- What is metabolism called?
- Functions
- Regulation
- Age characteristics
- Kinds
- Diseases
- Reasons for acceleration and deceleration
- Symptoms of disorders
- Diagnosis of pathologies
- Recovery methods
- Normalization results
- Complications
- Prevention
Human health depends on many factors. Metabolism plays an important role; when it is disrupted, various pathologies begin to develop and the quality of life deteriorates significantly. Most often it slows down, and this leads to obesity. Much less often it accelerates, and this is also fraught with consequences. But well-functioning, uninterrupted metabolic processes are a guarantee of good health and a slim figure. That's why it's so important to know what affects them and how to normalize them.
What is metabolism called?
In the minds of many, it is associated only with weight. If your metabolism slows down, wait for it to increase; if it accelerates, wait for it to decrease. However, this concept is not limited to this.
Metabolism is the process of continuous intake of nutrients into the body, their breakdown into components, partial absorption and subsequent release of breakdown products. Its active participants:
- amino acids;
- proteins;
- bilirubin;
- vitamins;
- glycans;
- glycoproteins;
- glycosaminoglycans;
- hormones;
- fats;
- cofactors;
- coenzymes;
- xenobiotics;
- lipids;
- lipoproteins;
- minerals;
- nucleotides;
- pigments;
- porphyrins;
- purines;
- pyrimidines;
- sphingolipids;
- carbohydrates, etc.
The final products that are released into the external environment are iron, carbon dioxide, lactic acid, water, salts, and heavy metals.
Stages
Metabolism is a stepwise process in which the following stages are distinguished:
First. Digestion is the mechanical and chemical processing of food in the gastrointestinal tract. At this stage, the decomposition of carbohydrates (converted into monosaccharides), protein compounds (synthesized into amino acids), lipids (split into fatty acids) occurs, followed by their absorption.
Second. At the tissue level, intermediate metabolism occurs, which involves the breakdown of nutrients into final products.
Third. Includes the assimilation and excretion of the resulting end products.
Processes
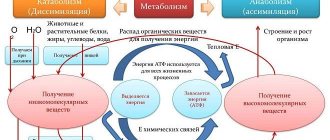
Human metabolism occurs in the form of two processes:
- Assimilation (anabolism), when absorption of substances and energy expenditure occurs.
- Dissimilation (catabolism), when organic compounds are broken down to produce energy.
Scheme
The general scheme looks like this:
Food → Gastrointestinal tract (digestion) → absorption of nutrients → transport of nutrients into the blood, lymph, cells, tissue fluid (breakdown of substances, formation of new organic compounds) → removal of breakdown products through the skin and kidneys.
Definition
From a physiological point of view, metabolism is all the chemical reactions that occur in your body that are necessary for normal functioning. In everyday life, metabolism is usually called metabolism.

What is this in simple terms? Metabolism is all the processes that occur to absorb and use certain nutrients. We regularly receive certain micro and macroelements from food, water, air, etc. Due to metabolism, we manage them: we use them as energy, accumulate them in the form of adipose tissue, use them to restore injured tissues, and much more.
Functions
What functions does metabolism perform?
Protein:
- genetic function: proteins are a structural part of DNA;
- protective: synthesize immune bodies during intoxication;
- catalytic: activate all biochemical reactions;
- regulatory: maintain biological balance;
- structural: part of cells;
- transport: promote the complete absorption of nutrients, ensure their delivery to the necessary organs;
- energetic: provide energy.
Fatty:
- protective function: lipids conserve heat, prevent bruises of internal organs;
- regulatory: form bile acids, sex hormones;
- structural: form nervous tissue;
- energetic: saturate with energy.
Carbohydrate:
- protective function: carbohydrates secrete viscous secretions that protect the gastrointestinal tract from pathogenic microorganisms.
- structural: form cellular structures, nucleic acids, enzymes, amino acids;
- energy: the main source of energy.
These are just the main functions that BZHU perform in the body. And besides them, more than 20 substances are involved in metabolism, and each of them plays a specific role.
Digestion
Molecules such as starch, proteins and cellulose are broken down before they are used by cells. The digestion process involves special enzymes that break down proteins into amino acids and polysaccharides into monosaccharides.

Animals can secrete such enzymes only from special cells. But microorganisms release such substances into the surrounding space. All substances that are produced thanks to extracellular enzymes enter the body using “active transport”.
Regulation
Hormones play an important role in metabolism - they are its regulators. This is why a failure in one system leads to serious disruptions in another. This is why metabolism most often slows down during pregnancy, the postpartum period, and at the time of menopause—serious hormonal changes occur in the female body.
Protein metabolism is regulated by the following hormones:
- somatotropic hormone of the pituitary gland;
- thyroid hormones - thyroxine and triiodothyronine;
- adrenal hormones - glucocorticoids (hydrocortisone and corticosterone).
Regulation of fat metabolism is carried out:
- hormones of the adrenal medulla - adrenaline and norepinephrine;
- somatotropic hormone of the pituitary gland;
- thyroxine;
- glucocorticoids.
Carbohydrate metabolism is regulated only by insulin.
Hormonal regulation of metabolism is used by endocrinologists to treat diseases associated with its disorders.
Minerals
Inorganic substances play a very important role in metabolism. All organic compounds consist of large amounts of phosphorus, oxygen, carbon and nitrogen.
Most inorganic compounds allow you to control the level of pressure inside cells. Also, their concentration has a positive effect on the functioning of muscle and nerve cells.
Transition metals (iron and zinc) regulate the activity of transport proteins and enzymes. All inorganic microelements are absorbed thanks to transport proteins and are never in a free state.
Age characteristics
To restore impaired metabolism, it is very important to take into account the age-related characteristics of its course.
In children
The metabolic rate is several times higher than that of adults. This means that they need much more nutrients for full development and growth. For example, to build a muscle corset, a 7-year-old child needs 3 times more protein than athletes with regular intense training.
At the same time, fats practically do not accumulate, but are consumed in the form of useful energy, so there should also be a lot of them. They strengthen the immune system, performing the protective function of the child’s body. For comparison, one interesting fact: a newborn’s diet consists of 90% fat. An adult’s gastrointestinal tract simply cannot withstand such a load.
In no case should you limit carbohydrates in your children’s diet, which protect them from diabetes.
In adults
After puberty, metabolism stabilizes for a while, but then gradually slows down. This often occurs due to hormonal disorders. Women are especially affected. To normalize it, adults should eat complex carbohydrates and proteins, but at the same time monitor the fat content. Weight control is a must.
In the elderly
In the absence of proper nutrition and physical activity, metabolism in the elderly proceeds very slowly. They can no longer consume a lot of protein to avoid eating disorders. Constant monitoring by a doctor and moderate exercise reduce the risk of complications.
Types of metabolic processes in the body
Depending on the rate of oxidative reactions, three types of metabolism are distinguished:
- fast, typical for people of thin build;
- slow – people who tend to be overweight have it;
- the third type is characterized by metabolic reactions occurring at an average speed.
The nature of metabolic processes is inherited and divides people according to body type into ectomorphs, mesomorphs, and endomorphs.
Ectomorph
Thinness, swiftness, energy are the defining characteristics of ectomorphs. Wrist girth is the first method of diagnosis based on body type - for ectomorphs it is no more than 15-17.5 cm. A thin physique is due to too fast a metabolism.
An ectomorph is a fragile person with long arms and legs and thin muscles. Since his metabolism occurs too quickly, it is very difficult for an ectomorph to gain weight.
Muscles and adipose tissue do not have time to form - proteins and fats are rapidly converted into energy. An ectomorph spends much more energy on the functioning of the brain, heart, lungs, and other internal organs than people of other body types.
Mesomorph

Happy owners of a balanced metabolic process are mesomorphs. Their metabolism proceeds at an average speed, which has its pros and cons.
Protein metabolism gives developed muscles, carbohydrates and fats are transformed into energy. Without additional exercise, they have a muscular body with a small percentage of fat tissue. Even if a mesomorph gains a little extra fat, he can easily get rid of it by increasing physical activity and adjusting his diet.
The disadvantage of mesomorphs is their frivolous attitude towards their body: they can indulge in any excesses, hoping to quickly restore their shape. As they age, they tend to become overweight due to an unbalanced diet and neglect of physical activity.
Endomorph
Slow metabolism is the reason that endomorphs quickly gain extra pounds even with a low-calorie diet.
Strict diets and cutting calories are not the answer for them. In simple words, the body will perceive a hunger strike as stress and will convert nutrients into fats - in reserve “for a rainy day.”
People with this body type are at risk of developing diabetes and atherosclerosis if they abuse foods high in carbohydrates and fats.

A calorie-balanced diet and aerobic exercise will help them maintain a normal weight. Unfortunately, playing sports is not the strong point of endomorphs.
Kinds

Metabolism is classified as follows.
Depending on the participants:
- protein;
- carbohydrate;
- fat (lipolysis);
- mineral;
- water-alkaline and other types.
Depending on the violations:
- fast;
- slow.
Depending on the processes:
- plastic - absorption of nutrients, synthesis, anabolism;
- energetic - breakdown of compounds, their elimination, catabolism.
It is very difficult to independently determine what kind of metabolism you have - intense, slow or normal. It is better to contact an endocrinologist with this question.
Diseases
Metabolic diseases are coded as E70-E90 (in accordance with ICD-10). This list contains more than 50 pathologies. The most common:
- albinism - lack of melanin;
- amyloidosis - accumulation of excess protein deposits in tissues;
- acidosis - increased acidity;
- Hartnup's disease - the inability of cells to absorb individual amino acids;
- galactosemia - improper conversion of galactose to glucose;
- hypercholesterolemia - increased lipid levels;
- cystic fibrosis - protein gene mutation;
- leucinosis - disturbances in the production of enzymes;
- mucolipidosis - hydrolase inactivity;
- mucopolysaccharidosis - metabolic disorders occurring in connective tissues;
- lactose intolerance;
- dehydration;
- oxaluria - accumulation of oxalic acid salts;
- ochronosis - problems with tyrosine synthesis;
- sarcosinemia - increased levels of sarcosine;
- Gilbert's syndrome - hepatosis associated with the production of pigments;
- Farber syndrome - accumulation of lipogranulomas under the skin;
- phenylketonuria - poor absorption of certain amino acids;
- cystinosis is a pathologically elevated level of cystines.
Recommendations from endocrinologists

Obesity begins with the body's normal reaction to poor nutrition: excess calories are stored in fat folds and slow down metabolic processes.
Endocrinologists are unanimous that only proper nutrition can effectively reduce weight and restore metabolism:
- Reduce your intake of sugar and fast carbohydrates. Make “slow” carbohydrates the main source of energy.
- Avoid consuming margarines and vegetable trans fats, which slow down metabolic processes.
- Drastically change your lifestyle by switching to a balanced diet and increasing physical activity.
- Eat often, but get up from the table with a slight feeling of hunger.
- Maintain water and drinking regime.
Losing weight is not difficult if you change your eating habits in accordance with these rules and follow them throughout your life until you are very old.
Reasons for acceleration and deceleration
Scientists are still studying what determines metabolic rate. A number of reasons have been scientifically confirmed, but in some cases the provoking factors are very difficult to identify.
Causes of slow metabolism:
- intrauterine hypoxia;
- age after 35;
- gender differences: in women it proceeds more slowly;
- genetics;
- deficiency of minerals and vitamins;
- diet, lack of calories;
- thyroid diseases;
- slagging of the body;
- menopause;
- improper functioning of the adrenal glands and pituitary gland;
- incorrect eating habits: lack of diet, snacking on the go, abuse of unhealthy foods;
- dehydration;
- constant stress, prolonged depression, frequent nervous breakdowns;
- birth injuries;
- childbirth;
- sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical activity.
Causes of accelerated metabolism:
- alcoholism;
- genetics;
- prolonged and very severe stress;
- long-term use of powerful medications;
- grueling workouts;
- addiction;
- heredity;
- lack of sleep, insomnia;
- excessive physical activity (at work or in the gym);
- extensive inflammatory processes;
- excess muscle mass;
- living or working in low temperatures;
- severe, complicated infections;
- traumatic brain injury if the hypothalamus was affected;
- endocrine pathologies: acromegaly, hypercortisolism, hyperthyroidism, thyroiditis, hyperaldosteronism, goiter, thyrotoxicosis, hyperprolactinemia, Stein-Leventhal syndrome, etc.
Most experts consider hormonal imbalance to be the main cause of metabolic disorders, since hormones are their regulators.
How does your metabolic rate change with age?
This is a purely individual point, but with age, for most people, the rate of metabolic processes decreases. This is usually noted before the age of 30. Every year your metabolism slows down more and more. Therefore, the older a person is, the higher the tendency to gain excess weight. Starting from the age of 25, special attention should be paid to proper nutrition. Your norm for calories, proteins, fats and carbohydrates should be clearly calculated. Deviations from this in one direction or another can be minimal, otherwise your metabolism will slow down and you will gain excess fat mass. You should try to eat small meals as often as possible. The basis of your diet is animal proteins and complex carbohydrates with a low glycemic index. After 6-7 pm it is recommended to completely give up carbohydrates. Food must be fully digested, so the more fiber in your diet, the better.
Symptoms of disorders
Increased metabolism in the human body is most often accompanied by weight loss and unhealthy thinness. Slowed down, on the contrary, first by obesity, then by obesity. But the symptoms of metabolic disorders are not limited to these signs.
Protein metabolism:
- alopecia;
- arthritis;
- fatty liver;
- muscular dystrophy;
- stool disorders: both diarrhea and constipation;
- nervous disorders;
- osteoporosis;
- salt deposits;
- lack of appetite;
- renal failure;
- premature skin aging;
- weak immunity;
- weight loss;
- drowsiness, lethargy and apathy;
- decrease in intellectual abilities.
Carbohydrate:
- uncontrollable tremors of the arms and legs;
- hyperactivity;
- obesity or, conversely, weight loss;
- increased cholesterol;
- heart failure;
- pressure surges - arterial, ocular and intracranial;
- tachycardia;
- worsening of diabetes mellitus.
Fatty:
- alopecia;
- atherosclerosis;
- high cholesterol;
- hypertension;
- hormonal disorders;
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- stones;
- obesity or weight loss;
- kidney problems;
- decreased immunity;
- frequent inflammations.
Mineral:
- allergies;
- alopecia;
- numerous acne on the face and back;
- stool disorders;
- lack of sexual desire;
- poor sleep;
- decreased vision;
- frequent infectious diseases due to decreased immunity.
Specific symptoms in women:
- infertility;
- hormonal imbalances;
- tearfulness, irritability, excessive emotionality;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- problems with the menstrual cycle;
- facial hair;
- endocrine pathologies.
Specific symptoms in men:
- muscle dystrophy;
- diseases associated with the prostate;
- impotence;
- lack of sexual desire;
- enlarged mammary glands and buttocks.
These symptoms may indicate poor metabolism. As soon as they appear, it is advisable to immediately seek medical help and not try to correct the situation on your own, so as not to make it even worse.
Diagnosis of pathologies
To diagnose metabolic pathologies, the following diagnostic measures may be needed:
- study of medical history;
- measurement of anthropometric data: height, weight;
- Based on the data obtained, BMI is calculated and the volume of visceral fat is determined;
- general assessment of physical development;
- multilateral blood test (biochemistry) for hormones and cholesterol;
- general urine analysis;
- dopplerography;
- positron emission tomography;
- Ultrasound of internal organs (prescribed by a doctor based on the general condition of the patient’s body);
- if necessary, ECG.
These laboratory tests will allow you to make an accurate diagnosis and determine a therapeutic course.
Recovery methods
You can start or, conversely, slow down your metabolism in different ways.
Medications
You should not take medications on your own, because you can achieve the opposite result. First, you need to understand what exactly needs to be done with your metabolism - speed it up, speed it up, or slightly adjust it. This can only be done by an endocrinologist together with other highly specialized specialists. And only he can prescribe the correct treatment.
To speed up:
- L-thyroxine;
- Glucophage;
- Lecithin;
- anabolics: methandienone, retabolil, riboxin, methyluracil, potassium orotate.
To slow down:
- yeast (in the form of dietary supplements);
- protein supplements (as sports nutrition);
- medications for weight gain: Apilak, Duphaston, Benzodiazepine, Elkar, Anadrol, Andriol;
- iron-containing preparations (Hemofer, Tardiferon, Ferrogluconate, Ferrogradumet, Heferol, Aktiferrin, Fenuls);
- antimetabolites: Azathioprine, Alexan, Vaidaza, Gemita, Gemcitabine, Decitabine, Zexat, Cladribine, Clofarabine, Lanvis, Methotrexate, Movectro, Nelarabine, Tegafur, Thioguanine, Trexan, Fivoflu, Fopurin, Ftorafur, Cytarabine, Cytogem, Evetrex.
For normalization - extracts of biostimulant plants (they are also called the “seven golden herbs”):
- high aralia;
- wild pepper;
- the lure is high;
- Golden root;
- root of life - ginseng;
- Schisandra chinensis;
- maral root.
To restore metabolism, individual vitamins (C, B1, B2, B9, B12, A, E), minerals (iodine, calcium, chromium, zinc, iron) and multivitamin complexes are also prescribed:
Alfa Vita (Japan):
- Mono Oxi helps restore the body after operations and illnesses;
- Min is designed for those losing weight who are on diets;
- Minerals is recommended for athletes;
- O2 is an innovative Japanese development that acts at the molecular level;
- Zeolite can be used on regular fasting days, as the complex perfectly cleanses the gastrointestinal tract, liver and kidneys.
Vision (Russia):
- chromium, ascorbic acid;
- chitosan;
- iodine, magnesium, thiamine, cobalamin, pyridoxine;
- iodine, chromium, ascorbic acid.
Other branded vitamin complexes:
- Zym-Complex. Astrum (USA);
- B-50 Complex 100 Tablets. Nature's Life (Russia);
- Selenium-DS. Dr. Skalny (Russia);
- Turboslim. Alpha lipoic acid with L-carnithiome. Evalar (Russia).
More detailed recommendations for taking tablets that speed up metabolism can be found at this link.
To treat diseases caused by metabolic disorders, specific medications are prescribed.

If problems are associated with hormonal disorders, they are eliminated with hormonal drugs. For example, with menopause they help well:
- Angelique;
- Atarax;
- Divina;
- Klimara;
- Klimonorm;
- Cliogest;
- Logest;
- Magnefar;
- Marvelon;
- Supradin;
- Trisiston;
- estrogen medications (Divigel, Estrofem, Ovestin).
In case of hormonal imbalance after childbirth, when a woman’s metabolism cannot return to normal, the following may be prescribed:
- antilipid tea;
- Dexamethasone;
- Cordyceps;
- Cyclodinone;
- Estrinol;
- Euthyrox.
Taking hormonal medications during the postpartum period should be under constant medical supervision. If the mother is nursing, the duration of treatment should be no more than 10 days, since powerful drugs can negatively affect the baby’s health through breast milk.
Healing procedures
- Aromatherapy;
- pool;
- hot baths;
- cold and hot shower;
- massage;
- wraps;
- special exercise therapy;
- phytotherapy.
Behavioral therapy
Eat properly according to the schedule. Take measures to strengthen the immune system: it is necessary to harden yourself, spend more time in the fresh air, and ventilate the premises.
Increase physical activity: do exercises, walk, go for daily jogging, go to the pool, gym or dance, ride a bike - there are many ways. Sports should be consistent and systematic. That is, you need to start small and simple, gradually complicating the chosen training program. There is no need to exhaust yourself with daily weightlifting: 3 times a week will be enough.
Don’t worry about anything, don’t stress yourself out—you need to strengthen not only your immune system, but also your nervous system. Give up bad habits, gradually reducing your daily consumption of nicotine and alcohol. If you have a drug addiction, you need to undergo treatment.
Maintain good body hygiene to prevent infections. And they often lead to various metabolic failures.
Follow a clear daily routine, in which there is a place for both work and rest. Sleep at least 7 hours, go to bed no later than 23.00. For those who need to slow down their metabolism, you can limit sleep to 6 hours.
Nutrition

General recommendations
- Mode
Meals should be small - about 5 times a day, not counting a glass of kefir at night. The interval between meals should be no more than 3 hours. Moreover, the regime must be strictly adhered to. In moments of force majeure, a deviation of half an hour (+/-) is allowed, but this should be a rare exception.
- Serving sizes
Portions should be small. They quenched the hunger - and that’s enough. If metabolism is regulated directly for weight loss, you should not eat more than 200 g at a time. The only exception may be lunch. If the reason is different, experts recommend consuming about 300 g for women and 450 g for men at a time.
- Meals
For breakfast you need to consume up to 25% of the total daily caloric intake, for lunch - 35%, for dinner - 20%. The rest are distributed between snacks. Morning meals should include as many complex carbohydrates as possible, in the afternoon the ratio of BJU should be balanced, in the evening preference is given to protein foods.
You must have breakfast and dinner no later than 3-4 hours before going to bed.
- BJU ratio
This indicator is individual and is calculated using special formulas. On average, the ideal ratio is 3:2:5 for men, and 2:2:4 for women. These parameters depend on the degree of physical activity and initial weight. If you correctly calculate and use it, it will greatly help restore impaired metabolism and subsequently maintain it normal. If it needs to be accelerated, the protein content in the diet increases; slow down - fat.
Proteins are evenly distributed among meals, but dinner must consist mainly of them. It is better to consume fats at lunch. The most beneficial are unsaturated omega-3, -6 and -9. Complex carbohydrates will help you fill up in the morning, but in the evening they will be inappropriate.
You definitely need to calculate for yourself the ratio of BZHU plus the daily calorie intake and adhere to the results obtained.
- Calorie content
To normalize metabolism, you need to give up low-calorie diets. To lose weight, you should not lower the bar below 1200 kcal per day. To maintain normal weight, it needs to be raised to 1500 kcal. For men these numbers will be 1500 and 1800 respectively.
Once a week you can arrange a so-called calorie swing. If your norm is usually 1200, on Sundays (or Saturdays) increase it to 1500. If the norm is 1500, then reduce it to 1200. This prevents the body from getting used to the same diet, which has a positive effect on the speed of metabolic processes.
Our tables will help you calculate the calorie content of food.
- Drinking regime
If the drinking regime is not organized correctly, no matter what a person does to restore metabolism, it will be useless. Water is the main catalyst for this process; it is what starts it, accelerates it, and normalizes it. Therefore, you need to make sure that there is enough of it in your diet.
One of the golden rules is that you should start your morning with a glass of clean water without carbon (you can add lemon or honey). By drinking it immediately after waking up, you force your body to wake up after the night. During the day, you need to continue the work you started: drink 200 ml between meals. The daily volume is calculated using the formula: for each kg of weight - 30 ml. On average, it turns out from one and a half to 3 liters. Some people drink 4 glasses before lunch and 4 after.
The main thing is not to overdo it. For example, after 18.00 it is no longer recommended to drink water, so as not to wake up with swelling the next morning. If you want to drink after dinner, it’s better to organize yourself a cup of soothing herbal tea or kefir.
- Other tips
If you want to get your metabolism in order, you will have to make some sacrifices in terms of nutrition. For example, give up fried foods as a source of cholesterol and harmful fats, which will pollute the body and slow down metabolism. Carbonated water and fast food are included in the list of prohibited products. Sweets, smoked foods, and baked goods are not excluded, but are limited in volume. At first, it seems very difficult to give up sweets and your favorite cake, however, if you wait 3 weeks, the right eating habits will form, and the body will stop demanding forbidden things from you.
List of recommended products
Eating to normalize metabolism is reminiscent of a diet, but here everything is not so strict and categorical. For example, the list below is not allowed, but only recommended products that are known as metabolism boosters. And only you can adjust it according to your own discretion and taste preferences.

Products to improve metabolism
It is necessary to enrich the diet with the following products:
- Pineapple and grapefruit are champions in accelerating metabolism, papaya, hard pears, kiwi, watermelon, pomegranates, lemons, melons, green grapes, peaches, avocados, bananas, oranges, plums, green apples, mangoes.
- Anise, cloves, horseradish, horned root, ginseng, mustard, Ceylon cinnamon, cardamom, curry, vanilla, dried basil, turmeric, ground pepper and peas.
- Brown rice, oats, buckwheat.
- Bitter chocolate.
- Kefir (required for daily use), yogurt, natural yoghurts, whey, fermented baked milk. If you need to lose weight, their fat content should be minimal. If such a task is not worth it, do not limit this indicator.
- Lettuce, caraway as greens, green onions, dill, parsley, basil.
- Honey.
- Seafood.
- Unrefined vegetable oils, especially olive oil.
- Vegetable broth.
- Nuts.
- Rose hips, raspberries, cherries, viburnum, gooseberries, strawberries and wild strawberries, cranberries, chokeberries, currants, lingonberries, rowan berries, sea buckthorn, blackberries, acai, blueberries, goji.
- Fish.
- Beans, bell peppers, cabbage, beans, garlic, tomatoes, chard, onions, beets, chickpeas, carrots, peas.
- Black coffee, drinks with ginger, lemon and cinnamon, Sassi water, berry smoothies, green tea, freshly squeezed juices, Cahors, dry red wine.
- Apple vinegar.
- Eggs.
A more detailed list of products to speed up metabolism can be found in a separate article.
Features of nutrition with accelerated metabolism
If you need to slow down your metabolism, slightly different principles of nutrition work:
- Three meals a day.
- Serving sizes are unlimited.
- The diet should contain as much fat and simple carbohydrates as possible. Moreover, the latter should be consumed for dinner. But you shouldn’t get carried away with fiber and proteins.
- Among the foods you should give preference to baked goods, fatty meats and fish, sweets, pasta, vegetable oils, and nuts.
You can find a step-by-step guide to slowing down your metabolism in the earlier article.
Diets
- For normalization
To restore impaired metabolism, there is a special therapeutic diet - the eighth table according to Pevzner. It is recommended for serious pathologies: obesity, diabetes, bulimia, compulsive overeating. Before practicing it, you need to consult an endocrinologist and nutritionist. Sometimes it is observed even with slight excess weight and bad eating habits. Duration - about a month. The results are normalization of metabolism, lowering sugar and cholesterol, launching lipolysis and losing weight.
A detailed menu for every day, a list of permitted and prohibited foods and other nutritional features according to Pevzner’s diet No. 8 can be found here.
- To speed up
To speed up metabolism, there is a separate diet developed by American nutritionist Haley Pomeroy. She became famous after Robert Downey (Jr.) and Jennifer Lopez lost weight and got back to normal. It is distinguished from other methods by the presence of 3 phases, each of which takes into account the biorhythms of the human body, which has a very beneficial effect on metabolism. With this stellar diet you can lose weight and improve your health.
Three phases: the first (Monday-Tuesday) - calming, the second (Wednesday-Thursday) - preparatory, the third (Friday-Saturday-Sunday) - lipolytic.
Hayley Pomeroy also gives recommendations for performing different exercises in different phases, which sets her apart from the rest.
The menu, described by phases, and other features of this system can be found at the link.
- For weight loss
A metabolic diet, which also includes several phases, but longer in time, will help you improve your metabolism and lose weight. Its difficulty is that you have to count the points of the consumed products.
Phases: first (2 weeks) - active fat burning, second (about 2 months) - stable fat burning, third (infinite) - weight normalization.
The table for the distribution of points by product and a detailed menu for the week for each day can be studied in our article.
Folk remedies

Medicinal herbs also have the ability to normalize metabolism and speed it up, if necessary. Some of them are even recognized by official medicine. Raw materials are either purchased at the pharmacy in the form of herbal preparations and packages, or collected by hand (but you need to be able to do this correctly). Which herbs should you pay attention to in this case:
- aloe;
- wild rosemary;
- Birch buds;
- immortelle;
- Highlander;
- angelica;
- chickweed;
- St. John's wort;
- nettle;
- buckthorn;
- linden;
- burdock;
- coltsfoot;
- mint;
- marigold;
- oregano;
- sagebrush;
- motherwort;
- chamomile;
- currants;
- bearberry;
- yarrow;
- thyme;
- rose hip.
You need to be able to prepare them correctly to stabilize metabolic processes. For infusion, take 30 g of dry or fresh crushed raw materials and pour boiling water (200 ml). Keep covered or in a thermos for about an hour. For a decoction, 15 g of leaves and flowers are enough for the same volume of water. Simmer over low heat for up to 15 minutes. Both drinks are filtered. Drink 100-200 ml after each meal.
Several ingredients can be used in a recipe (for example, currant leaves, rose hips and burdock root). But in this case, you need an exact recipe to find out the ratio of the components. They cannot be combined arbitrarily, since some plants do not combine with each other and, if prepared incorrectly, can be harmful to health.
The use of folk remedies must be agreed with a doctor. Natural medicines, just like medications, have their own lists of contraindications that must be observed. In addition, they cannot always be combined with taking any other medications.
The essence of metabolism
In order for all these nutrients that we consume to be fully absorbed by the body, they must be broken down into simpler substances. For example, our muscles do not need protein as such to repair and grow. We only need individual amino acids (22 in total) that are needed for muscle activity. During the digestion process, protein breaks down into individual amino acids, and the body assimilates them for its needs. For example, leucine and valine immediately go to restore muscles damaged during training, tryptophan goes to the production of dopamine, glutamine goes to maintaining the immune system, etc. The breakdown of a complex substance into simpler ones is called anabolism. With anabolism, the body receives energy in the form of calories that we spend during physical activity. This is the first stage of our metabolism.
The next stage of metabolism is catabolism. This phenomenon is usually associated with the breakdown of muscle tissue or the burning of fat, but its significance is much broader. In a broad sense, catabolism is the synthesis of complex substances from simple ones. Tissue regeneration is directly related to catabolism; we see this when healing wounds, renewing blood and other processes that constantly occur in the body without our knowledge.
Protein metabolism

Our bodies need protein for a number of important biological functions, including:
- Regeneration and creation of new muscle cells.
- Restoration of microtraumas in muscle tissue after strength training.
- Acceleration of all biochemical processes.
- Synthesis of sex hormones and normal functioning of the endocrine system.
- Transport of nutrients: vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates, hormones, etc.
During digestion, protein breaks down into individual amino acids. This process is called protein metabolism.
Not only the quantity, but also the quality of protein is important. The amino acid composition is what determines the biological value of a protein. If it is scarce, then it covers only a small part of the body's needs. This mainly applies to proteins from plant products. Some nutritionists consider legumes to be an exception, since they contain a fairly large amount of essential amino acids.
Things are different with animal proteins. Usually its amino acid composition is much more extensive, and it contains large quantities of essential amino acids, which are so necessary for athletes during periods of intense training.
Carbohydrate metabolism

Carbohydrates are “fuel” for our body. Glucose, to which carbohydrates are broken down during metabolism, tends to accumulate in the liver and muscles in the form of glycogen. It is glycogen that makes muscles visually voluminous and full. It has been proven that muscles filled with glycogen are stronger and more resilient than “empty” muscles. Therefore, full-fledged strength training in the gym is impossible without a sufficient amount of carbohydrates in the diet.
Without carbohydrates, you will be ineffective, lethargic and sleepy. This is why athletes often complain of feeling unwell and lethargic during a low-carb diet. There are high glycemic index (simple) and low glycemic index (complex) carbohydrates.
Simple carbohydrates include all sweets, confectionery, baked goods, white rice, most fruits, juices and other sugary drinks. Their glycemic index ranges from 70 to 110. Complex carbohydrates include all cereals, durum wheat pasta, vegetables, whole grain bread and some dried fruits.
The metabolism of simple and complex carbohydrates is fundamentally different. Simple carbohydrates are also called fast carbohydrates, as they quickly saturate the body with energy, but this energy does not last long. Yes, you feel an increase in performance, a surge of strength, improved mood and concentration, but this only lasts about 40 minutes. Their absorption rate is too fast, they quickly break down into glucose. This provokes a strong surge of insulin, which promotes the accumulation of fatty tissue and also harms the pancreas. In addition, taking large quantities of simple carbohydrates completely kills your appetite, and this is fundamentally important during the period of gaining muscle mass, when you need to eat 6-8 times a day.
Yes, the end product of the breakdown of any carbohydrate is glucose. But the fact is that with complex carbohydrates this process takes much longer - from 1.5 to 4 hours. This does not lead to fat accumulation as there are no sudden spikes in insulin levels in the blood. Complex carbohydrates should form the basis of your diet. If you have enough of them, you can be productive in the gym and outside of it. If not, your efficiency will decrease.
Fat metabolism

The liver plays an important role in fat metabolism. It serves as a kind of filter through which fat breakdown products pass. Therefore, liver problems are common among those who do not follow the principles of proper nutrition. The amount of fat in your diet should be strictly limited. Most nutritionists recommend consuming up to one gram of fat per kilogram of body weight. Moreover, the emphasis should be on unsaturated fatty acids, which are rich in fish and seafood, nuts, vegetable oils, avocados and eggs. They have a beneficial effect on the functioning of the cardiovascular system, as they help reduce cholesterol levels in the blood.
Often fat is deposited not only under the skin, but also between internal organs, and outwardly it is completely invisible. It is called visceral fat. It is very difficult to get rid of it. Fat metabolism disorders lead to increased accumulation of visceral fat. Because of this, they receive less oxygen and beneficial nutrients, and their performance gradually deteriorates, which can lead to the development of serious diseases.
Exchange of water and mineral salts

The most important thing in diet and proper nutrition is not calories, proteins, fats and carbohydrates. Our body simply cannot exist and function normally without water. Our cells, internal organs, muscles, blood, lymph consist almost entirely of water. Many athletes forget how important it is to consume enough fluids and how fluid balance affects your well-being and performance.
Normalization results
Once your metabolism is restored to normal, this will affect your health and well-being:
- normalization of digestion, liver and kidney function, blood pressure;
- general improvement in well-being;
- increasing concentration and performance;
- losing weight or, conversely, gaining weight;
- reducing the risk of exacerbations of chronic diseases;
- stabilization of hormonal levels;
- in women - normalization of the menstrual cycle;
- improvement in appearance: the skin becomes smooth, hair becomes thick and begins to grow, nails become strong, without splitting;
- elimination of chronic fatigue, cheerfulness, energy, high spirits, absence of depressing thoughts.
Complications

Improper metabolism can trigger the development of the disease:
- anemia;
- atherosclerosis;
- infertility;
- painful muscle contractions;
- hepatosis;
- hyper- or hypoglycemia;
- glycogenosis;
- dystrophy;
- gout;
- weight problems;
- mental disorders;
- rickets;
- diabetes.
And this is not the entire list of sad forecasts for those who neglect themselves and do not control metabolic processes.
Prevention
To never encounter the problem of slow or accelerated metabolism, it is enough to lead a healthy and active lifestyle. It includes:
- Leisure.
- Favorable psychological atmosphere.
- High physical activity.
- Spa treatment and relaxation.
- Limit alcohol (no more than 1 glass of dry red wine per day).
- Limiting harmful products.
- To give up smoking.
- Passing a medical examination at least once a year.
- Fasting days 2-4 times a month.
- Varied menu.
- Calculation of the individual ratio of BZHU, using it to compile a diet.
- Regular weight control.
- Daily schedule by the hour.
- Timely contact with doctors if health problems arise.
- Strengthening the immune system.
- Taking multivitamins 2 times a year.
It is difficult to overestimate the role of metabolism in the body. If it proceeds without failures, it means that your health is good, your mood is excellent, and the person looks amazing. But as soon as biochemical reactions slow down (or speed up), this immediately manifests itself in the form of all kinds of sores, hormonal surges, and deterioration of external data. This is why it is so important to keep your metabolism under control and, in case of the slightest deviation, go to an appointment with an endocrinologist.