy costs. They form important enzymes and hormones.

Carbohydrates are found in foods in the form of glucose, fructose, lactose, sucrose, fiber, pectin, starch and glycogen. They can be grouped into:
- simple – greatly raise blood sugar levels;
- complex – slightly raise blood sugar levels.
The glycemic index (GI) is responsible for the ability of food to raise blood sugar levels. This makes it the most important indicator of every carbohydrate product. To improve the quality of nutrition you need:
- choose foods with a lower GI content;
- eat foods with high GI in smaller quantities.
This will allow you to receive the microelements the body needs, reduce the risk of diseases and lead a full, active life.
The metabolism of carbohydrates is determined by the glucose content in the blood, i.e. on the time and nutritional composition of the last meal. The blood glucose level is minimal in the morning after sleep, during which its level was not maintained.
Once you wake up, the body is in the best condition to use stored fat as an energy source, so walking and aerobics before breakfast are important.
The formation of reserves of carbohydrates entering the body in the form of intramuscular glycogen is observed when they are taken in the first half of the day. This leads to the recommendation to consume the bulk of carbohydrates before evening. In addition to providing energy, carbohydrates help build muscle and burn fat.
To build 1 kg of muscle mass, a large amount of energy is expended - approximately 5000 kcal. After this, daily maintenance of a more energy-consuming body is required. Carbohydrates provide energy to cells most quickly and the body prefers them to fats and protein. This allows proteins to perform their main function - building and repairing body tissue, including muscle.
During weight loss, the body converts fat into energy inside its cells. This process depends on the lack of the required amount of energy, which requires the use of one’s own reserves. However, even in this case, a certain part of carbohydrates is necessary to maintain basic processes and break down fat.

Since excessive and low consumption of carbohydrates leads to negative consequences, it is important to find your optimal amount. Feeling good will be a sign of how correct the chosen diet is.
Foods containing carbohydrates
Foods containing complex carbohydrates and low GI include:
- various cereals (buckwheat, rice, oatmeal);
- vegetables (green peas, cucumbers, tomatoes, onions, etc.);
- individual fruits (figs, oranges, grapefruit, etc.);
- some sweets (marshmallows, butter cookies, etc.).
Almost all sweets, fruits and berries are simple carbohydrates and have a high GI value.
Harm from boiled peas
Despite all the benefits this product has on the human body, it may not be beneficial for everyone. The amount of boiled pea grains should be reduced for elderly people, pregnant and lactating women, and young children. Large amounts of product may cause increased gas formation. The product also increases the level of uric acid and salt accumulation.
Those who suffer from gout, kidney disease, stones in the body or any intestinal pathologies should not eat dishes with the addition of peas.
Squirrels
Proteins are an essential substance for life. This is the main plastic material for the construction of cells, tissues, organs, the formation of most hormones and hemoglobin. Proteins are involved in the metabolism of all nutrients and form antibodies that protect a person from infections.
When assessing the quality of protein in the diet, one should take into account not only its quantity, but also its biological value, which is determined by the amino acid composition, and their absorption by the body.
Proteins contain 8 essential amino acids that must be supplied to the body through food.

Products containing protein
Based on the degree of absorption and availability of amino acids, proteins are divided into complete and incomplete.
Complete sources of protein are meat, fish, seafood, eggs, and dairy products. Incomplete proteins include plant proteins, which are found in legumes, cereals and vegetables. The exception is soy, which has a rich amino acid composition, but a lower degree of absorption.
Obtaining a full set of essential amino acids is possible with proteins of animal origin or a combination of plant proteins.
When choosing animal protein, it is important to limit the intake of vegetable fats. This can be done by giving preference to low-fat dairy products, chicken breast and fish, boiling or steaming food.
Harm from boiled and raw beets
Like every type of product, beets can cause some harm, and also have contraindications for various categories of people.
The harm and contraindications of boiled root vegetables are as follows:
- It should not be consumed by people who suffer from high acidity in the stomach, since the vegetable contains a large amount of its own acids, which can lower the pH balance.
- A large amount of the product can harm the absorption of vitamin calcium, since the vegetable reduces the level of absorption of this element
- The product is contraindicated for people with diabetes mellitus; the vegetable contains large amounts of sugar.
- The use of the vegetable is contraindicated for people who suffer from indigestion; the product can cause diarrhea.
The harms and contraindications of raw root vegetables are as follows:
- It should not be used by people who suffer from urolithiasis.
- For kidney diseases
- For low blood pressure
- In case of allergic reactions.
When choosing a root crop, great importance must be given to the area where the product was grown to avoid saturating the body with harmful substances and nitrates.
Fats
Fats are one of the main food components. This is a valuable energy material that is part of cells, especially in the tissues of the nervous system. They participate in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) and some minerals.

The optimal fat requirement is 1.1 g/kg body weight, at least 30% should be vegetable fats. This amount allows you to improve the functioning of the intestines and urinary system, and prevents the development of gallstones and other diseases.
A deficiency of plant (unsaturated) fatty acids slows down the growth and physical development of the body and reduces resistance to infections. Excess fat leads to the threat of damage to the liver and pancreas, obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
Products containing fats
According to their chemical structure, fatty acids are divided into:
- saturated (filled to the limit with hydrogen), which includes fats of animal origin;
- unsaturated, which include fats of vegetable origin, with the exception of coconut and palm oil.
The most healthy foods containing fats include: fish (an important source of healthy omega-3 fats), avocados, nuts, olive oil.
Other components
Adequate nutrition also depends on sufficient amounts of vitamins, minerals, dietary fiber, antioxidants and water. If the intake of some of these components from food is insufficient, it is possible to compensate for this by using biological food additives.
Vitamins
Vitamins are organic substances, some of which must be obtained from food, since they are either not synthesized in the body, or this occurs at a low rate. The exception is vitamin D, which is synthesized under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. Vitamins regulate the processes of metabolism, energy synthesis, nerve conduction, and help prevent cell destruction.

Vitamins can be grouped into:
- water-soluble (B, C), the reserves of which are small and require regular replenishment;
- fat-soluble (A, D, E, K), which accumulate in tissues and can be toxic.
Basically, people do not get enough vitamins due to the use of an incorrect diet, malnutrition (for example, due to lack of appetite or other reasons).
Minerals
Minerals participate in plastic and enzymatic processes, in protein synthesis and the formation of body tissues, regulate acid-base balance and water metabolism.
The most important are:
- Calcium. The main component of the skeletal system and teeth.
- Phosphorus. Necessary for bone mineralization.
- Magnesium. Necessary for phosphorus-calcium metabolism.
- Iron. Part of hemoglobin and oxidative enzymes.
- Potassium. Regulates the acid-base balance of the blood.
Water
Water makes up almost 60% of an adult's total body weight. It maintains constant body temperature and pressure, dissolves vital nutrients, helps absorb and transport nutrients, and remove waste.
Water replacement is vital. The amount of drinking water should be sufficient for normal kidney function. When it is deficient, muscle strength weakens, motor control deteriorates, mental energy decreases, and fatigue occurs. Dehydration can lead to deterioration of the entire body.

The required amount of daily water consumption ranges from 2.5 liters in winter to 3.5 liters in summer.
Calculation of energy costs
Each product has its own nutritional value. Its source is the substances it contains.
Energy value (calorie content) is the amount of energy obtained from food. It is used by the body for a variety of purposes, including mental and physical exercise, anaerobic and aerobic physical activity.
Caloric content is measured in kilocalories (kcal) or kilojoules (kJ) per 100 g of product.
How does the calorie content of foods affect weight?
Eating food with nutrients contributes energy to the human body. Not eating enough calories slows down your metabolism, impairs mental and physical performance, and forces the body to replenish needed energy reserves with fat and protein. High-calorie foods, as well as excessive consumption of foods, fill the body with excess energy, which leads to an increase in the amount of adipose tissue.
How to count calories?
Counting the calorie content of foods is not a difficult task. To do this, it is advisable to use tables or calorie calculators. If you enter the data into an Excel document, you can easily calculate this indicator yourself by multiplying the approximate weight of the dish by its energy indicator.
Calorie content and nutritional value of boiled beets
The root vegetable is a very low-calorie product, therefore it is widely used for preparing dishes during dietary nutrition. Boiled vegetables have a calorie content of only 40 calories per hundred grams.
The vegetable has the following BJU indicators per hundred grams:
- Carbohydrates - 13g.
- Proteins - 3 gr.
- Fats - 0.1 g.
The boiled vegetable contains practically no fat, and contains carbohydrates in small quantities, which allows you to use a large amount of the product without harming your figure.
In addition, the vegetable contains a large amount of useful substances that are necessary for the normal functioning of the body.
Calorie content raw and baked
Depending on the cooking method, the calorie content of beets can vary significantly.
Raw beets contain only 42 calories per hundred grams.
- Carbohydrates - 9 g.
- Belkov - 2 g.
- Fats - 0.1 g.
Note! The carbohydrates found in vegetables are classified as complex carbohydrates that take a long time to be absorbed by the body, which allows you to not feel hungry for a long time, while receiving all the necessary energy.
Baked beets have the following indicators, namely, one hundred grams contains 39 calories:
- Carbohydrates - 8.9 g.
- Proteins – 1.5g.
- Fats – 0.1g.
Despite its low calorie content, the product has a unique taste, which will make any dietary dish tasty and healthy.
Table. Proteins, fats, carbohydrates and caloric content of foods
The content of proteins, fats and carbohydrates in foods is an important characteristic of the diet. Using this data allows you to plan and monitor dietary changes. Important indicators in food products are the number of calories and the glycemic index.

| Product name | GI | Kcal | B | AND | U |
| Vegetables | |||||
| Broccoli | 10 | 27 | 3 | 0,4 | 4 |
| Brussels sprouts | 15 | 43 | 4,8 | – | 5,9 |
| Salted mushrooms | 10 | 29 | 3,7 | 1,7 | 1,1 |
| Green vegetables (peas, onions) | 40 | 72 | 5 | 0,2 | 12,8 |
| Eggplant caviar | 40 | 146 | 1,7 | 13,3 | 5,1 |
| Squash Cavier | 75 | 83 | 1,3 | 4,8 | 8,1 |
| Cabbage | 10 | 25 | 2 | – | 4,3 |
| Sauerkraut | 15 | 17 | 1,8 | 0,1 | 2,2 |
| Stewed cabbage | 15 | 75 | 2 | 3 | 9,6 |
| Boiled potatoes | 65 | 75 | 2 | 0,4 | 15,8 |
| Fried potato | 95 | 184 | 2,8 | 9,5 | 22 |
| French fries | 95 | 266 | 3,8 | 15,1 | 29 |
| Mashed potatoes | 90 | 92 | 2,1 | 3,3 | 13,7 |
| Potato chips | 85 | 538 | 2,2 | 37,6 | 49,3 |
| Boiled corn | 70 | 123 | 4,1 | 2,3 | 22,5 |
| Bulb onions | 10 | 48 | 1,4 | – | 10,4 |
| Leek | 15 | 33 | 2 | – | 6,5 |
| Black olives | 15 | 361 | 2,2 | 32 | 8,7 |
| Raw carrots | 35 | 35 | 1,3 | 0,1 | 7,2 |
| Fresh cucumbers | 20 | 13 | 0,6 | 0,1 | 1,8 |
| Green olives | 15 | 125 | 1,4 | 12,7 | 1,3 |
| Green pepper | 10 | 26 | 1,3 | – | 5,3 |
| Red pepper | 15 | 31 | 1,3 | 0,3 | 5,9 |
| Tomatoes | 10 | 23 | 1,1 | 0,2 | 3,8 |
| Radish | 15 | 20 | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 |
| Boiled beets | 64 | 54 | 1,9 | 0,1 | 10,8 |
| Fruits and berries | |||||
| Apricots | 20 | 40 | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9 |
| Pineapples | 66 | 49 | 0,5 | 0,2 | 11,6 |
| Oranges | 35 | 38 | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,3 |
| Watermelon | 72 | 40 | 0,7 | 0,2 | 8,8 |
| Bananas | 60 | 91 | 1,5 | 0,1 | 21 |
| Cowberry | 25 | 43 | 0,7 | 0,5 | 8 |
| Grape | 40 | 64 | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16 |
| Cherry | 22 | 49 | 0,8 | 0,5 | 10,3 |
| Blueberry | 42 | 34 | 1 | 0,1 | 7,7 |
| Pomegranate | 35 | 52 | 0,9 | – | 11,2 |
| Grapefruit | 22 | 35 | 0,7 | 0,2 | 6,5 |
| Pears | 34 | 42 | 0,4 | 0,3 | 9,5 |
| Melon | 60 | 39 | 0,6 | – | 9,1 |
| Blackberry | 25 | 31 | 2 | – | 4,4 |
| Strawberries | 25 | 34 | 0,8 | 0,4 | 6,3 |
| Raisin | 65 | 271 | 1,8 | – | 66 |
| Figs | 35 | 257 | 3,1 | 0,8 | 57,9 |
| Kiwi | 50 | 49 | 0,4 | 0,2 | 11,5 |
| Strawberry | 32 | 32 | 0,8 | 0,4 | 6,3 |
| Cranberry | 45 | 26 | 0,5 | – | 3,8 |
| Gooseberry | 40 | 41 | 0,7 | 0,2 | 9,1 |
| Dried apricots | 30 | 240 | 5,2 | – | 55 |
| Lemon | 20 | 33 | 0,9 | 0,1 | 3 |
| Raspberries | 30 | 39 | 0,8 | 0,3 | 8,3 |
| Mango | 55 | 67 | 0,5 | 0,3 | 13,5 |
| Tangerines | 40 | 38 | 0,8 | 0,3 | 8,1 |
| Nectarine | 35 | 48 | 0,9 | 0,2 | 11,8 |
| Sea buckthorn | 30 | 52 | 0,9 | 2,5 | 5 |
| Peaches | 30 | 42 | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,5 |
| Plums | 22 | 43 | 0,8 | 0,2 | 9,6 |
| Red currants | 30 | 35 | 1 | 0,2 | 7,3 |
| Black currant | 15 | 38 | 1 | 0,2 | 7,3 |
| Dates | 70 | 306 | 2 | 0,5 | 72,3 |
| Persimmon | 55 | 55 | 0,5 | – | 13,2 |
| Cherries | 25 | 50 | 1,2 | 0,4 | 10,6 |
| Apples | 30 | 44 | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 |
| Dried fruits | |||||
| Dried cherries | 30 | 290 | 1,5 | 0 | 73 |
| Dried pear | 30 | 293 | 2 | 0 | 62 |
| Raisin | 65 | 270 | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66 |
| Dried apricots | 30 | 240 | 5,2 | 0,3 | 51 |
| Candy sugar chocolate | |||||
| Marshmallow | 65 | 308 | 0,8 | 0 | 80,3 |
| Iris | 60 | 387 | 3,3 | 7,5 | 81,8 |
| Sugar | 100 | 374 | 0,3 | 0 | 99,5 |
| Dark chocolate | 40 | 540 | 5,4 | 35,3 | 52,6 |
| Milk chocolate | 70 | 547 | 6,9 | 35,7 | 52,4 |
| Cakes and other confectionery products | |||||
| Verona cake | 100 | 350 | 5 | 19,8 | 39,3 |
| Honey cake | 100 | 478 | 6 | 29 | 48,9 |
| Napoleon cake | 100 | 413 | 5,9 | 32,7 | 23,8 |
| Bread, bakery products, flour | |||||
| Pancakes made from premium flour | 69 | 185 | 5,2 | 3 | 34,3 |
| Dumplings with potatoes | 66 | 234 | 6 | 3,6 | 42 |
| Dumplings with cottage cheese | 60 | 170 | 10,9 | 1 | 36,4 |
| Waffles | 80 | 545 | 2,9 | 32,6 | 61,6 |
| Toast | 100 | 381 | 8,8 | 14,4 | 54,2 |
| Cornflakes | 85 | 360 | 4 | 0,5 | 80 |
| Wholemeal pasta | 38 | 113 | 4,7 | 0,9 | 23,2 |
| Durum wheat pasta | 50 | 140 | 5,5 | 1,1 | 27 |
| Muesli | 80 | 352 | 11,3 | 13,4 | 67,1 |
| Cereals | 40 | 305 | 11 | 6,2 | 50 |
| Dumplings | 60 | 252 | 14 | 6,3 | 37 |
| Cookies, pastries, cakes | 100 | 520 | 4 | 25 | 70 |
| Bread crumbs | 74 | 360 | 11,5 | 2 | 74 |
| Bread made from premium flour | 80 | 232 | 7,6 | 0,8 | 48,6 |
| Cereals | |||||
| Buckwheat porridge on water | 50 | 153 | 5,9 | 1,6 | 29 |
| Oatmeal with milk | 60 | 116 | 4,8 | 5,1 | 13,7 |
| Oatmeal on water | 66 | 49 | 1,5 | 1,1 | 9 |
| Pearl barley porridge on water | 22 | 109 | 3,1 | 0,4 | 22,2 |
| Millet porridge on water | 70 | 134 | 4,5 | 1,3 | 26,1 |
| Unpolished boiled rice | 65 | 125 | 2,7 | 0,7 | 36 |
| Rice porridge milk | 70 | 101 | 2,9 | 1,4 | 18 |
| Rice porridge on water | 80 | 107 | 2,4 | 0,4 | 63,5 |
| Legumes | |||||
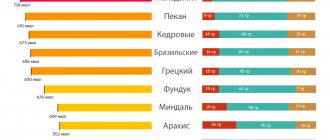
| Peanut | 20 | 612 | 20,9 | 45,2 | 10,8 |
| Jam | 70 | 271 | 0,3 | 0,3 | 70,9 |
| Walnuts | 15 | 710 | 15,6 | 65,2 | 15,2 |
| Egg (1 piece) | 0 | 76 | 6,3 | 5,2 | 0,7 |
| Mushrooms | |||||
| Salted mushrooms | 10 | 29 | 3,7 | 1,7 | 1,1 |
| Butter | 15 | 19 | 0,9 | 0,4 | 3,2 |
| Walnuts | 15 | 27 | 4,3 | 1 | 1 |
| Meat, offal, poultry | |||||
| Beef Stroganoff | 56 | 207 | 16,6 | 13,1 | 5,7 |
| Fried beef liver | 50 | 199 | 22,9 | 10,2 | 3,9 |
| Goose | – | 319 | 29,3 | 22,4 | – |
| Boiled turkey | – | 195 | 23,7 | 10,4 | – |
| Boiled sausage | 34 | 300 | 12 | 28 | 3 |
| Pork cutlets | 50 | 262 | 11,7 | 19,6 | 9,6 |
| Roasted rabbit | – | 212 | 28,7 | 10,8 | – |
| Boiled chicken breast | – | 137 | 29,8 | 1,8 | – |
| Fried chicken | – | 262 | 31,2 | 15,3 | – |
| Omelette | 49 | 210 | 14 | 15 | 2,1 |
| Stewed kidneys | – | 156 | 26,1 | 5,8 | – |
| Fried pork | – | 407 | 17,7 | 37,4 | – |
| Grilled pork | – | 280 | 19,9 | 22 | – |
| Boiled veal | – | 134 | 27,8 | 3,1 | – |
| Roast duck | – | 407 | 23,2 | 34,8 | – |
| Sausage and sausage products | |||||
| Sausages | 28 | 266 | 10,4 | 24 | 1,6 |
| Doctoral | 27 | 257 | 12,8 | 22,2 | 1,5 |
| Roast duck | – | 407 | 23,2 | 34,8 | – |
| Canned meat and smoked meats | |||||
| Tourist breakfast (beef) | – | 175 | 20,5 | 10,4 | – |
| Tourist breakfast (pork) | – | 206 | 16,9 | 15,4 | – |
| Tourist breakfast (turkey) | – | 130 | 21,6 | 12 | – |
| Fats, margarine, butter | |||||
| Soy sauce | 20 | 12 | 2 | – | 1 |
| Ketchup | 15 | 90 | 2,1 | – | 14,9 |
| Mustard | 35 | 143 | 9,9 | 12,7 | 5,3 |
| Mayonnaise | 60 | 621 | 0,3 | 67 | 2,6 |
| Margarine | 55 | 743 | 0,2 | 82 | 2,1 |
| Olive oil | – | 898 | – | 99,8 | – |
| Vegetable oil | – | 899 | – | 99,9 | – |
| Pork lard | – | 841 | 1,4 | 90 | – |
| Butter | 51 | 748 | 0,4 | 82,5 | 0,8 |
| Milk and dairy products | |||||
| Brynza | – | 260 | 17,9 | 20,1 | – |
| Yogurt 1.5% natural | 35 | 47 | 5 | 1,5 | 3,5 |
| Fruit yoghurt | 52 | 105 | 5,1 | 2,8 | 15,7 |
| Low-fat kefir | 25 | 30 | 3 | 0,1 | 3,8 |
| Natural milk | 32 | 60 | 3,1 | 4,2 | 4,8 |
| Skim milk | 27 | 31 | 3 | 0,2 | 4,7 |
| Condensed milk with sugar | 80 | 329 | 7,2 | 8,5 | 56 |
| Soy milk | 30 | 40 | 3,8 | 1,9 | 0,8 |
| Ice cream | 70 | 218 | 4,2 | 11,8 | 23,7 |
| Cream 10% fat | 30 | 118 | 2,8 | 10 | 3,7 |
| Sour cream 20% fat | 56 | 204 | 2,8 | 20 | 3,2 |
| Processed cheese | 57 | 323 | 20 | 27 | 3,8 |
| Sulguni cheese | – | 285 | 19,5 | 22 | – |
| Tofu cheese | 15 | 73 | 8,1 | 4,2 | 0,6 |
| Chees Feta | 56 | 243 | 11 | 21 | 2,5 |
| Cottage cheese pancakes | 70 | 220 | 17,4 | 12 | 10,6 |
| Hard cheeses | – | 360 | 23 | 30 | – |
| Cottage cheese 9% fat | 30 | 185 | 14 | 9 | 2 |
| Low-fat cottage cheese | 30 | 88 | 18 | 1 | 1,2 |
| Curd | 45 | 340 | 7 | 23 | 10 |
| Eggs | |||||
| White of one egg | 0 | 17 | 3,6 | – | 0,4 |
| Yolk of one egg | 0 | 59 | 2,7 | 5,2 | 0,3 |
| Fish and seafood | |||||
| Beluga | – | 131 | 23,8 | 4 | – |
| Hot smoked pink salmon | – | 161 | 23,2 | 7,6 | – |
| Boiled squid | – | 140 | 30,4 | 2,2 | – |
| Flounder | – | 105 | 18,2 | 2,3 | – |
| Fried carp | – | 196 | 18,3 | 11,6 | – |
| Boiled mullet | – | 115 | 19 | 4,3 | – |
| Smoked cod | – | 111 | 23,3 | 0,9 | – |
| Fish cutlets | 50 | 168 | 12,5 | 6 | 16,1 |
| Crab sticks | 40 | 94 | 5 | 4,3 | 9,5 |
| Boiled crabs | – | 85 | 18,7 | 1,1 | – |
| Shrimps | – | 95 | 20 | 1,8 | – |
| Sea kale | 22 | 5 | 0,9 | 0,2 | 0,3 |
| Fried perch | – | 158 | 19 | 8,9 | – |
| Cod liver | – | 613 | 4,2 | 65,7 | – |
| Boiled crayfish | 5 | 97 | 20,3 | 1,3 | 1 |
| Saira in oil | – | 283 | 18,3 | 23,3 | – |
| Sardine in oil | – | 249 | 17,9 | 19,7 | – |
| Boiled sardine | – | 178 | 20 | 10,8 | – |
| Herring | – | 140 | 15,5 | 8,7 | – |
| Boiled salmon | – | 210 | 16,3 | 15 | – |
| Mackerel in oil | – | 278 | 13,1 | 25,1 | – |
| Cold smoked mackerel | – | 151 | 23,4 | 6,4 | – |
| Zander | – | 97 | 21,3 | 1,3 | – |
| Boiled cod | – | 76 | 17 | 0,7 | – |
| Tuna in its own juice | – | 96 | 21 | 1 | – |
| Smoked eel | – | 363 | 17,7 | 32,4 | – |
| Boiled oysters | – | 95 | 14 | 3 | – |
| Boiled trout | – | 89 | 15,5 | 3 | – |
| Boiled hake | – | 86 | 16,6 | 2,2 | – |
| Sprats in oil | – | 363 | 17,4 | 32,4 | – |
| Boiled pike | – | 78 | 18 | 0,5 | – |
| Caviar | |||||
| Red caviar | – | 261 | 31,6 | 13,8 | – |
| Pollock caviar | – | 131 | 28,4 | 1,9 | – |
| Nuts | |||||
| Walnuts | 15 | 710 | 15,6 | 65,2 | 15,2 |
| Coconut | 45 | 380 | 3,4 | 33,5 | 29,5 |
| Almond | 25 | 648 | 18,6 | 57,7 | 13,6 |
| Pistachios | 15 | 577 | 21 | 50 | 10,8 |
| Hazelnut | 15 | 706 | 16,1 | 66,9 | 9,9 |
| Soft drinks | |||||
| Pure still water | – | – | – | – | – |
| Dry white wine | 44 | 66 | 0,1 | – | 0,6 |
| Dry red wine | 44 | 68 | 0,2 | – | 0,3 |
| Carbonated drinks | 74 | 48 | – | – | 11,7 |
| Dessert wine | 30 | 150 | 0,2 | – | 20 |
| Cocoa with milk (no sugar) | 40 | 67 | 3,2 | 3,8 | 5,1 |
| Kvass | 30 | 20,8 | 0,2 | – | 5 |
| Fruit compote (no sugar) | 60 | 60 | 0,8 | – | 14,2 |
| Ground coffee | 42 | 58 | 0,7 | 1 | 11,2 |
| Natural coffee (no sugar) | 52 | 1 | 0,1 | 0,1 | – |
| Pineapple juice (no sugar) | 46 | 53 | 0,4 | – | 13,4 |
| Orange juice (no sugar) | 40 | 54 | 0,7 | – | 12,8 |
| Juice in packaging | 70 | 54 | 0,7 | – | 12,8 |
| Grape juice (no sugar) | 48 | 56,4 | 0,3 | – | 13,8 |
| Grapefruit juice (no sugar) | 48 | 33 | 0,3 | – | 8 |
| Carrot juice | 40 | 28 | 1,1 | 0,1 | 5,8 |
| Tomato juice | 15 | 18 | 1 | – | 3,5 |
| Apple juice (no sugar) | 40 | 44 | 0,5 | – | 9,1 |
| Green tea (no sugar) | – | 0,1 | – | – | – |
| Alcohol | |||||
| Gin | – | 220 | – | – | – |
| Cognac | – | 239 | – | – | 0,1 |
| Brandy | – | 225 | – | – | 0,5 |
| Whiskey | – | 235 | – | – | 0,4 |
| Rum | – | 220 | – | – | – |
| Absinthe | – | 83 | – | – | 8,8 |