Women are constantly worried about how not to gain excess body weight, as well as how to lose the pounds that are so quickly and readily deposited on the sides and stomach. Not everyone adheres to the principles of a healthy diet, and the current lifestyle is in no way conducive to physical activity. The main risk group is expectant mothers who are just preparing for the birth of their baby. Therefore, women are concerned about how not to gain excess weight during pregnancy or how to lose it if necessary, without harming the child through your actions.
Normal body weight for a woman at the time of pregnancy
The rate of weight gain during pregnancy is different for everyone. There are no generally accepted standards. But there is an approximate table that shows the permissible weight gain as the baby grows in utero.
| Month of pregnancy | Weight gain every 7 days (g) |
| First | Weight remains virtually unchanged |
| Second | +100-150 |
| Third | +200 |
| Fourth | +150-200 |
| Fifth | +100-200 |
| Sixth | +300-500 |
| Seventh | +300-500 |
| Eighth | +300-500 |
| Ninth | -300/+300 |
In the last month of pregnancy, many women experience a slight decrease in body weight. The reason is the body’s preparation for childbirth (decrease in the volume of amniotic fluid, active cleansing of the intestines).
If you notice that the arrow on the scales begins to show 300-500 grams less, then you need to prepare things for the maternity hospital; within a few weeks, or maybe even days, the baby is expected to be born.

Doctors cannot say for sure how much weight you can gain during pregnancy. It all depends on the individual patient. On average, during a full pregnancy cycle you can “accumulate” from 8 to 15-16 kilograms.
After the birth of the child, the weight slowly but returns to normal.
If a woman’s weight already greatly exceeds normal values at 2-4 months, then she needs to think about changing her usual diet.
When not to panic
Experts have compiled a list of reasons why a pregnant woman’s body weight may exceed the norm:
- large size and weight of the fetus;
- the presence of not one, but two or more children in the womb;
- a lot of amniotic fluid;
- age (from 30 years);
- low body weight before conceiving a child (the thinner a woman is, the higher the likelihood of active weight gain);
- metabolic disruptions due to hormone imbalance;
- tendency to be overweight (if the woman had a large body weight before giving birth).
Almost all of them are natural and do not require weight loss measures.
Diabetes
Obese pregnant women are more likely than others to suffer from gestational diabetes, when there is an excess of glucose and damage to almost all body systems.
The danger is that diabetes may not go away after childbirth, but may develop into a chronic form.
This also causes overweight children to be born, which leads to:
- birth injuries;
- fetal death;
- infections.
Features of losing weight during pregnancy
It is impossible to completely stop weight gain during pregnancy, but you can slow down this process if you follow a few rules:
- You need to eat in small portions, but often. For example, if you used to eat a full plate of food at one time, now it should be divided into 2-3 parts. The interval between snacks should be at least 1 hour.
- Not all foods are good for weight loss. For example, breakfast cereals (sweet oatmeal in boxes) instead of reducing body weight, lead to active weight gain. They contain a lot of sugar and refined carbohydrates, which are dangerous for pregnant women. You should also avoid granola and combination seed and nut bars.
- The basis of a pregnant woman's diet is fruit. However, in large quantities they put a lot of stress on the stomach and slow down the process of digesting food. The best solution is to make fruit juices at home. Store-bought ones are full of chemicals, primarily taste enhancers, which negatively affects body weight.
- Fermented milk products help intestinal function. It clears faster, and this, although not significant, helps maintain normal weight.
- How to avoid gaining excess weight during pregnancy? Stop eating salty foods. Salt is the main enemy of a slim figure. It causes fluid to retain in the body, promotes the formation of edema and increases the weight of the pregnant woman by 3-4 kilograms. In addition, a large amount of water in the body disrupts the metabolic process, which is why fat accumulates more actively.
- You can't overeat at night. When a person sleeps, the work of his body slows down, food is digested less well, and the expenditure of internal energy decreases. This negatively affects the figure and leads to rapid obesity. The most optimal time to eat is two hours before going to bed. If you really want to eat, you can drink milk with crackers or eat some fruit.
- Doctors categorically prohibit women from limiting themselves to flour products during pregnancy. This is explained by the fact that the body draws energy from this type of food and if you completely stop eating bread and buns, it will be difficult for it during childbirth. To maintain energy reserves, but not gain weight, you should eat bran or black bread, and choose sweet pastries without fillings.
Another useful tip to avoid gaining excess weight during pregnancy is to eat more foods containing iron (fish, lean meats, green lettuce).

This microelement not only improves blood quality indicators, but also has a positive effect on the metabolic process, which is disrupted during gestation.
Causes of excess weight
There are several factors that cause weight gain in pregnant women. The main ones:
1. Overeating is one of the most common causes. The feeling of hunger is regulated by a special center located in the brain - the hypothalamus. With systematic overeating, a malfunction of the hypothalamus can occur. In this regard, the body needs increasingly larger portions of food to satiate.
2. Sedentary lifestyle - in this regard, the energy generated as a result of food consumption is not completely consumed. Therefore, fat deposits begin to accumulate in the body.
3. Genetic predisposition (heredity).
4. Endocrine system disorders – hormonal imbalance.
Sample menu
A diet for pregnant women with excess weight must necessarily include:
- secondary meat and vegetable broths;
- unprocessed vegetable oil;
- chicken, rabbit, turkey;
- milk and fermented milk products;
- vegetables, fruits, herbs;
- fish and other seafood;
- eggs;
- whole grain porridge.
Spices, black tea and sugar should be avoided. You also need to control the amount of potatoes. You can’t eat it a lot, as it contributes to obesity.
It will be possible to stop rapid weight gain during pregnancy if you follow a non-strict diet for one week a month.
Sample menu for one day:
- morning - a bowl of porridge with milk, any fruit and a glass of juice;
- lunch - liquid soup with vegetables and a piece of boiled chicken, a mug of green tea and a handful of dried fruits;
- afternoon snack - yogurt or a little cottage cheese with kefir and raisins;
- dinner - vegetable salad, a piece of fish, a glass of milk or juice.
You can eat between meals, but you shouldn’t overdo it. If you don’t feel like eating, you shouldn’t force a snack. In case of severe hunger, it is recommended to drink juices or fruits.
Obesity levels
There are the following degrees of obesity during pregnancy:
- First. The difference is no more than 30%.
- Second. The difference is 50%, which is more difficult to adjust.
- Third. There is a discrepancy of more than 50%, but not reaching 100%. It becomes almost impossible for a woman to bear a fetus.
- Fourth. This condition is dangerous even for a woman, exceeding the norm by 100%.
There is also endocrine obesity; you can read about this disorder in the article.
If obesity begins at the time of pregnancy, then it is difficult to determine its degree; it is only possible to track weekly growth.
What pregnant women should absolutely not eat
If a woman has already gained weight and is wondering how not to gain it all during pregnancy in the future, then first of all she needs to remove from her diet:
- smoked meats;
- candies and other sweets;
- fatty meats;
- semi-finished products;
- sausages, sausages;
- white bread (replaced with black or bran bread);
- marinades;
- pickles;
- salo;
- baking.
You should also reduce the amount of fluid you consume. This mainly applies to coffee, strong black tea, and cocoa.
Nutrition
The nutrition of a pregnant woman with an increased BMI should be organized in such a way as to restore energy balance and reduce the risk of complications. Drug therapy and surgical methods of weight correction are unacceptable.
Rules
- Nutrition during pregnancy should be balanced and fractional.
- The basis of the diet is fresh vegetables and fruits.
- The recommended cooking method is steaming. Eliminate or minimize fried foods.
- Reduce daily caloric intake by 10%.
- Reduce salt intake to 5 g per day.
- Half an hour before each meal, drink a glass of plain water.
- Diets, fasting and fasting days are prohibited. They can provoke the formation of large amounts of ketones, which have a toxic effect on the fetus.
- You should eat according to a clear meal schedule by the hour.
- Chew food thoroughly.
Recommended Products
The diet for pregnant women has a conditional name, since the list of prohibited foods includes only harmful ones, which corresponds to the principles of proper nutrition. It assumes that the diet contains all the necessary nutrients.
Healthy fats:
- cheeses, sour cream, whole milk, yogurt - low in fat;
- white sauce;
- eggs;
- avocado;
- nuts, seeds;
- turkey, chicken, red meat;
- salmon, tuna;
- vegetable, butter (no more than 10 g per day), nut butter.
Complex unrefined carbohydrates:
- whole wheat bread;
- porridge;
- brown rice;
- vegetables, berries, herbs, unsweetened fruits, dried fruits;
- dried beans, peas;
- hot jacket potatoes.
Drinks include rosehip decoction, dried fruit compote, freshly squeezed homemade juices (it is better to dilute them slightly with water), fruit drinks, unsweetened milk and fruit cocktails.
Prohibited Products
Refined simple carbohydrates:
- white, yeast, puff pastry, butter pastries;
- syrups;
- confectionery;
- sweets, milk chocolate;
- White rice.
Unhealthy fats:
- fat meat;
- dairy products with a high percentage of fat content;
- mayonnaise;
- creams;
- fast food with its trans fats.
And:
- spicy, salty, fried foods;
- broths;
- crab sticks;
- canned food, smoked meats, marinades, preserves;
- sausages;
- snacks;
- spices and seasonings;
- coffee, tea, carbonated drinks, store-bought juices, alcohol.
You should be more careful with herbal teas, many of which have a stimulating effect on the uterus and can cause miscarriage or premature birth.
Sample menus
Sample menu for the first trimester. The main task is to stock up on the necessary vitamins, ease the course of early gestosis, develop correct eating habits, and take control of body weight.
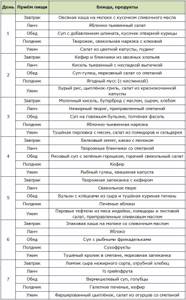
Sample menu for the second trimester. The task is not to overdo it with calories, be careful with fats, and return your BMI to the normal range for this period of pregnancy.
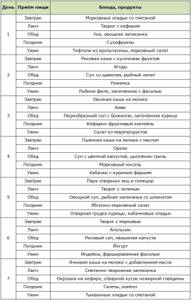
Sample menu for the third trimester. The goal is maximum relief of the digestive tract, prevention of late gestosis, and control of body weight.
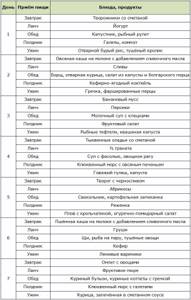
If you have any problems regarding nutrition due to excess weight, it is better to contact a nutritionist.
What doctors say about losing weight during pregnancy
Very often, patients turn to gynecologists asking whether it is possible to lose weight during pregnancy. The answer to this question depends on several factors:
- general health of the woman and the unborn child;
- current body weight;
- rate of weight gain in recent months.
If a woman is completely healthy and deviations in weight from the norm do not exceed 2-3 kilograms, then she does not need to lose weight. There is no need for extra stress for the body and the baby.
In the case where signs of obesity are visible, losing weight is not only possible, but also necessary. The main thing is to do everything carefully and correctly. A doctor - gynecologist or nutritionist can help with this.
Should you lose weight immediately before giving birth?
If a woman has been rapidly gaining weight throughout her pregnancy and in the ninth month begins to worry about her figure, then it is too late to go on a diet. Express weight loss before childbirth is a dangerous activity that can result in a lot of problems for both the mother and the baby.

The best solution is to lose weight after giving birth. At this moment, nothing threatens him.
However, if the mother plans to breastfeed him, then she should not sharply limit herself in food.
The diet should still contain foods rich in vitamins, minerals and other substances that are beneficial to a child’s still fragile body.
Why is it developing?
The main reason for the development of obesity in pregnant women is poor nutrition, abuse of sweets and fried foods, and a large amount of animal fats in the diet.
As a result of this, the fat layer constantly thickens, and a sedentary lifestyle and a minimum of activity only aggravate the situation.
Other causes of obesity include:
- type 2 diabetes mellitus;
- heredity, in particular improper metabolism and eating habits of parents;
- hormonal imbalances or disorders, such as leptin deficiency and problems with the functioning of the placenta;
- decreased physical activity;
- toxicosis.
What does this threaten?
Obesity affects the course of pregnancy, the condition of the mother and the fetus. According to various sources, 45-85% of pregnant women develop complications of varying severity. The danger lies in the fact that visceral obesity is combined with metabolic and hormonal changes, which manifest themselves clinically in the form of pathologies of various organs.
Maternal comorbidities lead to an increase in the number of children with congenital defects, resulting in high perinatal morbidity and mortality. Complications of pregnancy with obesity can be the following:
- Cardiovascular pathologies are a consequence of disturbances in blood composition and changes in its viscosity. There is an increase in blood pressure. Violation of the ratio of lipoproteins of different densities leads to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques and narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels. Obese pregnant women are much more likely to develop varicose veins in the legs.
- Infectious complications are a consequence of decreased immune resistance. They are registered in 59% of cases of obese pregnant women. This is often a chronic yeast infection that can affect not only the vagina, but also the folds of skin in the armpits, under the breasts and in the groin. Infectious diseases lead to pathology during gestation and after childbirth.
- Digestive pathologies. This can be reflux esophagitis, gastritis, cholestasis, fatty hepatosis.
Also, in women with obesity of degree 2 or more, pathologies of the respiratory system and urinary organs become more frequent.
Diabetes
Such patients are at risk for developing gestational diabetes mellitus. Adipose tissue leads to insulin resistance of cells. Excess glucose in the blood has a damaging effect on blood vessels and causes damage to target organs: heart, kidneys, brain.

Diabetes mellitus that manifests itself during the gestational period may not go away after childbirth. For a child, high glucose levels are dangerous for the development of congenital diabetes, as well as macrosomia - high weight, often exceeding 4 kg. This is not a sign of good health, but an additional risk:
- birth trauma;
- stillbirths;
- adaptation disorders;
- infectious complications.
Severe gestosis, preeclampsia and eclampsia
Women with impaired fat metabolism are three times more likely to experience late gestosis, in which blood pressure rises above 140/90 mm Hg. Art., there is edema and proteinuria. This affects the development of the fetus. Preeclampsia (read more about this pathology in a separate article) causes fetoplacental insufficiency and intrauterine growth retardation. Therefore, children are born with low weight, sometimes immature at full term.
Pregnant women who have suffered gestosis are seven times more likely to develop heart and vascular pathology in the future.
Thrombotic complications
In the 3rd trimester, there is a natural increase in blood clotting due to plasminogen, TNF-alpha. In obesity, there is a significant increase in the concentration of these substances, which causes the frequent development of thrombotic complications.
Obstetric pathologies
Most often these are the following conditions:
- threat of miscarriage;
- premature birth;
- anomalies of labor;
- intrauterine fetal hypoxia;
- post-term pregnancy;
- FPN;
- macrosomia.
Children born to mothers with pathological body weight are more susceptible to respiratory diseases, they are more likely to experience birth asphyxia or apnea during the newborn period. This requires increased attention from both the expectant mother and the maternity hospital staff.
The risk of early miscarriage is associated with hyperandrogenism, which develops due to the metabolism of steroids in adipose tissue. Therefore, with stage 4 obesity, pregnancy itself can be problematic due to hormonal changes.
In 15-17% of pregnant women, the formation of a generic dominant does not occur by the end of the gestation period. This is fraught with a post-term fetus, which has a high chance of getting a birth injury.
The frequency of birth of children with macrosomia, accompanied by a weight of more than 4 kg, is 20-40% according to various sources. The child's size increases unevenly, with the upper body and head growing to a greater extent. This becomes one of the reasons for the functional discrepancy between the size of the pelvis and the fetal head. Therefore, the woman may be offered a caesarean section.