- Home /
- Articles /
- Gastric ballooning
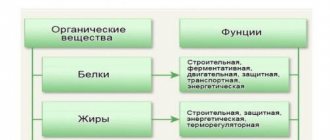
Gastric ballooning is a technically simple, non-surgical, non-drug treatment for obesity. An inflatable balloon, a biocompatible silicone ball with a valve, is inserted into the gastric cavity using an endoscope—a fiber-optic probe with a microvideo camera. It is filled with sterile saline solution (standard volume - 500 ml).
A filled intragastric (intragastric) balloon occupies the internal volume of the stomach and leaves less space for food (about 100 ml). Already after a small portion eaten, the brain receives a signal of satiety. The amount of calories consumed is reduced to the lower physiological norm. The procedure is reversible - after achieving the treatment goals, the balloon is removed (to prevent wear of the walls under the influence of gastric juice - after 6 months). If necessary, 2 months after removing the old balloon, a new one can be installed.
Benefits of Gastric Ballooning
- It is performed without incisions - through the mouth and esophagus.
- Does not disrupt the physiology of the digestive tract and does not reduce the absorption of nutrients.
- Allows you to avoid relatively more severe bariatric surgeries, such as gastric suturing.
- The result of the procedure is based on natural reflex reactions and therefore does not require volitional efforts on the part of the patient.
- Aimed at normalizing eating behavior - a person gets used to eating in small portions.
- It is not accompanied by anesthetic and surgical risks.
- May be prescribed to patients with contraindications to bariatric surgery.
The disadvantage of this method is that ballooning may be less effective for weight loss compared to bariatric surgery.
Gastric banding
Speaking about gastric bypass, it makes sense to take a closer look at other alternative options for radically combating obesity. Not so long ago, bandaging occupied a leading position. The procedure was described in a nutshell above. Separately, it should be clarified that with banding, weight loss occurs rather slowly, and in case of hyperobesity it is not prescribed, since it does not have the desired effect. The advantage of banding is that it is reversible. That is, the bandage can be removed, and the body will continue to function normally. No organs are truncated during this procedure.
Contraindications
- BMI ≤ 30.
- Anatomical restrictions due to previous operations.
- Acute gastrointestinal pathologies - esophagitis, ulcers, Crohn's disease, oncology.
- High risk of gastric bleeding - varicose veins of the esophagus or stomach, telangiectasia, stenosis, etc.
- Hiatal hernia.
- Diverticula and strictures of the esophagus and pharynx.
- Severe diseases of the kidneys, liver, lungs.
- Contraindications to gastroscopy.
- Alcoholism, drug addiction, mental disorders.
- Low discipline.
- Taking anticoagulants or steroids.
- Pregnancy and lactation.
- Age up to 18 years.
Laparoscopic sleeve gastroplasty
Another well-known surgical treatment option is sleeve gastroplasty. Usually performed using a minimally invasive method. During the operation, the patient's longitudinal part of the stomach, which makes up 75% of the entire organ, is removed. The remaining 25% of the stomach connects the esophagus and small intestine. The stomach secretes glerin, a hunger hormone. Once most of it is removed, glerin levels drop and the person eats less. This effect is enhanced by reducing the capacity of the stomach.
Sleeve gastroplasty has its advantages. Firstly, during its implementation, a foreign body is not introduced, as with ballooning and banding. Secondly, there is no restructuring of internal organs, as with bypass surgery. But this option is irreversible, that is, it is impossible to return the condition of the organs to their original state after sleeve gastroplasty. And after a few years, the patient’s weight may return again, then the operation will have to be repeated.
How does the procedure work?
The procedure can be performed without anesthesia, but in order to eliminate the patient’s emotional experiences, he is put into a medicated sleep. The balloon is placed under the control of a microvideo camera, which is inserted into the stomach through the esophagus. Medical pigment is added to the saline solution for timely control of leaks. The solution is injected with a syringe through a probe. When the required volume is reached, the valve is closed and the probe is removed. The duration of the procedure is up to 30 minutes.
If you notice that the urine has turned blue, then inform your doctor, he will make a correction. This situation does not pose any danger.
Where can treatment with a balloon be performed?
First of all, such treatment should be carried out by a specialist working in the field of obesity treatment and who has undergone special training in the use of this technique. Manipulations associated with installation and especially removal of the balloon require the participation of a qualified endoscopist, as well as an anesthesiologist. Therefore, the use of this technique is most justified in clinics where these specialists are available. The Center for Endosurgery and Lithotripsy has all the conditions for carrying out such manipulations: a team of experienced surgeons, many years of experience in performing endoscopic operations, highly qualified doctors and nursing staff. It is important that all this is supported by the latest medical equipment from leading companies in Japan, the USA, and Germany, which makes a task of any complexity feasible. It is difficult to imagine the work of such a large multidisciplinary clinic as CELT, where more than 3,000 operations are performed per year, without the presence of a serious anesthesiology and resuscitation service. The combination of the vast practical experience of the department’s staff, modern equipment and the latest medications allows us to perform operations of any complexity at the safest level for patients. After the operation, the patient falls into the caring hands of doctors and nurses in the anesthesiology and intensive care unit. Their task is to eliminate the risk of postoperative complications, block postoperative pain, provide careful care for the patient and prepare him for transfer to a specialized department, under the supervision of the attending physician. The combination of all these factors suggests that CELT is one of the optimal places for surgical treatment of overweight patients.
Recovery period
If the patient wishes, he can leave the clinic after 2 hours. However, it is recommended to spend the first night in the clinic. To stop attacks of nausea and vomiting, the patient is administered antiemetic drugs.
In the first 3-4 days there may be a feeling of discomfort, then the body adapts and it goes away. During this time, semi-liquid pureed food is recommended. You need to eat and drink slowly, using teaspoons. Intense physical activity should be avoided during the day. You can return to normal training in a week.
After gastric ballooning, split meals are recommended at least 5 times a day. High-calorie foods are excluded from the menu. The diet is based on lean meat and fish, vegetables, whole grain cereals, vegetable oils, fruits, and dairy products.
The diet can be normal, but the best results are achieved with a caloric intake of up to 1500 kcal per day: with a normal diet, the average weight loss over six months is up to 10 kg, with a limited diet - up to 20. It is recommended to regularly consult a nutritionist.
Intragastric balloon Obalon
The Obalon system is the newest type of product available. It is a system consisting of three cylinders. This type of device is filled with air rather than liquid.
When choosing Obalon, you swallow a small capsule that is attached with a thin catheter used to inflate the balloon with air. Three balloons can be placed gradually over three months. Each inflated balloon occupies approximately one cup of stomach volume, about the size of an orange. The device helps people feel full and less likely to overeat. Both during and after treatment, patients receive counseling to help them learn about healthy eating and exercise habits. At the end of treatment, the balloons are deflated and removed using an endoscopic procedure.
Recommended for:
This single system is approved for people with a body mass index (BMI) of 30-40 kg/m2 and those who have already tried other methods of losing weight but have not received results. As with other systems, Patients must be prepared to undergo a full weight loss program including diet, exercise and counseling to improve their health and lose weight.
Contraindications
Some patients may not be eligible for the device. This list includes people who have disorders that may affect swallowing function, those who have had surgery that narrows the intestinal tract, and those who are taking medications that irritate the gastrointestinal tract, including NSAIDs or aspirin.
Side effects
If you choose the Obalon system, you may experience abdominal pain or nausea. Less common side effects include vomiting, upset stomach, bloating, diarrhea, stomach irritation or bleeding, esophageal bleeding and abrasions, constipation, or difficulty sleeping. During your initial consultation, your doctor will list a full list of possible side effects and risks.
Application results
A clinical study of more than 400 patients found that those who used Obalon along with diet, exercise and counseling lost more weight than those who did the same without the gastric balloon. People who used the Obalon system lost an average of 7 kg or 6.6 percent of their total body weight, while patients who did not use it lost an average of 3 kg or 3.42 percent of their total body weight.
Medical recommendations after balloon installation
After installing the balloon, a person may, out of habit, experience discomfort, nausea and slight pain in the epigastrium. This occurs due to constant fullness of the stomach. If there is little liquid in the ball, then the patient, on the contrary, may experience a constant feeling of hunger. In any case, it is necessary to consult the doctor who performed the bypass procedure.
Immediately after installing the balloon, a person’s appetite decreases. For the first few days, the patient is advised to consume only liquid foods. Solids are introduced into the menu gradually, according to a schedule determined by the doctor. Exceeding the established single volumes of food or liquid is strictly prohibited.
Also, all foods that can cause flatulence are excluded from the diet. While the balloon is in the stomach, you need to take medications that reduce acidity. Omeprazole is mainly prescribed.
Risks and complications
Bypass surgery carries the same risks that accompany any abdominal surgery. These include such phenomena as bleeding, infections, complications of the cardiovascular system, adhesions, intestinal obstruction, and much more. Complications of this kind occur extremely rarely. To reduce their likelihood to a minimum, you need to go to a good clinic (focus on reviews, not prices), strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations, and approach the process of preoperative preparation and postoperative rehabilitation with all responsibility.
Preoperative examination
Before the operation, a full examination is carried out, including a number of tests, as well as x-rays of the stomach and chest, gastroscopy, and ECG. If the patient has chronic diseases, consultations with specialized specialists are also needed. After all examinations, you need to obtain a physician’s opinion.
If the examination reveals health problems, the operation is postponed. In some cases, the operation is canceled altogether. For example, a cardiologist can prohibit it. Contraindications to bypass surgery are:
· pregnancy, lactation period;
· intolerance to anesthesia;
· presence of malignant tumors;
· respiratory tract diseases;
· problems with the cardiovascular system.
How is gastric bypass performed?
The patient, under general anesthesia, is minimally invasively injected with titanium clips, which are used to stitch the stomach along the line dividing it into the working and bypass parts. After this, an anastomosis is formed connecting the upper part of the stomach to the small intestine. The entire procedure requires 4 to 6 small incisions. During the operation, all manipulations are visualized on the monitor.
Due to the fact that only a few incisions are required to carry out the manipulations necessary for bypass surgery, the recovery process is quite fast. First, the patient is observed in a hospital setting, then continues to be treated on an outpatient basis until complete recovery. However, you will need to constantly see a doctor. After bypass surgery, you must take nutritional supplements and vitamins as prescribed by your doctor.
After the operation, the patient's appetite level sharply decreases, as a result, his portions will be significantly reduced. For some time, you may even experience an aversion to food. The first year after bypass surgery is contraindicated for women, and it is almost impossible to get pregnant. In the future, the patient can become pregnant, carry and give birth to a child without any complications.
Preoperative fasting
In obese people, a lot of fat accumulates in the liver cells. It increases in size, so it can overlap the bypass area, which leads to the need to make more global incisions. To avoid this, patients are advised to follow a strict diet for a week before surgery. The fat in the liver cells burns quickly, and within a week the organ returns to normal size.
Fasting before surgery is also necessary so that all internal organs can be fully examined without difficulty. The less food there is in the digestive organs, the more accurate the data from ultrasound, gastroscopy, and other types of examination. In addition, complete fasting is often recommended by anesthesiologists on the eve of surgery. The patient does not need to know all the nuances of preoperative preparation; he should simply strictly follow all the doctors’ instructions without violating them.
Preparation and execution
Stages:
- An examination is carried out by a gastroenterologist.
- Tests are taken to eliminate the risk of complications.
- Local anesthesia is administered.
- The balloon is inserted into the stomach.
- A catheter (diameter up to 7 mm) with a conductor inside is attached.
- The conductor is removed and the container is filled with physiological solution (500-700 ml).
- The tube is disconnected and removed.
- The doctor visually determines the correctness of the procedure and installation.
Without assessing the motor and enzymatic functionality of the stomach and the structure of the organ mucosa, installation of a balloon is impossible.
Why is it needed?
Installing a balloon allows you to adjust portions and stop the process of overeating. Helps reduce the patient's weight and narrow the volume of the organ. This is an alternative to diets and physical procedures when a person cannot limit his diet on his own. When the patient's weight is reduced to the required standards, from a medical point of view, the functioning of the cardiovascular, endocrine, autoimmune and digestive systems is restored, the body is restored and the load on the musculoskeletal system is reduced. Such properties help prevent or cure pathologies of internal organs.
Technical description of the cylinder
The intragastric balloon is made of high quality medical silicone transparent rubber. It is made in the form of a ball with thin walls, has softness and elasticity. The surface of the cylinder is absolutely smooth. Its volume after filling the internal space ranges from 400 to 700 ml.
Air or water is used to fill the balloon. In the latter case, methylene blue is added to the water. Filling is carried out through a special valve. When filled, the balloon has a diameter of 12-15 cm.
The balloon is supplied deflated in a case and equipped with devices for inserting and inflating it. Factory packaging contains:
- The container is tightly rolled up and covered with a cover.
- A tube with a diameter of 6.5 mm inserted into the cylinder valve. Designed to inflate the balloon. Inside the tube has a wire guide, which provides rigidity and facilitates insertion of the balloon.
- Inflation system.
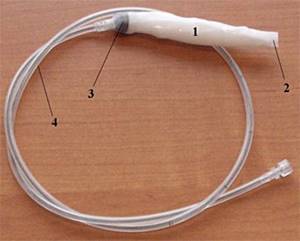
Collapsed intragastric balloon before insertion.
1. Rolled cylinder 2. Cover 3. Valve 4. Tube
Briefly about the anatomy and physiology of the stomach
The stomach is part of the digestive system. The organ is located between the small intestine and the esophagus, in the left hypochondrium. Normally, food that enters the stomach remains in it for approximately a couple of hours. At this time, it is treated with gastric juice. The main function of the organ is the destruction of proteins in the food mass.
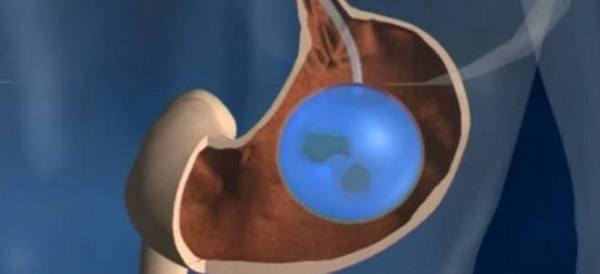
Anatomically, the stomach has a body, a fundus and a pyloric region. At this point, the organ connects to the duodenum and is equipped with a pylorus (sphincter). It regulates the flow of food into the intestines. Digestion takes place in the body of the stomach, at the bottom there are sensitive baro-receptors. They send a signal to the brain when saturation has occurred.