The main means of non-surgical treatment of joint diseases are analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs. Their action is aimed only at reducing pain and preventing further degeneration (destruction) of cartilage; treatment of already damaged cartilage tissue does not occur. Glucosamine and chondroitin, together or separately, are increasingly used as options for the treatment of osteoarthritis and joint support under intense stress, that is, they potentially act as chondroprotectors and correctors of the pathological process.
Glucosamine and chondroitin in medical practice in various countries
In Europe, both of these compounds are considered drugs and belong to a class of drugs under the general term SYSADOA (Slow Acting Drugs for Osteoarthritis). Under this name, glucosamine and chondroitin are mentioned, for example, in the recommendations (2003, pdf., English) of the European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR). The list of drugs based on glucosamine chondroitin, registered under various trademarks, consists of more than a hundred names.

In Europe and Russia, glucosamine and chondroitin are recognized as beneficial to health: these substances are included in many medicines produced in these countries. In Russia, there are both dietary supplements and medicines based on glucosamine and/or chondroitin. As of May 2021, the following drugs based on the glucosamine and chondroitin complex were listed in the State Register of Medicines:
- Tazan,
- Chondroglucide,
- Chondroflex,
- Teraflex,
- KondroNova,
- Arthra and others.
As for dietary supplements, several dozen products in this category, both domestic and foreign, are registered on the Rospotrebnadzor website.
In the United States, glucosamine and chondroitin are approved for use exclusively as dietary supplements due to mixed opinions in the scientific community.
Joint structure
Any joint includes:
- Articular surfaces covered with articular cartilage, which provide joint mobility;
- Ligaments that fix the joint within certain limits;
- Synovial (joint) bursa, covering the outside of the joint and producing synovial fluid.
- Synovial fluid that nourishes joint structures and ensures smooth gliding of cartilage.
At the same time, almost all components of articular cartilage tissue play an important role in the health of the joint: specialized cells (chondrocytes and chondroblasts), a collagen framework with hyaluronic acid molecules, as well as a certain amount of chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine produced by the body.
Mechanism of development of osteoarthritis
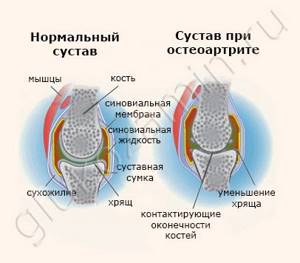
The main causes of joint diseases:
- Hereditary factors
- Metabolic disease
- Poor environmental situation
- Stress
- Chronic fatigue
- Lack of physical activity or, on the contrary, constant heavy load on a certain group of joints (professional sports, standing work, etc.)
- Improper nutrition, in which the joint does not receive the proper amount of necessary micro and macroelements
- Overweight
- Untreated injuries and bruises
- Hypothermia
- Age-related changes (due to the above reasons, joint diseases become noticeably younger, but age only increases the likelihood of their development)
In order to prevent the disease from developing, effective measures should be taken at the first signs of joint diseases. Otherwise, they can lead to the most disastrous consequences: significant limitation of mobility, ability to work, and disability.
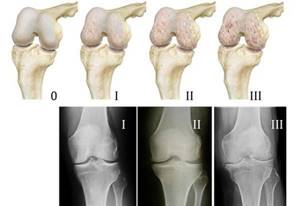
Effect on joints with osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the most common joint disease. It affects 20% of the world's population, and in people over 55 years of age the incidence of the disease increases to 50%, and over 65 – up to 70%. In Russia, a third of patients with this disease receive a disability group .
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen, nimesulide, celecoxib, etc.) are traditionally prescribed for the treatment of osteoarthritis. In severe cases, anti-inflammatory hormones are used. These drugs are unsafe when taken continuously, causing side effects from the gastrointestinal tract (ulcer) and cardiovascular system (hypertension, angina, even heart attack). In addition, they do not affect the destruction of cartilage tissue, but only reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Therefore, many doctors agree that it is better in this case to take chondroitin and glucosamine.
Glucosamine and chondroitin are natural components of cartilage tissue . They are safe when taken over a long period of time and, most importantly, can stop the process of cartilage destruction, thereby preventing disability.
Glucosamine for osteoarthritis:
- Reduces the production of inflammatory mediators (P.Chan, 2006, google translate);
- Reduces the production of enzymes that destroy cartilage (EJ Uitterlinden, 2006, pdf, English);
- Slows down oxidative stress, which stimulates the activity of inflammatory mediators (V. Calamia, 2010, google translate).
Chondroitin sulfate for osteoarthritis:
- Reduces the activity of inflammation (F. Legendre, 2008, google translate);
- Slows down the destruction of cartilage, providing a chondroprotective effect (M. Kubo, 2009, google translate);
- Stimulates cartilage cells to synthesize the intercellular matrix (M. Kubo, 2009, google translate).
The role of chondroitin in the human body
Chondroitin performs several important functions in the human body:
- stimulates the formation of glycosaminoglycans - the main building material of connective tissue, slowing down the destruction of cartilage and promoting its restoration;
- activates the formation of hyaluronic acid, which retains water in the tissues - this is important for maintaining the elasticity necessary for full shock absorption of the joint;
- interacts with all other components of cartilage, uniting and structuring them, providing the necessary strength;
- forms small water cavities in the cartilage, increasing shock absorption;
- stimulates the production of intra-articular fluid necessary to nourish cartilage tissue and smooth movement of articular surfaces relative to each other;
- makes synovial fluid more fluid, maintaining its natural viscosity;
- reduces pain in joint diseases and increases mobility in them, including by increasing the amount and fluidity of intra-articular fluid;
- prevents the growth of blood vessels into the cartilage;
- suppresses the formation of reactive oxygen species, which accumulate in large quantities during joint aging;
- blocks enzymes that destroy connective tissue;
- suppresses lipid synthesis, thereby preventing the development of atherosclerosis in the walls of blood vessels.
Studies on the effectiveness of a combination of glucosamine and chondroitin in osteoarthritis
Glucosamine and chondroitin are effective for osteoarthritis and alone. But their combination enhances the therapeutic effect . Proof of this, in particular, is the large-scale study GAIT (Glucosamine/chondroitin Arthritis Intervention Trial), which was conducted over 24 weeks and cost $1.5 million. The study involved 1,583 patients from 16 clinics. The average age is 58 years, the average duration of illness is 10 years. , the effectiveness of glucosamine chondroitin for relieving pain in various joint disorders was established :

Does collagen work and which one is better to choose?
Let's look at some studies that have confirmed that collagen actually works.
An 8-week study showed that oral collagen supplementation helps relieve dry skin, including during winter.
“The effect of oral collagen peptide supplementation on skin moisture”
Another study found that collagen helps fight cellulite in women.
"Collagen Peptides Has Beneficial Effect on Cellulite Morphology"
Undenatured collagen type II (UC-II) may reduce joint swelling and pain in moderate to severe osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Moreover, its effect is significantly higher than that of glucosamine and chondroitin. Research shows that UC-ll can help not only reduce joint pain, but also improve joint mobility.
"Undenatured type II collagen (UC-II®️) for joint support James P Lugo"
Despite the effectiveness of this type of collagen, I recommend first seeing a doctor to find out the cause of your joint problems.
The effectiveness of collagen supplements for bones has only been confirmed in experiments on rats. Human studies have shown that collagen supplements do not improve bone health.
"Hydroxyapatite Synthesis: Influence of Collagen on Its Structural and Morphological Characteristic"
Manufacturers advertise that collagen supplements help maintain and gain muscle mass. And this is true, but all the studies were conducted on older people (over 70 years old), for whom any protein supplement will have a similar effect. For the average person, other sources of protein will be much more effective.
"Effects of Whey and Fortified Collagen Hydrolysate Protein Supplements"
Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects
Relatively recently, a similar-scale study was conducted comparing the effectiveness of glucosamine and chondroitin with celecoxib (M. Hochberg, 2014, pdf, English). The six-month clinical trial included 606 patients from Poland, Spain, Germany, and France. The analgesic effect of the combination of glucosamine and chondroitin (pain reduction was noted by 50.1%) was almost identical to the effect of celecoxib (50.2%) . In addition, in more than half of the patients, swelling in the affected joints and stiffness decreased, that is, the overall functional state improved.
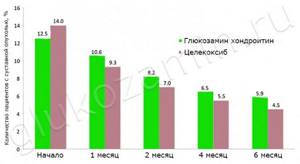
Russian authors did not stand aside either. Rodionova S.S. and Eskin N.A. conducted a large study (S. Rodionova, 2021, Russian) that included 3077 patients. The analgesic properties of glucosamine and chondroitin were studied. At the beginning of the study, 56.2% of patients needed non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve pain. After 3 months of taking glucosamine and chondroitin, only 18.9% of subjects still needed painkillers . The authors of the work concluded that the combination of glucosamine and chondroitin provides pain relief no worse than traditional analgesics.
An integrated approach to treatment
However, it should be remembered that joint restoration, recovery and successful prevention of joint diseases are possible only with an integrated approach to solving these important problems. In addition to taking chondroprotectors and applying ointments, it is important to change your lifestyle, otherwise the effect of use is minimized, or even completely absent. Among the primary tasks is adherence to a diet, which is aimed at achieving the following goals: weight loss, which means the load on the joints, providing the body with natural “chondroprotectors”. Glucosamine and chondroitin are found, for example, in meat and fish, legumes, and avocados. These components are best supplied by jellied dishes, meat and fish broths, and dishes stewed with bones. A necessary element, in addition, is physical activity. Moreover, the complex of therapeutic exercises is selected in such a way as to minimize the load on the diseased joint - many exercises are performed while sitting or standing.
Chondroprotectors help a person remain active and productive. Together with other means to maintain a healthy lifestyle, they can provide joints with long-term functioning, relieve pain, swelling and inflammation - it is only important to pay attention in time to the slightest deviations from the norm, both external and internal.
Chondroprotective properties
In addition to painkillers, glucosamine and chondroitin have chondroprotective properties, although the effect becomes noticeable only after a long time. A group of Canadian scientists led by J. Raynauld (J. Raynauld, 2021, google translate) studied the effect of a combination of glucosamine and chondroitin on the volume of articular cartilage in osteoarthritis for 6 years. Control was carried out using magnetic resonance imaging. After 6 years, cartilage loss was less in patients taking the combination of glucosamine and chondroitin , and the difference between the groups did not become apparent until after 2 years of regular use.
This information is confirmed by a review article by C. Vangsness (C. Vangsness, 2009, pdf, English) in which the scientist analyzes the results of studies on the effectiveness of glucosamine and chondroitin published since 1969. In many studies, the difference between the control and experimental groups became noticeable only after 6–9 months of taking the drug. From this, the authors conclude that the chondroprotective effect of glucosamine and chondroitin directly depends on the duration of use . The review also confirmed the pain-relieving properties, the ability to improve joint function, and the exceptional safety of the products.
What is glucosamine?
Glucosamine is an important substance for the synthesis of proteoglycan molecules - structural components of articular cartilage.
Cartilage consists of a matrix of collagen fibers into which large proteoglycan molecules are “inserted.” One of the functions of these molecules is to attract fluid into the joint, which provides high mechanical strength to the cartilage.
In osteoarthritis/ostearthrosis (the most common joint disease, characteristic of both older people and athletes), there is a disruption in the functioning of the collagen matrix, one of the reasons for which may be a decrease in the concentration of proteoglycans.
Glucosamine is a substrate for the creation of proteoglycans.
It is believed that taking it can slow down the development of osteoarthritis, as well as reduce joint pain.
Glucosamine is obtained mainly from the protective coverings of shellfish or crabs. It can also be synthesized chemically.
Scientific research does not clearly support the benefits of glucosamine for joints.
Reviews from patients indicate that glucosamine has an analgesic effect, which doctors/scientists tend to attribute to a strong placebo effect.
Glucosamine is a material for creating the structural components of cartilage (including chondroitin), which provide its mechanical strength. Scientific studies do not clearly confirm the benefits of taking it for the treatment and prevention of joint diseases
We recommend : Whey protein: types, benefits for gaining muscle mass and losing weight, harm
Criticism of effectiveness

Doubts about their effectiveness are much less common. Meanwhile, discussions on this issue continue in the medical community. Both glucosamine hydrochloride and glucosamine sulfate have been questioned as effective drugs. For example, in 2010, a group of European scientists from Switzerland and Germany led by Simon Wandel (S. Wandel, 2010, google translate), after conducting a meta-analysis of studies, came to the conclusion that glucosamine, chondroitin and their combinations are no more effective than placebo .
Some experts believe that most of the studies conducted are not of sufficient quality. Therefore, the compilers of the latest American clinical guidelines (2016, pdf, English) for the treatment of osteoarthritis considered only one study to meet scientific criteria, and, based on a lack of data, did not recommend including glucosamine and chondroitin in the first line of therapy . The international society for the treatment of osteoarthritis OARSI writes about the same thing in clinical guidelines from 2014 (T. McAlindon, 2014, pdf, English), defining their effect as “unreliable”.
On the other hand, European guidelines (Olivier Bruyère et al. 2014, pdf) for the treatment of osteoarthritis still recommend SYSADOA (i.e. glucosamine and chondroitin alone or together) as first-line drugs. Russian clinicians agree (Denisov L.N., 2016) with the opinion of European colleagues, calling glucosamine and chondroitin the preferred agents in the initial stages of the development of osteoarthritis .
Numerous users of the World Wide Web, who decided to study the effect of glucosamine and chondroitin on their own, mostly speak positively about it. And since official medicine continues to debate, going through endless pros and cons, this is perhaps the only way to fully evaluate the properties of glucosamine chondroitin in joint therapy.
To make an informed decision, read other materials on our site:
What diseases does Glucosamine Chondroitin help with?
Source glukozamin.ru
Destructive processes in cartilage and joints occur due to a lack of substances chondroitin and glucosamine, which are produced by the cells of the body. Therefore, together both elements are an integral part of many chondoprotective drugs. Natural glucosamine and chondroitin are found in synovial interarticular fluid. It is a natural component of cartilage and is involved in the formation of joint lubrication and shock-absorbing tissue. To replenish substances, doctors recommend taking chondroprotectors.

Harm and possible side effects
The health safety of chondroitin and glucosamine when taken long-term has been confirmed in numerous studies and meta-analyses.
Glucosamine is recognized by scientists as safe in doses up to 2000 mg per day, chondroitin sulfate - 1200 mg per day.
During the 6-month GAIT study described above, 61 of 1,583 participants experienced serious side effects during the experiment, but of these only three were considered relevant to the subject of the study: chronic heart failure (in the group taking chondroitin and glucosamine), stroke ( in the celecoxib group) and chest pain (in the glucosamine group).
Most side effects were mild and evenly distributed between groups, indicating that they were independent of the type of drugs taken.
Relevant side effects include mostly mild digestive disorders .
There was also no effect on blood glucose levels, one of the potential side effects associated with glucosamine.
Because most glucosamine is derived from shellfish, it may cause allergic reactions in people with this type of food allergy.
Glucosamine, chondroitin and their combination are considered safe for health. Possible side effects include mild eating disorders
What are chondroitin and glucosamine?
Chondroitin in its natural form is a combination of 2 tissues - cartilage and bone. Produced by the body, it participates in biochemical processes, which ensures bone strength and restoration of cartilage and joints. Prevents exacerbations of rheumatism and arthrosis. Natural glucosamine is synthesized from glucose and amino acids by cartilage cells - chondrocytes. It is a modified sugar and is involved in the formation of collagen.
If the body produces insufficient quantities of these components, the deficiency is compensated for by special drugs - chondroprotectors, which are used to reduce joint pain. The need to use analgesics may no longer be necessary. The body's tolerance is good, adverse reactions are rare.
How to take glucosamine-chondroitin complexes and is it worth it? Recommendations
Connective tissue is involved in the formation of stroma, the framework for all organs of our body, and their outer capsule. It protects, nourishes and supports tissues and organs. Most connective tissue elements are found in musculoskeletal structures: bones, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, joints, and even joint fluid.
Main functions of collagen:
- participates in regenerative processes;
- provides firmness and elasticity of connective and other tissues;
- ensures the phenomenon of cell adhesion;
- stimulates the formation of epithelial cells;
- has good bioabsorption.
Collagen for oral administration is used in medicine for the treatment of dystrophic-degenerative diseases of the joints, in cosmetology to improve the appearance of the skin, as a bioconstructive material in tissue engineering, as well as in pharmacology for the production of external medicines with regenerative properties and preparations for oral administration.
What type of collagen is used in sports nutrition and how to choose the right drug?
There are more than 28 types of collagen, but according to the main classification there are three (now the classification has been expanded to seven types, but this has nothing to do with sports). I and III are more often used in cosmetology to create anti-aging cosmetics.
Type II is indispensable for joints and ligaments. It is actively used in sports nutrition, to restore flexibility and mobility to joints, for rheumatism, arthritis, etc. It is especially effective at stages of functional changes, when the cartilage is still practically intact, but there are already problems with full movement.
The most inexpensive and difficult to digest is animal. It is produced from cartilage, bone, and dermal tissues of poultry and cattle. To make the drug better absorbed, it is hydrolyzed into peptide chains - smaller molecules.
Fish or sea - very effective, well absorbed by humans. The compound is extracted from fish bones, but due to the similarity of the collagen formula, the absorption process is much better. Unfortunately, the cleaning process makes production more expensive, so the price with delivery to Moscow is higher than for the animal species.
For vegetarians. Since the substance is of animal origin, vegetarian collagen simply does not exist in nature. As for the well-known agar-agar, it is extracted from seaweed and has a structure different from gelatin; accordingly, it does not affect collagen synthesis in any way. Taking this substance internally will not give any result.
Collagen synthesis occurs in fibroblasts, connective tissue cells. Its formation occurs with the participation of certain enzymes, the activity of which requires the presence of divalent iron.
Fibroblasts not only synthesize the substance, but also actively destroy it. After 25-30 years, destruction begins to prevail over production.
After 35, only 50% of the previous amount is restored (hence wrinkles and age-related joint problems). Therefore, starting from a certain age, doctors and trainers recommend taking collagen preparations.
Considering the high sports loads, especially in bodybuilding, you can start taking the drug earlier.
In hydrolyzed form, the compound is well absorbed. Effects after oral administration:
- the ligamentous apparatus is strengthened;
- articular cartilage is restored;
- the intensity of pain in joint diseases decreases;
- the density of connective tissue in “weak” areas increases;
- bone tissue is strengthened, since collagen has an activating effect on osteoblasts (young bone cells).
The product is available in the form of tablets, capsules, and liquid form. There's even collagen powder and gummies. It is the powder that is most effective in absorption. Liquid is also absorbed quickly, but the price is more expensive. Those who cannot tolerate powders can purchase capsules. Tablets take the longest to be absorbed in the digestive tract, but their cost is usually lower.
Chewable is somewhere in the middle, but its concentrations are so small that taking the product is not economically profitable.
The supplement is of natural origin and safe, and its benefits in sports nutrition are invaluable.
How to use
Bodybuilders recommend taking the substance in a daily dosage of 10 g, dividing the volume into two servings. The product can be washed down with water or dissolved in it. Some trainers in Moscow fitness clubs, in order to increase the effectiveness of the drug, advise taking it together with vitamin C, glucosamine, hyaluronic acid, and chondroitin.
Why can't you take regular food gelatin? Despite the obvious cheapness of the product, it often leads to constipation, exacerbation of hemorrhoids, and gastroenterological problems. Products produced by representatives of sports nutrition are highly purified, so the risk of side effects from taking them is minimized.
It is not recommended to take:
- for those who have difficulty digesting food gelatin;
- with a tendency to thrombosis;
- in the presence of thrombophlebitis, varicose veins;
- if you are allergic to food gelatin;
- suffering from cholelithiasis or urolithiasis;
- persons with renal failure;
- patients with oxaluric diathesis.
If you have cardiovascular problems, take collagen only after consulting your doctor.
Do you want to buy collagen for joints in Moscow? The online store "TrainerIzDoma.rf" offers a wide variety of collagen supplements at a low price. The reasonable price and high quality will pleasantly surprise you, and the rich assortment will allow you to purchase the product based on your individual needs.
Choose what you really like! You can order the drug directly on the website or by calling.
Effect on joints
One of the important components of cartilage is chondroitins, which are involved in maintaining the shape of connective tissue and performing a shock-absorbing function. They are part of the walls of blood vessels, supporting the normal process of blood circulation. As a result of severe degenerative processes in the joints or stressful situations, the synthesis of glucosamine by chondrocytes stops and cartilage tissue begins to break down. Normally, this component is produced in sufficient quantities to keep cartilage healthy.
The difference between chondoprotectors and other drugs intended for joints is their neutral effect in advanced forms of joint diseases and effectiveness at the beginning of the development of the disease.
Chondroprotectors are secondary and are used in the treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system:
- osteochondrosis;
- osteoarthritis;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- periarthritis;
- inflammation of the spinal column and joints.
For preventive purposes, drugs are used to mitigate:
- pathological manifestations of age-related changes in joints and spine;
- postoperative period;
- complications from excessive physical exertion.
Return to contents
Useful properties of Glucosamine
Over the years, a person not only acquires valuable life experience, but the body ages and weakens, and ceases to easily cope with stress. The flying gait that was so familiar in youth is replaced by a slow gait, “tired” joints make themselves felt.
From year to year, each joint clearly performs its functions. Each one has a different configuration for an individual range of motion. The ends of the bones (epiphyses) that form the joint are covered with cartilage. While a person is young and active, this surface is smooth and even; over the years it becomes more fragile and thinner. The synovial fluid, which washes the surface of the joint, thereby reducing load and friction, also “dries out” over the years, and its properties weaken.
Cartilage is found not only in joints - it is a kind of shock-absorbing system of the body. Their task is to give and maintain the shape of connective tissue, soften shocks when a person makes various movements, and protect the spinal vertebrae. Thinning cartilage leads to dislocations, joint damage and a variety of diseases.
In recent years, joint diseases have become significantly “younger” - among patients, more and more often young and middle-aged people. The gradual progression and insignificance of the initial symptoms of joint diseases is the main danger - a person does not understand the seriousness of the situation, ignores the first signs of the disease, and as a result, the disease can no longer be treated. It is almost impossible to reverse the process.
Typically, treatment of this type of disease is carried out according to the same scheme: using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and chondroprotectors . The former reduce pain, while the latter protect cartilage tissue from destruction and accelerate its regeneration.
The leaders here are 2 main chondroprotectors : glucosamine and chondroitin .
Chondroitin is a structural analogue of human cartilage tissue. It is obtained from the cartilage and bones of fish and farm animals. Chondroitin sulfate has an anti-inflammatory effect; it is an excellent stimulator of cartilage tissue regeneration. But the bioavailability of this drug turns out to be higher when used externally, that is, chondroitin sulfate is more useful in ointments and gels . The drug is not so effective in tablets, although this form of release is much cheaper.
Glucosamine is the second in order, but not the most important, chondroprotector. Glucosamine has a positive effect on the metabolism of cartilage tissue, stimulates collagen synthesis, and acts as a catalyst for the regeneration of the cartilage layer . Scientists have proven that glucosamine also relieves swelling and increased sensitivity, restores hardened joints, and has an anti-inflammatory effect. There are several forms of this drug:
- Glucosamine Hydrochloride - produced from crustacean chitin or plant sources;
- Glucosamine Sulfate - the raw material for it is crustacean chitin (stabilized with sodium or potassium chloride). By the way, in a separate article you can find out which is better - glucosamine hydrochloride or sulfate;
- N-Acetylglucosamine;
- Poly-N-acetylglucosamine.
Read more about what glucosamine and chondroitin are in our special material.
Japanese scientists proposed Chondroitin and Glucosamine in the form of dietary supplements, which have virtually no side effects, back in the early 80s, successfully using them in the treatment of such serious diseases as:
- Arthritis;
- Osteoarthritis;
- Osteochondrosis of peripheral joints and spine;
- Primary osteoarthritis affecting the knee and/or hip joints;
- Periodontopathy (disease of the tissues of the supporting apparatus of the tooth);
- Degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the spine and joints (spondylosis and spondyloarthrosis);
- Humeroscapular periarthritis;
- Deformation of joints (ankylosis, subluxation);
- The drug can be prescribed as an additional source of glucosamine and a corrector of reproductive functions, as well as in case of increased functional load on the joints (overweight, physical activity).
Also, chondroitin in combination with substances of the glucosamine group is useful for the skin, cancer prevention and other diseases. The naturalness of the drug guarantees high-quality absorption by the body and a more pronounced therapeutic effect. It is now possible to replenish the level of glucosamine necessary for proper joint function. The Japanese managed to prove through numerous tests and studies that with the use of the dietary supplement Glucosamine, joint diseases not only stop progressing, but their qualitative regression is observed .
What is Glucosamine Chondroitin?
What diseases does Glucosamine Chondroitin help with?
Forum of the online sports nutrition store www.5lb.ru.
Glucosamine-Chondroitin-Collagen (Everything for ligaments) Experience and myths!
Glucosamine-Chondroitin-Collagen (Everything for ligaments) Experience and myths!
Amarok » 26 Nov 2013, 14:19
How do the substances differ and what is more effective?
The decision about what is more effective in each specific case is made by the doctor, taking into account the degree of the destructive process occurring in the cartilage itself, concomitant diseases, age and condition of the patient. Since glucosamine and chondroitin are different substances, they cannot be different, although the difference is insignificant. Both substances are synthesized by the cells of the body, have many common characteristics, and are interchangeable. Used as food additives, they are often mixed to complement each other. Designed to alleviate arthritis and relieve pain symptoms. At the same time, glucosamine differs from chondroitin in that it performs a function that the other cannot perform.
Osteoarthritis develops faster if the body is deficient in chondroitin sulfate.
Chondroitin is usually found in chondroitin sulfate, which is present in human tissue. It is considered an important component of bone tissue and cartilage. Loss of chondroitin sulfate leads to the progression of osteoarthritis. Glucosamine has many similarities with chondroitin. It is part of cartilage as an important component, slowing down the processes of its destruction.
What is the difference between chondroitin and glucosamine?
Chondroitin is an organic compound produced by the cartilage tissue of joints. It is an integral component of healthy synovial fluid. The main component of chondroitin is the polysaccharide glucosamine.
Chondroitin enhances the synthesis of hyaluronic acid, thereby strengthening cartilage and other connective tissue structures. It blocks the action of enzymes that destroy joint tissue. Under its influence, cathepsin, elastase, peptidase, interleukin-1 and some other aggressive substances that are formed during the breakdown of chondrocytes lose their destructive ability.
By correctly using chondroitin and understanding what it is needed for, you can reduce pain in the affected joints when walking. And during the rest period, it improves the shock-absorbing properties of cartilage tissue and enhances its regeneration. The participation of chondroitin in the process of sulfur fixation during the synthesis of chondroitin-sulfuric acid ensures improved calcium deposition in bone tissue.
An important feature of chondroitin, compared to glucosamine, is its ability to retain water inside cartilage.
The resulting “water cushions” create excellent shock absorption and perfectly absorb shock, increasing the density of connective tissue.
By the way, in a separate publication on our website the question of whether glucosamine hydrochloride or sulfate is better, the therapeutic properties of which vary somewhat.
The tandem of glucosamine and chondroitin (what it is is described in detail in another article) is widely used for the treatment and prevention of joint disease.
They have an analgesic effect, so their use reduces pain, and this is an opportunity to improve the quality of life of people suffering from chronic diseases of the spine or joints.
The significant difference between chondroitin and glucosamine is that the first is more effective when applied externally (ointments, creams, gels), and the second when taken orally.
Regardless of the form in which glucosamine chondroitin enters the body, like its analogues, serves as an additional substance for the formation of a healthy cartilage matrix and enhances the synthesis of proteoglycans, hyaluron and collagen .
Glucosamine is indicated for use not only to eliminate pathological processes in various connective tissues, but with its help you can speed up the process of restoration of damaged tendons.
Cosmetology is another area of application of chondroitin and glucosamine . Here they belong to the conventional group of enteral cosmetic preparations. Dermatologists also came to the conclusion that the use of these drugs helps to enhance the production of collagen and elastin, which allows you to restore elasticity and youth to the skin without the intervention of plastic surgeons.
Both products are safe and have no side effects on the body . They are easily digestible and do not cause allergies. Glucosamine and chondroitin can be used either separately or in combination with other drugs. You can purchase Japanese Glucosamine in our online store.
Can Glucosamine Chondroitin be harmful?
Source glukozamin.ru
Destructive processes in cartilage and joints occur due to a lack of substances chondroitin and glucosamine, which are produced by the cells of the body. Therefore, together both elements are an integral part of many chondoprotective drugs.
Natural glucosamine and chondroitin are found in synovial interarticular fluid. It is a natural component of cartilage and is involved in the formation of joint lubrication and shock-absorbing tissue.
To replenish substances, doctors recommend taking chondroprotectors.
What are chondroitin and glucosamine?
Chondroitin in its natural form is a combination of 2 tissues - cartilage and bone.
Produced by the body, it participates in biochemical processes, which ensures bone strength and restoration of cartilage and joints. Prevents exacerbations of rheumatism and arthrosis.
Natural glucosamine is synthesized from glucose and amino acids by cartilage cells - chondrocytes. It is a modified sugar and is involved in the formation of collagen.
If the body produces insufficient quantities of these components, the deficiency is compensated for by special drugs - chondroprotectors, which are used to reduce joint pain. The need to use analgesics may no longer be necessary. The body's tolerance is good, adverse reactions are rare.
Effect on joints
One of the important components of cartilage is chondroitins, which are involved in maintaining the shape of connective tissue and performing a shock-absorbing function. They are part of the walls of blood vessels, supporting the normal process of blood circulation.
As a result of severe degenerative processes in the joints or stressful situations, the synthesis of glucosamine by chondrocytes stops and cartilage tissue begins to break down. Normally, this component is produced in sufficient quantities to keep cartilage healthy.
The difference between chondoprotectors and other drugs intended for joints is their neutral effect in advanced forms of joint diseases and effectiveness at the beginning of the development of the disease.
Chondroprotectors are secondary and are used in the treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system:
- osteochondrosis;
- osteoarthritis;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- periarthritis;
- inflammation of the spinal column and joints.
For preventive purposes, drugs are used to mitigate:
- pathological manifestations of age-related changes in joints and spine;
- postoperative period;
- complications from excessive physical exertion.
How do the substances differ and what is more effective?
The decision about what is more effective in each specific case is made by the doctor, taking into account the degree of the destructive process occurring in the cartilage itself, concomitant diseases, age and condition of the patient. Since glucosamine and chondroitin are different substances, they cannot be different, although the difference is insignificant.
Both substances are synthesized by the cells of the body, have many common characteristics, and are interchangeable. Used as food additives, they are often mixed to complement each other. Designed to alleviate arthritis and relieve pain symptoms.
At the same time, glucosamine differs from chondroitin in that it performs a function that the other cannot perform.
Osteoarthritis develops faster if the body is deficient in chondroitin sulfate.
Chondroitin is usually found in chondroitin sulfate, which is present in human tissue. It is considered an important component of bone tissue and cartilage. Loss of chondroitin sulfate leads to the progression of osteoarthritis. Glucosamine has many similarities with chondroitin. It is part of cartilage as an important component, slowing down the processes of its destruction.
A complex of drugs for the treatment of joints
Chondroitin and glucosamine correct metabolic processes, enhancing each other's effects. It is this property that is used during the creation of complex-action drugs. They are 3rd generation chondoprotectors that have proven themselves in the treatment of joint diseases. The following tools are popular:
- "Artron Triactive". In addition to the main components, it contains a sulfur compound that enhances anti-inflammatory properties.
- Movex Active. Includes diclofenac, which relieves inflammation and pain symptoms.
- "Teraflex Advance". Contains ibuprofen, which provides pain relief and relieves fever.
Glucosamine and chondroitin preparations
Glucosamine-containing drugs include:
- "Elbona" is administered intramuscularly.
- “Dona” is a powder and capsules for oral use, as well as a solution for intramuscular injection.
Preparations containing chondroitin sulfate:
- "Chondrolone" - contained in ampoules, administered intramuscularly.
- "Chondroitin AKOS" - capsules intended for oral administration and ointment.
- "Structum" - also available in capsules.
Complex preparations that include both substances are also “Arthra” and “Teraflex”.
In cases where the pain syndrome is severe, drugs that are injected into the joint cavity may be recommended.
Also used are products that replace joint fluid and improve the nutrition of cartilage tissue, for example, Duralan, Ostenil, Synvisk. But they are not suitable for everyone due to the high price.
Source etosustav.ru
Chondroprotectors such as glucosamine and chondroitin are prescribed by doctors for age-related joint deformation and other pathological abnormalities that cannot be avoided even by leading a correct lifestyle.
Over the years, joint tissue wears out, cartilage is broken down by enzymes, and shock-absorbing abilities are lost. That is why it is necessary to choose the best product that will help maintain healthy joints.
What are chondroitin and glucosamine?
In composition, both of these substances are monosaccharides. Chondroitin sulfate is an obligatory and irreplaceable component of cartilage tissue, produced by it independently.
In addition, it is also contained in the synovial fluid, which fills the cavity of the joint capsule.
Glucosamine is an important building component of chondroitin and joint fluid, without which there is an acute deficiency of chondroitin sulfate in cartilage tissue, resulting in crunching and pain in the joints.
What properties do these substances have?
Chondroitin, due to its viscous structure, retains water in cartilage, improves its elasticity and flexibility, relieves pain and improves the strength of cartilage tissue. In addition, chondroitin has the following functions:
- Protects cartilage tissue from the negative effects of substances that destroy it.
- Improves tissue absorption of nutrients.
- Helps synthesize collagen, building proteins and other elements of cartilage and bone tissue.
- Maintains the required level of synovial fluid in the joint.
Glucosamine reduces joint pain.
Glucosamine stimulates the synthesis of hyaluronic acid, accelerates the regeneration of joint tissues and reduces pain. In addition, thanks to it, degenerative processes in cartilage are slowed down and the risk of joint diseases is reduced.
It has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect and, like chondroitin, helps restore joint mobility and strength. Together they form a powerful tool that maintains the human articular system in normal condition.
What is better and what is the difference?
These substances do not show significant differences in their effects on the body. They are identical in structure, and the only difference is that glucosamine is an element in chondroitin and is considered an essential component that complements it.
Glucosamine is absorbed better thanks to chondroitin sulfates, and the former becomes a necessary component for the protection and restoration of cartilage tissue.
Due to their compatibility, most drugs from the group of chondroprotectors consist only of these 2 compounds, or they are included in the drug as additional auxiliary elements.
What is more effective: glucosamine or chondroitin?
Among all drugs, chondroitin and glucosamine occupy an uncertain position. To maintain the health of the joint system and the body as a whole, doctors recommend taking these medications to athletes and older people.
But most studies do not prove their effectiveness in serious diseases such as arthrosis, osteoarthritis, osteochondrosis and osteoarthrosis.
They do not cause harm to the body, but also do not have healing properties, so doctors tend to replace them with other drugs.
Often the effect is not noticeable immediately, but after several months after administration, up to six months.
Complex use
Chondroitin and glucosamine combine well and work together.
Therefore, most chondroprotectors presented in pharmacies are complexes, the main active ingredients of which are precisely these 2 drugs with a small amount of auxiliary elements.
Their effectiveness when taken separately can be several times higher, only in isolated cases, and depends on the individual characteristics of the people’s body.
Contraindications and side effects
These chondroprotectors are not capable of harming the body and rarely cause serious consequences. But doctors do not advise taking them to people who have had allergic reactions to other drugs with similar effects.
It is not advisable for pregnant and nursing mothers to use chondroprotectors due to the unstudied effect of the substances on the child. It is also contraindicated for people with diseases of the excretory system (liver or kidneys).
Side effects are rare, but they do happen. These include the following conditions:
Sometimes after taking the drug a person may experience flatulence.
- worsening insulin resistance;
- vomiting, diarrhea, nausea;
- constipation;
- bloating;
- flatulence;
- toxic hepatitis (very rare);
- arrhythmias;
- dizziness.
List of drugs containing chondroitin and glucosamine
The range of chondroprotectors presented in pharmacies includes drugs of different price segments, but in this case, more expensive does not mean better or more effective, so when choosing, you should rely not on price, but on the doctor’s recommendations. In addition, they differ in the dosage of substances and composition.
Positive reviews from doctors were received by the drug “Chondroxid”, “Arthra”, “CONDROnova”, the special complex “Optimum Nutrition” developed for athletes, “Doppelherz Active Chondroitin + Glucosamine”, “Teraflex” and “Teraflex Advance”.
Despite the contradictions, chondroprotectors cannot be considered a useless remedy, because when combining dietary supplements with physical activity and proper nutrition, they help slow down the development of diseases.
Source osteokeen.ru
Source: https://osteohondrozgala.ru/chem-otlichaetsja-hondroitin-ot-gljukozamina/
A complex of drugs for the treatment of joints
Chondroitin and glucosamine correct metabolic processes, enhancing each other's effects. It is this property that is used during the creation of complex-action drugs. They are 3rd generation chondoprotectors that have proven themselves in the treatment of joint diseases. The following tools are popular:
- "Artron Triactive". In addition to the main components, it contains a sulfur compound that enhances anti-inflammatory properties.
- Movex Active. Includes diclofenac, which relieves inflammation and pain symptoms.
- "Teraflex Advance". Contains ibuprofen, which provides pain relief and relieves fever.
Return to contents
Glucosamine and chondroitin preparations
Glucosamine-containing drugs include:
- "Elbona" is administered intramuscularly.
- “Dona” is a powder and capsules for oral use, as well as a solution for intramuscular injection.
Preparations containing chondroitin sulfate:
- "Chondrolone" - contained in ampoules, administered intramuscularly.
- "Chondroitin AKOS" - capsules intended for oral administration and ointment.
- "Structum" - also available in capsules.
Complex preparations that include both substances are also “Arthra” and “Teraflex”. In cases where the pain syndrome is severe, drugs that are injected into the joint cavity may be recommended. Also used are products that replace joint fluid and improve the nutrition of cartilage tissue, for example, Duralan, Ostenil, Synvisk. But they are not suitable for everyone due to the high price.
Source etosustav.ru
For the therapeutic correction of joint pathologies and their prevention, chondroprotective drugs are prescribed, the basis of which is glucosamine and chondroitin. To understand how they are useful for the musculoskeletal system, you need to understand their pharmacological properties.

Description and composition of chondroprotectors
Attempts were once made to provide evidence of the ineffectiveness of chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine through a systematic review of all clinical trials with drugs in this group from 1980 to 2002. This review found that they do not act as chondroprotectors and do not repair damaged cartilage tissue. However, they have been noted to have analgesic effects that are comparable to those of pain medications used for osteoarthritis.
In other words, the ineffectiveness was justified by the fact that the chondroprotective molecules are too large and do not pass through the intestinal channels, which are very tiny.

Side effects of drugs
As a rule, side effects in chondroprotectors are limited to a few points. These include:
- diarrhea;
- allergic reactions;
- gastrointestinal disorders;
- headache.
But in fact, there are quite a lot of side effects from them, it’s just not profitable for manufacturers to indicate all the points, especially since most of these groups of drugs are sold as dietary supplements and only a few of them have the status of a medicine. There are reports of people who have had chronic liver disease after taking these drugs. In addition, their intake had a bad effect on general well-being and health, bilirubin and amylase increased.
Moreover, chondroprotectors are often used by professional athletes whose activities involve increased physical activity - weightlifters, bodybuilders and powerlifters. Due to the fact that most of them use a number of pharmacological drugs, taking chondroprotectors increases the toxic effect on the liver. In general, several negative side effects from taking the drug can be identified:
- toxic effects on the liver;
- factor of the purity of the drug, which affects the occurrence of allergic reactions;
- influence on blood pressure.
A poorly purified drug usually causes allergic reactions. Glucosamine is obtained from the remains of the shells of crustaceans and various mollusks. In Russia, this substance can be made from the remains of Kamchatka crab. It is very difficult to completely purify this raw material and some impurities will certainly remain. However, it all depends on how responsibly the manufacturer approaches the production of raw materials. If a person has allergic reactions to seafood products, then it is better for him to avoid using these drugs.
Therefore, when purchasing it, you need to focus on the brand of the drug itself, its source, that is, what it was made from. This information may be contained in manufacturer certificates. It is also worth noting that there are nuances with the production of glucosamine hydrochloride. It is produced from corn seeds, and the purification technology is somewhat different. Accordingly, there will be fewer allergic reactions in people with intolerance to animal products.
Oddly enough, the use of chondroprotectors, in particular glucosamine sulfate, is not recommended for older people, as they often suffer from high blood pressure and take various diuretics.
The thing is that the production of glucosamine sulfate requires its stabilization with the help of a number of substances, including table salt. As a result, when taking one and a half grams of glucosamine, approximately 400 mg of table salt enters the body in parallel, which, in general, is the daily norm for older people.
For hypertensive patients, this is a very important point, since they usually monitor their salt intake, and, as a rule, they have little of it in their diet. Increased salt intake leads to sharp increases in blood pressure. Often, a person taking glucosamine and watching the amount of salt in their diet may still experience an increase in blood pressure. It is the salt content in these drugs that causes hypertension.
Efficiency of intra-articular injection
Despite the low effectiveness of oral administration of chondroprotectors, they still have beneficial properties for cartilage tissue. There have been many in vitro studies done with substances such as glucosamine sulfate and chondroitin. With their help, in vitro, they acted directly on cartilage cells. As a result, it was found that cartilage cells respond very well to the introduction of these substances in fairly high doses.
But the interesting thing is that these methods cannot be reproduced in real life, since in large doses chondroitin and glucosamine cannot be absorbed through the intestinal walls, much less get to the right place. All experiments that were successful and showed good results involved the use of high doses of these substances, sometimes even 1000 times higher than normal.
But there are some types of chondroprotectors, usually prescribed by the attending physician, which are injected directly into the articular capsule of the damaged joint. Typically, ampoules with a mixture of high contents of chondroitin sulfate, glucosamine and hyaluronic acid are used for injections. Such procedures often give good results; they are not done in a clinic with the participation of a doctor.
Main types of glucosamine
There are two main types of glucosamine, which differ in their effectiveness. Usually a person is faced with a choice between taking drugs such as glucosamine hydrochloride or sulfate.
What works best and what doesn't can be determined in part by the price of the drug. Hydrochloride is cheaper, but it also works worse. Glucosamine has the most useful and effective effect, its properties are as follows:
- stimulates the formation of cartilage cells;
- prevents the destruction of cartilage structures;
- relieves the inflammatory process.
It is worth noting that the effect of glucosamine will appear only after several months of use. There is no point in expecting results after several weeks of using it.
Sources and properties of glucosamine
It is important to know! Doctors are shocked: “An effective and affordable remedy for joint pain exists. " Read more.
There are several sources for obtaining this substance. Depending on the specific source, the different forms of glucosamine, listed below, are named.
Glucosamine of animal origin
Glucosamine hydrochloride or glucosamine sulfate is obtained from raw materials of animal origin. They are made from the shells of crabs, shrimp, crayfish, lobsters, and lobsters . Glucosamine hydrochloride is a common and available form of the substance. However, it may contain admixtures of allergenic substances. Therefore, glucosamine supplements made from animal sources should not be taken by people with seafood allergies.

Glucosamine sulfate is less stable and therefore requires stabilization with potassium or sodium chloride during production. These supplements are safe, but if you consume sodium chloride-stabilized sulfate, you should adjust your diet and reduce your intake of salty foods.
N-acetylglucosamine can be found somewhat less frequently in mono- and complex chondroprotective drugs. It is also obtained from crustaceans. The substance has good bioavailability and has a positive effect on the musculoskeletal system, the structure of blood vessels, skin and mucous membranes.
Plant-derived glucosamine
Glucosamine hydrochloride is also obtained from plant materials. The source of the active substance is corn husks, which are ground and fermented . The production technique allows us to obtain highly purified glucosamine hydrochloride, which cannot cause hypersensitivity reactions. This form of the substance is considered the best, but is more expensive.
First, let's figure out what collagen is.
Collagen is a protein (amino acids) that forms part of connective tissue and is found in hair, skin, joints, muscles, veins and various organs. More than 30% of our body's protein consists of it. Collagen is like a glue that holds tissues together and helps them withstand stress.
Where is collagen found?
Eggs, chicken, bone broth, dairy. Our body produces collagen using certain amino acids, vitamins A, C and copper. After 25-30, collagen synthesis decreases by 1% per year. Our body begins to heal wounds more slowly, joint pain appears more often and bone fractures occur.
Collagen supplements.
It seems logical to solve the problem, we just need to buy ourselves a collagen supplement and the problem seems to be solved, but not everything is so simple. Collagen, like all proteins, consists of amino acids. When you consume collagen powder, it is broken down into these same amino acids by enzymes in the stomach. And then a process begins that we cannot control. When we eat pizza, burgers and cake, we can't tell our body where to store fat, just like we can't tell it how to use amino acids. The amino acids produced by digesting collagen (or any other protein you eat) are distributed throughout the body based on which area needs them most. Since our main and priority organs for maintenance are the heart and brain, which also use collagen to function, it is likely that they will take up most of the amino acids.
Properties of preparations containing glucosamine
Glucosamine is included in both single preparations and complexes (usually in combination with chondroitin). The list of medications containing exclusively glucosamine as an active ingredient includes:

Forms of production of products containing glucosamine:
- injection solution;
- pills;
- powder for preparing a solution for internal use.
The active substance has the following range of effects:
- replenishment of the lack of endogenous glucosamine;
- stimulation of hyaluronic acid biosynthesis processes;
- normalization of metabolic reactions in cartilage tissue cells;
- acceleration of calcification reactions of bone structures of the joint.
Glucosamine inhibits degeneration processes and accelerates regenerative reactions in the cartilage tissue of joints.
Properties of drugs containing chondroitin
Chondroitin sulfate will be included in monopreparations and complex supplements. Among the monopreparations there are:
- Chondroflex;
- Mucosat;
- Artron Hondrex;
- Artiflex Chondro;
- Structum.
Forms of release of medicines containing the active substance:
The spectrum of biological effects of chondroitin sulfate can include:
- stimulation of the biosynthesis of hyaluronic acid and proteoglycans;
- inhibition of degeneration in the cartilage matrix;
- correction of manifestations of the inflammatory process in the joint.
Complex drugs
Glucosamine or chondroitin: which is better? Preferred are complex preparations that contain both active components:
- Artra;
- Teraflex;
- Teraflex Advance (also contains ibuprofen);
- Doppelhertz Active Glucosamine + Chondroitin;
- Kondronov;
- Inoltra (additionally includes vitamins E and C, manganese, omega-3 fatty acids);
- Glucosamine-Chondroitin Plus;
- Glucosamine-chondroitin complex.

The listed medications differ in the content of active ingredients, place of production, and price. The choice of a specific complex depends on the required dosage and the preferred cost level. Before visiting a pharmacy, it is better to consult a doctor.
Recommendations for dosing of bioactive substances
Before starting to take medications that contain glucosamine, chondroitin, or both substances together, you should consult with a specialist about the most appropriate dosage regimen, which depends on the individual characteristics of the clinical case.
Dr. Jason Theodosakis suggested prescribing drugs with chondroitin and glucosamine based on the patient’s body weight:
| Body mass | Recommended dosage (per day) |
| less than 55 kg | 800 mg chondroitin, 1000 mg glucosamine |
| 55-90 kg | 1200 mg chondroitin, 1500 mg glucosamine |
| more than 90 kg | 1600 mg chondroitin, 2000 mg glucosamine |
Even “advanced” joint problems can be cured at home! Just remember to apply this once a day.
These recommendations are based on research conducted by this specialist. The daily dose can be divided into 2 or 3 doses. The drugs should be taken orally with food.
The duration of the course of taking chondroprotective drugs should not be less than 3 months. Doctors advise that after 3-4 months of taking it, take a break for 2-2.5 months, then resume the course.
In order for the course use of chondroprotectors to be as effective as possible, you should eat properly, drink a sufficient amount of fluid, not overload the body as a whole and the musculoskeletal system in particular, but exercise regularly in a gentle manner.
Preparations with chondroitin and glucosamine should not be taken in case of hypersensitivity to the components, with a tendency to bleeding, with thrombophlebitis, impaired renal function and phenylketonuria.
Patient reviews
Elena, 35 years old, Podolsk: “I took collagen from Neocell for 3 months. The supplement did not disappoint. The back pain went away, the cramps in my legs stopped, and the wrinkles became less deep.”
Anna, 40 years old, Voronezh: “After taking hormonal medications, my knee began to hurt. It turned out that the cartilage was thinning. The treatment did not help, and the doctor prescribed the dietary supplement glucosamine with chondroitin. I took the product for a month. Attacks of pain began to occur less frequently, and there were no side effects. Another advantage of the supplement is the price. The downside is that the pain returns when the course is stopped.”
What do clinical studies say?
Numerous studies have been conducted to confirm the effectiveness of various chondroprotective drugs in the correction and prevention of pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. The results of some of them will be reviewed below.
The drug Artra in the treatment of osteochondrosis and intervertebral osteochondrosis
Author - V.V. Badokin, publication 2012, journal “Neurology, neuropsychiatry, psychosomatics” . The work examines the results of a number of clinical trials confirming the effectiveness of this complex remedy for restoring the functionality of joints, inhibiting degenerative processes, preventing pathologies of the musculoskeletal system and improving the quality of life of patients in general.
Conclusions from the analysis of the results of using the drug Artra:
- the drug is an effective, slow-acting symptom-modifying medication;
- confirmed analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects;
- taking the complex improves the functionality of the joints;
- safety and good tolerability;
- taking the Artra complex creates the opportunity to reduce the daily dosage of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
To confirm the structure-modifying properties of the drug, further long-term studies are required with analysis of the results of radiography, magnetic resonance imaging, sonography, and laboratory tests.
The effectiveness of Theraflex in patients not taking NSAIDs
The authors of the work are I. Z. Gaidukova, I. A. Romanova, A. P. Rebrov. The results were published in the journal Modern Rheumatology, 2015.
The work examines and analyzes data from a clinical study that involved 84 patients diagnosed with arthrosis of the knee joint, aged from 47 to 62 years, with a disease duration of 5 to 7 years, among whom there were 78 women and 6 men. Patients were randomized blindly into two groups. Patients from the main group received Teraflex with/without acetaminophen, patients from the comparison group received only acetaminophen. At the beginning of the study, and then after 3 months and six months, the severity of arthrosis was assessed using various indices and an analogue scale. The occurrence of adverse reactions was taken into account.
The study allowed us to draw the following conclusions:
- patients who took Theraflex for six months experienced a decrease in Lequesne and WOMAC indices, relief of pain, and a decrease in the need for analgesics;
- While taking Theraflex, no adverse reactions occurred, including among patients who had diagnosed diseases of the kidneys, digestive system, and hypertension.
Dynamics of antioxidant protection against the background of glucosamine and chondroitin
Authors of the work: E. S. Elovikova, O. V. Bugrova, V. G. Leizerman, S. I. Krasikov. The results of the study were published in the Kazan Medical Journal in 2009.
The dynamics of antioxidant protection was assessed in 34 patients while taking glucosamine hydrochloride and chondroitin sulfate. It was found that the use of these substances normalizes the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as catalase and superoxide dismutase.
Evaluation of the effectiveness and safety of simultaneous use of the drugs Artradol and Artracam
Authors of the work: S. A. Lapshina, M. A. Afanasyeva, E. V. Sukhorukova, I. F. Akhtyamov, L. I. Myasoutova. The test results were published in the journal “Bulletin of Modern Clinical Medicine” in 2021.
A study was carried out on 30 patients diagnosed with osteoarthritis of the knee joints with intense pain. The age of the patients ranged from 53 to 63 years, the duration of the pathology was from 3 to 9 years. The drugs Artradol (active component - chondroitin sulfate) and Artracam (active component - glucosamine sulfate) were prescribed in addition to the course of therapy with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The effectiveness of treatment was assessed after 1 and 2 months of treatment using the WOMAC index, pain intensity, need for NSAIDs and a number of other indicators.
The following conclusions were drawn:
- while taking Artradol and Artracam, a significant decrease in the intensity of pain was observed;
- a decrease in the WOMAC index was recorded;
- the time to travel a distance of 15 meters has decreased;
- the need for non-steroidal drugs has decreased.
Patients and doctors rated the effectiveness of therapeutic correction as “good” or “satisfactory.” The study confirmed the effectiveness of the combination of Artradol and Artracam in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee joint.
Thus, clinical trials confirm that substances such as glucosamine and chondroitin have a positive effect when necessary in the treatment of various joint pathologies. Only a qualified doctor can select a combination of drugs and their dosage. It is recommended to combine the use of chondroprotective agents with proper nutrition and moderate physical activity, then the effectiveness of treatment and prevention of diseases of the musculoskeletal system will be maximum.
Comparison of glucosamine sulfate, glucosamine hydrochloride and N-acetylglucosamine - which is better?
Glucosamine is one of the important components of articular cartilage, synovial (intra-articular) fluid, heart valves and other types of connective tissue. Externally obtained glucosamine stimulates joint renewal, which has given rise to its widespread use as a supportive supplement for osteoarthritis.
Three types of glucosamine are used in medicines and dietary supplements:
- N-acetylglucosamine (n-acetylglucosamine);
- Glucosamine sulfate;
- Glucosamine hydrochloride.
N-acetylglucosamine is a component of many natural polymers, including the well-known hyaluronic acid, so this form of glucosamine is most often used in the production of cosmetics.
It is less known as a component of dietary supplements for maintaining healthy joints.
Nevertheless, research in this direction has been ongoing for a long time (the first patent for the use of this substance in joint pathology was issued in 1968).
“Glucosamine sulfate and glucosamine hydrochloride are most often used for the production of drugs and dietary supplements”
Glucosamine sulfate and glucosamine hydrochloride are much better known. However, quite often the description of the properties of glucosamine-based drugs does not mention which particular form was used. However, differences between these compounds may significantly influence their therapeutic efficacy.
Acetylglucosamine, glucosamine sulfate and glucosamine hydrochloride - chemical properties
Glucosamine sulfate is a compound of glucosamine and a sulfuric acid salt residue. Such a substance is unstable under normal conditions: it absorbs water from the air and quickly oxidizes.
Therefore, to stabilize it, sodium chloride (table salt) or potassium chloride is added, with which glucosamine sulfate forms complex salts that are more chemically stable.
The finished glucosamine sulfate preparation contains from 13 to 24% sodium chloride, which should be taken into account by those suffering from hypertension and other diseases that require limiting salt intake.
Glucosamine hydrochloride is a compound of glucosamine and a hydrochloric acid salt residue. Unlike the analogue discussed above, it is stable in the external environment. Therefore, at equal concentrations, the effectiveness of glucosamine hydrochloride compared to sulfate is higher.
N-acetylglucosamine is a compound of glucosamine, a nitrogenous base and a salt of acetic acid. The substance is stable in the external environment: insoluble in water, soluble in concentrated organic and inorganic acids, does not require stabilization. But such high stability also reduces the health-promoting effects of this substance.
Digestibility by the human body
All three compounds are capable of penetrating into the bloodstream when taken orally. Absorbed in the intestines, they enter the liver through the portal vein system, from where they pass into the blood. In the blood they join globulin proteins, with which they spread throughout the body.
Considering that a compound such as glucosamine hydrochloride does not require stabilization and is used almost in its pure form, some scientists believe that it is better to use glucosamine hydrochloride in therapy than glucosamine sulfate.
Beth Anne Fox from the University of Tennessee states (2007, Google translation) that 1500 mg of glucosamine hydrochloride is equivalent to 2608 mg of glucosamine sulfate.
But the effectiveness of any product depends not only on its concentration and dose, but also on how well it penetrates the blood (bioavailability).
"Due to impurities, 2608 mg of glucosamine sulfate is equivalent to 1500 mg of glucosamine hydrochloride"
In 2004, American scientist Stephen Owens spoke (google translate) about the high bioavailability of all forms of glucosamine - up to 90% . The same study notes a high (up to 70%) absorption of chondroitin into the blood, which is often used in combination with the substances in question.
However, most other works do not confirm such outstanding results. The bioavailability indicators in animal experiments turned out to be quite modest: the maximum obtained in experiments on rats was 21% (A. Aghazadeh-Habashi, 2002, pdf, English).
Also, a group of Canadian scientists led by M. Molizer in 2008 conducted (pdf) a comparison of the bioavailability of various forms of glucosamine in horses. They examined the concentration of the substance in the blood plasma and synovial fluid of the wrist joint after oral administration of the drugs. A dosage of 20 mg/kg body weight was used.
Blood samples were taken at 5, 15, 30, 60, 120, 360, 480 and 720 minutes after administration. Bioavailability (the amount of unchanged substance in the blood) of glucosamine sulfate was 9.4%, glucosamine hydrochloride – 6.1%.
Approximately the same difference in concentration was observed in the synovial (intra-articular) fluid 1, 6 and 12 hours after administration.
Shortly before this, the results of a comparative analysis (S. Persiani, 2007, pdf, English) of the bioavailability of glucosamine hydrochloride and glucosamine sulfate in the human body were published.
Healthy volunteers took either glucosamine sulfate or glucosamine hydrochloride. In this experiment, the peak concentration of glucosamine hydrochloride in the blood was half the peak concentration of glucosamine sulfate (see.
graph), which indicates its lower bioavailability.
“50% more glucosamine sulfate is absorbed into the blood than glucosamine hydrochloride”
A comparison of the metabolism of N-acetylglucosamine and glucosamine hydrochloride was conducted in the doctoral dissertation (pdf) of Jerry Capps of the University of Oklahoma. The researcher found no difference between the absorption of these two substances. In addition, it turned out that part of glucosamine sulfate is decomposed by intestinal microflora and does not enter the blood.
Summarizing the information obtained, we can conclude: despite the “purer” composition of glucosamine hydrochloride, its bioavailability is lower than that of sulfate, which reduces the overall therapeutic effectiveness of this substance .