People who calculate diets suspiciously often forget about basal metabolism. According to their formulas, a person spends calories only when he runs, jumps or lifts weights. It turns out that paralyzed people don’t need to eat at all - they don’t move!
Such “experts” treat a living organism like a car: if there is a trip ahead, we fill it with gasoline; the car is parked in the garage - no gasoline required! No, my friends, a living organism is not a machine, and the lion’s share of all calories eaten comes from this very basal (or main) metabolism!
Friends, read the article further, there will be a lot of interesting things in it! And for those who want: “Find out the degree of slagging in your body” or “Find out what’s stopping you from losing weight?” Take Selection TEST
Hello friends! Svetlana Morozova is with you. Today we will look at the very basis of life of any living organism: what is basal or basic metabolism and why it should never be forgotten.
Calculation methods
Accurate calculation of basal metabolic rate requires that the human sympathetic nervous system is not stimulated. It can be measured by gas analysis using direct or indirect calorimetry.
You can also calculate your basal metabolic rate using an equation using age, gender, height, and weight. Studies using both methods provide evidence for the validity of the respiratory quotient, which measures the inherent composition and utilization of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins as they are converted into energy substrate units.
How to change your basal metabolic rate?
A combination of factors determines your basal metabolic rate.
Genetic factors, age, gender and body composition play a role. There is little you can do to control genetics, age or gender. But you can change your body composition to boost your metabolism. So how do you change your BMR? Build muscles! Even when your body is at rest, muscle mass burns more calories than fat. And you don't even have to be a bodybuilder to see the benefits. Several studies have shown that after just a few weeks of resistance training, you can see a 7-8% increase in resting metabolic rate.
Phenotypic flexibility
Basal metabolism is a flexible trait. It can be reversibly corrected within the body. For example, lower temperatures, which usually leads to higher metabolic rates. There are two models that explain how basal metabolism changes with temperature: the variable maximum model (VMM) and the variable fractional model (VFM).
PMM states that metabolic rate increases during the cold season. PFM says that the level of basal metabolism is a constant value.
How to calculate basal metabolic rate
If you do not take into account what kind of life a person leads, how physically active he is and how much food he eats, then we can talk about calculating basal metabolism. Basic metabolism or basal metabolism is the amount of energy required by the human body to maintain its own life at rest (this energy is spent on breathing, blood circulation and digestion of food). The indicator is determined by the amount of heat per unit of human body mass per day.
The basal metabolic rate is determined using measurements taken in a special breathing chamber based on the respiratory coefficient. These measurements are carried out during the period of least physical activity of a person - in the morning, at rest, on an empty stomach in conditions of temperature comfort. To quickly and easily calculate your basal metabolic rate, use our online calculator.
Research
Early work by scientists J. Arthur Harris and Francis G. Benedict showed that approximate metabolic rates could be obtained using body surface area (calculated from height and weight), age, and sex. In this case, oxygen and carbon dioxide indicators taken from calorimetry are taken into account.
By eliminating sex differences that arise in the accumulation of adipose tissue by expressing metabolic rate per unit of “fat-free” body mass, the meaning of basal metabolic rate (BMR) calculations between sexes is essentially the same.
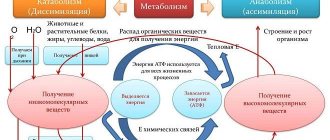
What is metabolism and UBM?
The transformation of substances or metabolism is a combination of all biochemical changes in living organisms and cells. The main purpose of metabolism is to convert food into energy necessary for the functioning of cellular processes. This also includes the processing of food into the building blocks of proteins, fats , some carbohydrates and the elimination of nitrogen waste. [13]
Metabolism in living organisms is divided into primary and secondary:
- primary metabolism includes the basic chemical processes on which the life and growth of the organism directly depends. This includes the metabolism of sugars, fats, amino acids and nucleic acids.
- Secondary metabolism includes chemical processes in certain groups of organisms, the production and decomposition of specific non-protein chemicals. These can be various protective elements, hormones, pigments and building molecules that are involved in maintaining skeletal health. [14]
The rate at which your metabolism processes food into energy is called metabolic rate . The minimum amount of energy that the body needs to function is called the basal metabolic rate or BMR .
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) is a formula that can be used to figure out how many calories your body needs to burn at rest to keep your body's basic vital functions healthy . In this state, energy is used only to maintain the functioning of important organs , which include the heart, lungs, kidneys, nervous system, intestines, genitals, muscles and skin. Most often, UBM is used to reduce weight . To maintain weight, you need to maintain a balance between energy intake and expenditure . Once you know your BBM, maintaining balance will be very easy. [12]
The energy your body burns during the day is called total daily energy expenditure (TDEE). This concept is divided into 3 subsections: basal metabolism, the thermic effect of food and the level of physical activity. It’s a paradox, but the most calories and energy at rest, because every organ in our body is considered a muscle. It is the muscles that need a lot of energy for their proper functioning. [14] [15]
Let's take a look at how many calories you burn during your daily energy expenditure:
- basal metabolism - in this state you burn 60-75% of total calories
- level of physical activity (movement and training) – in this state you burn 15 – 30% of calories
- the thermic effect of food (calories burned during the digestion process) is 10% of the total calories burned daily [5] [11]

Physiology
The main organ responsible for regulating metabolism is the hypothalamus. It forms part of the lateral walls of the third ventricle of the brain. The main functions of the hypothalamus:
- Control and integration of the activity of the autonomic nervous system (ANS). It regulates the contraction of the heart muscle and the secretion of many endocrine organs (thyroid gland).
- Regulating feelings of rage and aggression.
- Body temperature control.
- Regulating food intake.
The nutrition center (hunger) is responsible for the sensations that make a person look for food. With enough nutrition, leptin levels become high. The satiety center is stimulated. Impulses are sent that block the feeling of hunger. If there is not enough food, ghrelin levels increase. The hypothalamic receptors are stimulated. There is a feeling of hunger.
The thirst center works in a similar way. The increased osmotic pressure of the extracellular fluid stimulates the cells of the hypothalamus. If your thirst is satisfied, your blood pressure will drop. These functions form a survival mechanism that forces a person to maintain body processes, measured by the level of basal metabolism.

Working Methods to Increase Metabolic Rate for Weight Loss
Of course, you cannot influence metabolic rate factors such as heredity, gender, age or body type. The good news is that your basal metabolic rate is not set in stone, and you can influence it by making some adjustments to your lifestyle. Do you want to avoid a metabolic crisis and improve your metabolism? Then follow these tips:
Burn calories
Here are the 3 most effective ways to burn calories:
1. Aerobic exercise
One of the most effective ways to help your body burn more calories is through aerobic exercise. It is recommended to do at least 75-100 minutes of aerobic exercise such as walking, cycling or swimming per week. You can achieve this minimum by doing such exercises for just 30 minutes a day, 5 times a week.
To achieve the best results and prevent a slowdown in metabolism, leading sports experts recommend periodically changing the types of aerobic activity.
The point is that the longer you perform the same exercise (be it kettlebell swings, squats or running), the stronger your body becomes and, therefore, the less energy it requires to complete the task at hand. From a metabolic point of view, it is most beneficial to perform different types of exercise. Regular changes in physical activity will not allow your body to quickly adapt to the proposed load, so your metabolism will always remain at a high level.
But to lose weight, you'll likely need to spend a little more than 150 minutes a week, as well as make changes to your diet.

2. Strength training
At rest, muscle burns more calories than fat. Therefore, increasing your overall muscle mass will undoubtedly help you lose weight.
There is nothing more effective for building muscle than strength training. Try to spend at least 2 days a week doing exercises that target all major muscle groups (legs, hips, back, stomach, chest, shoulders and arms). In addition to standard weight training and intense strength training, gardening also has a positive effect on strengthening and building muscle mass.

3. Active lifestyle
Yes, regular exercise helps keep your metabolic rate normal. However, if after training you just lie on the couch or sit in front of the computer, preferring not to make unnecessary movements, then the number of calories you burn per day decreases. As a result, even your less athletic colleagues may be leaner than you. Why?
To investigate this phenomenon, scientists conducted one experiment involving 168 men and women of various ages. Following these people, it was found that, regardless of the amount of exercise they did, those who broke their sedentary position more often had a leaner body type, a lower BMI, and healthier fat and blood sugar levels than those who I preferred not to get up from my workplace once again.
And researchers from the University of Missouri (USA) found that people who did not exercise but spent little time sitting burned more calories than those who ran 50 km a week but were otherwise sedentary.
Make physical activity a healthy habit. Walk more, stop using the elevator in favor of the stairs, stretch during breaks at work, ride a bike, or just do housework.

Is it true that exercise stimulates metabolism?
When you exercise, your metabolism speeds up, and for several hours after exercise, your body experiences what is called an afterburn effect. In the sports environment, this phenomenon is called the “post-exercise EPOC effect” (from the English excess post-exercise oxygen consumption). EPOC is the process of increased post-exercise energy expenditure that occurs due to excess post-exercise oxygen consumption . The more intense your workout, the stronger the EPOC effect will be.
In one study, researchers measured athletes' metabolic rates immediately after an intense 45-minute spin class at 70 to 75% of VO2max. Then the scientists again measured the metabolic rate of the athletes, but on a rest day. It was found that after a hard workout, the athletes' metabolism remained elevated for 14 hours, and they burned 37% more calories compared to what they burned on a rest day.
Scientists also found that it is the intensity of training, and not its duration, that has a significant impact on the EPOC effect. Therefore, if you want to speed up your metabolism in order to lose weight faster, then high-intensity interval training HIIT is perfect.
A 10-minute HIIT workout that will wake up your metabolism
Do you want to speed up your metabolism and strengthen your muscles? Do this high-intensity interval training at home for just 10 minutes a day to improve your metabolism! Well, let's get started.
Perform each exercise for 40 seconds, then take a 20-second rest before moving on to the next exercise. By training with this complex 3 times a week, after 2 months you will see noticeable results.
Exercise 1: Charleston

Take the starting plank position. Lunge forward with one leg so that your foot is between your palms. Using this leg as a support, stand on it and lift the knee of the other leg up. Reverse the movement to return to the starting position and repeat the exercise, alternating sides.
Note: To make this exercise more challenging, you can jump as you lift your other leg.
Exercise 2: Eye of the Needle

Get into a plank position. Bring one leg under your body and touch it with the opposite hand, as shown in the picture. Reverse the movement to return to the starting position and repeat this movement for the other leg. Continue doing the exercises, alternating sides.
Exercise 3: Plank Squat Jumps

Standing in a plank position, push off with both feet and jump into a wide squat position (toes pointing outward). Along with this movement, place your hands as if you are ready to catch the ball. Reverse the movement and return to the starting position and repeat the exercise.
Exercise 4: Lateral push-ups

While standing in a plank position, move your right arm and right leg to the side, thereby shifting your body weight to the right. Do one push-up and return to the starting position. Repeat this exercise on the other side.
Exercise 5: Jumping from prone position

Get into a plank position, then push off with your feet and transfer your body weight to your palms, jump up and move both feet forward, as shown in the picture. Jump high with your arms stretched up. Reverse the movement and return to the starting position and repeat the exercise.
Exercise 6: Jack Jumps + Knees to Chest

Take the starting plank position. Push off with your feet, jump up and spread your legs to the sides. Then, push up again, jump up and pull your knees towards your chest. Jump back to plank position and repeat the exercise.
Exercise 7: Superman

Get into a plank position and then lie face down on the floor. Stretch your arms above your head and straighten your legs completely. Squeeze your glutes and lower back to lift your upper torso and lift your legs straight off the floor. Hold at the top for two seconds and return to plank. Repeat.
Exercise 8: Side to Side Squat Jumps

Get into a plank position. Push off with both feet and bend your knees, moving them forward and to the side so that your knees are at the back of your arms, as shown in the picture. Reverse the movement to return to the starting position and repeat the exercise on the other side. Continue jumping from side to side for 40 seconds.
Exercise 9: Walking on hands in a plank

While standing in a plank position, begin to “step” your palms back until they almost touch your feet. Return to the plank position with reverse movements and repeat the exercise.
Exercise 10: Burpees with Lunges

Get into a plank position. Raise your elbows slightly to the sides and perform one push-up. Then jump to your feet and make 2 lunges forward, alternating sides. After this, jump high, stretching your arms up. Then squat down again and, leaning on your hands, throw your legs back, taking the starting position. Repeat the exercise.
Eat well
If you want to activate your metabolism and lose excess weight, then first of all you need to think about proper nutrition. As you know, the key to successful weight loss is a calorie deficit. But too much of a calorie deficit can backfire. The thing is that due to an insufficiently nutritious diet, your body will simply have nowhere to get the energy for training. In addition, a lack of energy will prevent your body from recovering from strenuous exercise, and it will not be able to keep all of its systems functioning optimally. This leads to your body going into a “saving” mode, reducing calorie consumption and increasing their accumulation in fat depots.
Reduce your calorie intake, but don't overdo it
If you want to lose weight, then there is no escape from reducing the caloric content of your diet, because this is the key to effective weight loss. However, cutting your calories too much can do double damage to your overall health and your metabolism in particular.
When you eat less than your body needs to perform its basic functions (about 2,000 calories a day for most women and about 2,400 calories for men), your body goes into “energy-saving” mode. In this state, your body, instead of taking energy from fat tissue, begins to “feed” from your muscles, destroying muscle cells. The result of this process is a decrease in muscle mass and, as a result, a slowdown in metabolism.
"Eat an amount of food that satisfies your hunger without filling you up," says Dan Benardo, RD, assistant professor of nutrition and kinesiology at Georgia State University. "A 150-calorie snack mid-morning and mid-afternoon between meals will keep your metabolism at optimal levels."
In the sports community, this condition was even given a name: “energy deficiency in athletes.” Such a deficiency occurs as a result of the fact that the body of a person engaged in intense physical activity does not receive enough energy. A lack of energy can cause a number of negative symptoms, such as a decrease in the body's response to training, decreased strength and endurance, weight fluctuations, bad mood, etc. All this leads to a decrease in your athletic performance.
Do you want to jumpstart your metabolism and lose weight without harm to your health?
Watch your diet
Eating plenty of protein will give your body the stimulus it needs to speed up its metabolism. Protein is not only a building material for muscles, which, as you already know, activate metabolism. Research has shown that consuming protein increases metabolism by increasing the thermic effect of food.
The thermic effect of food (TEF) is an increase in metabolic rate after eating, associated with the need for additional energy expenditure for the digestive process, which includes the digestion, transportation and absorption of nutrients by the body. The thermic impact of food accounts for approximately 5-10% of your daily energy expenditure.
One study found that eating protein-rich foods increases metabolic rate by 15-30%, while metabolism increases by 5-10% after eating carbohydrates, and 0-3% after eating fat. The optimal protein content in each meal is 30 grams.
A proper diet will not only saturate your body with the necessary amount of energy, but will also speed up your metabolism. If you want to consume enough calories and continue to lose weight, then you should diversify your diet with these foods:
Foods that will jump-start your metabolism

Want to know how to boost your metabolism and lose weight without resorting to questionable nutritional supplements? Then here is a list of foods that will make your body burn calories much more efficiently.
- Almond
The beneficial fatty acids and protein that come from almonds can temporarily speed up your metabolism. 12-14 whole almonds will provide you with essential nutrients and make a great snack during the work day. Or spread natural food-grade almond butter on pieces of fruit, vegetables or whole grain toast for an even tastier, healthier option.
- Apples
It’s not for nothing that they say: “Eat an apple a day and you won’t need a doctor.” The thing is that apples are a rich source of pectin - a type of fiber that helps digestion and helps eliminate toxins from the body naturally. Apples can be added to salads, made into smoothies, or eaten whole.
- Avocado
Apart from the fact that avocado contains a lot of fiber and vitamins such as C, B3, B6, this fruit is also an excellent source of amino acids that support efficient metabolism. There are countless ways to eat avocado - soups, salads, desserts, you just have to use your imagination!
- Broccoli
Broccoli can safely be called a superfood, because it contains a lot of useful vitamins, minerals, antioxidants and dietary fiber. This versatile vegetable can be consumed in almost any form, for example, you can make a smoothie with the addition of broccoli or prepare a dietary vegetable soup from it.
- Carrot
This bright and sweet vegetable is rich in fiber, which forces your body to work during digestion, resulting in even more calories burned! Carrot salad, freshly squeezed carrot juice or steamed carrots - all this is very tasty and healthy.
- Chilli
Add chili pepper to your healthy menu as one of the seasonings. This variety of pepper is thermogenic - it causes the body to naturally produce heat, which burns even more calories.
- Coffee
If you are a notorious coffee lover, then you are incredibly lucky. Coffee helps temporarily speed up your metabolism, making it the perfect start to your work day. However, keep in mind that coffee drinks in cafes are very high in calories. Therefore, try to avoid them if you want to lose weight.
- cucumbers
In addition to containing a lot of water and virtually no calories, cucumbers are a rich source of fiber, an essential component of weight loss. This vegetable can be consumed either as part of other dishes or on its own.
- Eggs
Don't give up eggs if you want to lose weight! Thanks to their amino acid content, eggs help boost metabolism, which helps burn fat more effectively. In addition, egg yolk contains a lot of vitamin B2, or riboflavin, which plays an essential role in maintaining metabolic activity.
- Garlic
Like chili peppers, garlic is also a thermogenic food that speeds up the body's metabolism, causing it to produce more heat and thereby burn more calories. Garlic is great as a seasoning in your diet menu, just don’t overdo it, otherwise you risk ruining the dish!
- Green tea
Almost no diet can do without this drink, because green tea is rich in epigallocatechin gallate, an antioxidant that stimulates fat burning. Plus, it contains no calories, making it a great alternative to regular drinking water.
- Lemon
This sunny fruit is a natural detoxifier that helps the liver maintain good metabolism.
- Oatmeal
Oats are a storehouse of fiber, which is known to speed up metabolism. In addition, fiber helps relieve constipation and bloating. But stay away from instant oatmeal, which contains excessive amounts of sugar and artificial sweeteners per packet.
- Spinach
Like many green vegetables, spinach is known to be low in calories and high in fiber. In addition, spinach is a rich source of beneficial microelements such as iron, zinc, and vitamins K and A.
- Tuna
Tuna (and other fish such as salmon) helps the body respond better to leptin, a hormone that affects metabolic processes.
- Blueberry
Because they contain no fat, cholesterol or sodium and are a rich source of beneficial nutrients, blueberries can rightfully find a place in your diet to boost your metabolism.
- Cinnamon
One study conducted by Scandinavian scientists found that when volunteers were given rice pudding with 3 grams of cinnamon, their bodies produced less insulin than usual after eating.
Since insulin is the hormone that converts excess sugar into fat, this means that cinnamon helps prevent weight gain. In addition to lowering blood sugar levels, cinnamon can also slow down and improve the digestion process. Thanks to this property of this spice, you will feel full for much longer.
Eat more foods containing vitamin D
Vitamin D is essential for maintaining your muscle tissue. Unfortunately, researchers estimate that only 4% of people over 50 consume enough of this vitamin.
Approximately 90% of the recommended daily intake of vitamin D (about 400 IU) is found in one 4-ounce serving of salmon. This nutrient is also found in large quantities in tuna, shrimp, tofu, eggs and fortified milk.
Drink clean water
To get the best results from your workouts, drink water often. In addition to helping you prevent dehydration, purified drinking water has a positive effect on your metabolism.
Studies have shown that within an hour of drinking 0.5 liters of water, the metabolic rate increases by 24%.

Find out about your needs
To find out how much energy you need during the day, you first need to figure out how much energy you use. Of course, the best way to calculate your required daily energy needs is to go to the laboratory. However, the Harris-Benedict formula is also suitable for these purposes. This formula will help you understand how many calories you need daily to lose or maintain weight and calculate your metabolic rate.
How to determine BMR (basal metabolic rate).
- For women : BMR = 655.1 + (9.563 ×weight in kg) + (1.850 ×height in cm) - (4.676 ×age in years)
- For men : BMR = 66.5 + (13.75 × weight in kg) + (5.003 × height in cm) – (6.755 × age in years)
To correctly calculate the amount of daily caloric intake needed for weight loss, you also need to take into account your level of physical activity. Multiply your BMR by one of the following values (this ratio reflects your level of physical activity):
- 1, 2 = sedentary lifestyle
- 1, 375 = low physical activity (light physical activity or exercise 1-3 times a week)
- 1.55 = moderate physical activity (3-5 workouts per week)
- 1.725 = high activity (intense exercise, 6-7 workouts per week)
- 1.9 = extremely high activity (athletes and people performing similar activities 6-7 times a week)
If you want to lose weight, then you should subtract several hundred kilocalories per day from this amount, while maintaining your current level of physical activity.
Relax
Not all fat comes from laziness. Our body contains so-called brown adipose tissue. Brown fat is metabolically active and helps regulate our body temperature and keeps us warm when we're cold.
Research has shown that exercising at a moderate pace in a low-heat environment can significantly increase our resting metabolism.
Recent studies have shown that metabolism changes throughout the day
As a result of a study conducted at the University of Surrey (England), scientists found that our fat cells have their own circadian rhythm, that is, their functioning is controlled by the so-called. "biological clock".
“We found that our metabolic rate changes throughout the day. In addition, important chemical processes occurring in human adipose tissue are rhythmic. This means that fat cells accumulate and change throughout the day, not just when we eat, says lead researcher Dr John Johnston.
This study suggests that the activity of processes occurring in fat cells occurs at different rates depending on the time of day, which can affect human metabolic processes.

"Identifying the rhythms of tissue made up of fat cells gives us more information about how a person's metabolism changes throughout the day and may explain why the body processes food differently during the day and at night," Dr. Johnston said.
Don't skip breakfast
Every day should start with a hearty and balanced breakfast . The morning meal is very important, because if you regularly neglect breakfast, your metabolism slows down and goes into “starvation mode.”
The study, published in the American Journal of Epidemiology, found that people who ate at least 22% and no more than 55% of their total daily calories for breakfast gained an average of about 3 pounds over four years. But those who ate less than 11% of calories for breakfast gained almost 1.8 kilograms.

Switch to healthy breakfasts containing fiber and slow-digesting carbohydrates. To prepare a delicious and healthy breakfast, combine foods that are rich in protein, complex carbohydrates and healthy fats.
To boost your energy in the morning, make yourself an omelette from one egg yolk and two whites, adding a handful of chopped peppers and onions. Oatmeal porridge seasoned with omega-3 flaxseed oil is also perfect for breakfast. You can add a handful of fresh or frozen berries, nuts and even honey to the porridge!
Coffee at work
Good news for coffee lovers. According to a study published in the American scientific journal Physiology & Behavior, the metabolic rate of people who regularly drank caffeinated coffee was 16% higher than those who drank decaffeinated coffee.
"Caffeine stimulates your central nervous system, thereby increasing your heart rate and breathing," says Robert Kenefick, a researcher at the US Army Research Institute of Environmental Medicine.

In addition, after a mug of coffee you should drink a glass of cold water . Researchers from the University of Utah (USA) found that drinking one glass of water can speed up your body's metabolism by 30% and maintain it at that level for 10 minutes. The thing is that your body will have to burn additional calories to maintain core body temperature, which increases calorie expenditure.
Gym
There's nothing better for boosting your metabolism than high-intensity interval training . HIIT is a training system in which 20 seconds of exercise at a very intense pace alternate with 10 seconds of recovery. That is, the exercises are performed at intervals and repeated a total of eight times within four minutes.
Research has shown that high-intensity workouts help speed up your body's metabolism as effectively as less intense types of workouts.

Recording parameters
Basal metabolic formulas were first published in the early twentieth century. They used the following concepts:
- P is the total heat production at complete rest;
- m—mass (kg);
- h—height (cm);
- a is age (years).
One of the popular evaluation methods is the Harris-Benedict formula:
- for women: BMR = 665 + (9.6 × m) + (1.8 × h) - (4.7 × a) ;
- for men: BMR = 66 + (13.7 × m) + (5 × h) - (6.8 × a).
Harris and Benedict will help you calculate
Since not everyone can undergo such a laboratory examination (and not everyone will want to), you can calculate your basal metabolic rate using formulas.
A hundred years ago, at the beginning of the twentieth century, American scientists Francis Benedict and James Arthur Harris published their research on metabolism, where they explained that the caloric intake required by each of us every day is made up of the needs of basal (basic) and active (active) calories. metabolism.
They developed a formula designed for an adult.
For the fair sex -
BM=655.0955 + 9.5634 x your mass in kg + 1.8496 x height in cm - 4.6756 x age in years
For the stronger sex -
BM=66.4730 + 13.7516 x your mass in kg + 5.0033 x height in cm - 6.7550 x age in years
For those who don’t want to bother with calculations, I suggest using a calculator, click here.
Why calculate?
Basal metabolic rate can be used to gain, lose, or maintain weight. Knowing how many calories are burned, you can calculate how much to consume. For example:
- To maintain weight, you should consume and burn an equal amount of calories;
- for a set - consumption must exceed combustion;
- To lose, you need to consume fewer calories than you burn.

How to calculate calories
After estimating your basal metabolic rate, the next step is calculating your calories based on your lifestyle:
- Sedentary. No physical activity. Multiply UBM by 1.2.
- Slightly active. Perform light exercise 1-3 times a week. Multiply BMR by 1.375.
- Moderately active. Physical activity 3-5 times every seven days. UBM multiplied by 1.55.
- Active. Up to seven workouts per week. Multiply BMR by 1.725.
- Hard labour. Constant physical activity. UBM multiplied by 1.9.
The formula would be more accurate if it included body composition, weight history and other factors.
Calculate basal metabolism with Muffin Jeor

Almost a hundred years later, in 2005, another American, Muffin Jeor, proposed his own formula and it is precisely this that the American Dietetic Association considers the most optimal. Here is this creation:
For the fair sex -
BM=9.99 x your weight (kg) + 6.25 x height (cm) - 4.92 x age - 161
For the strong -
BM=9.99 x your weight (kg) + 6.25 x height (cm) - 4.92 x age + 5
Causes of individual differences
A study of basal metabolic rate in 150 adult subjects was conducted in Scotland. Indicators ranged from 1020 to 2500 kcal/day. The researchers estimated that 62.4% of this variation was explained by differences in “fat-free mass.” Other reasons included fat mass (6.8%), age (1.8%), and experimental error (2.1%). The remainder of the variation (26.6%) was unexplained. It was not affected by gender or the size of the tissues of such high-energy organs as the brain.

Factors that influence UBM
Several factors influence UBM:
- weight – people with high weight will receive a higher BMR number
- body type – adipose tissue is known to have lower metabolic activity than muscle tissue. As muscle mass increases, your metabolic rate also increases.
- gender - basal metabolism in men is approximately 5 - 10% higher than in women. The reason for this is that women have more body fat than men of the same weight and height.
- age – metabolic rate decreases with age, the reason for this is the loss of muscle tissue, the growth of fatty tissue, as well as hormonal and neurological changes.
- body temperature – for every increase in body temperature by 0.5°C, BMR increases by 7%. Chemical reactions in the body occur faster at high temperatures.
- health status – illness or injury can double your metabolic rate because the body needs more energy to recover. [4] [7]

Your BMR is also affected by your macronutrient :
- fats increase BMR by 5%
- carbohydrates increase BMR by 5 – 10%
- proteins increase BMR by 20–30% [8]
Biochemistry
An increase in postprandial thermogenesis in basal metabolism occurs depending on the composition of food consumed. Almost 70% of the total human energy expenditure is associated with life support processes that occur in the body. Approximately 20% of energy expenditure comes from physical activity. About 10% is for digesting food. To carry out these processes, oxygen consumption with coenzymes is required. This provides energy to survive and expel carbon dioxide.
The body spends most of its energy on maintaining the required level of fluid in the tissues. About one tenth is devoted to mechanical work (breathing, digestion and heartbeat).
The breakdown of large molecules into smaller ones is called catabolism (for example, the breakdown of proteins into amino acids). Anabolism is the process of their creation (proteins are converted into amino acids). Metabolism is the result of these reactions.

Where do almost all the received values go?
A person is a complex biological system in which numerous processes occur every moment. For example, 2.5 million erythrocytes (red blood cells that deliver oxygen to tissues) are born every second and the same number die. About a million intestinal epithelial cells are renewed in a second, and in the bones, no matter how strong and unchangeable they may seem, all the cells completely change in 10 years.
In addition to the constant birth of new cells, it is necessary to provide energy for the work of the heart, the breathing process, the release of decay products, the continuous synthesis of hormones and much, much more. Even if we lie down and do not move, all the necessary work of our organs and systems requires a lot of nutrients and energy.
Heartbeat hypothesis
In 1925, Raymond Pearl proposed that life expectancy was inversely related to basal metabolic rate. Support for this theory comes from the fact that larger animals have longer life spans. This hypothesis is supported by several new studies linking lower basal metabolic rates to increased life spans in the animal kingdom, including humans. Calorie restriction and lower thyroid hormone levels have been linked to higher longevity in animals.
However, the ratio of total daily energy expenditure to resting metabolic rate can vary from 1.6 to 8.0 among different mammalian species.
With allometric scaling, maximum potential lifespan is directly related to metabolic rate.
What is regulated
Basal (general) metabolism is a dynamic system, i.e. the distributed energy is directly affected by external and internal factors of the body. Acceptable limits are known at which a person feels satisfactory, looks good, and has no complaints about the functioning of the digestive system. The amount of energy expended is regulated by the following factors:
- Level of hormones in the blood. For example, in diabetics, the overall metabolism differs in speed and cost from the average statistical metabolism, which is important to consider when drawing up a daily menu.
- Metabolic rate. It is determined by the ratio of a person’s general mobility to the presence of excess internal energy. With an active lifestyle, the basal metabolism is much faster, which is important for keeping fit.
- Oxygen level. With a large volume of oxygen, the rate of release from the body increases, increasing the energy costs of basal metabolism.