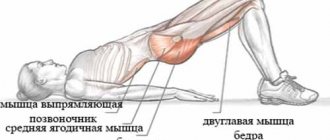
The bench press (on a bench) is a basic free weight exercise. It develops the muscles of the chest, shoulders (front deltoids) and arms (triceps). This is the most effective exercise for developing strength and building muscle in the upper body because you lift most of the weight above you (more than with a chest press). The larger the bench, the larger your chest.
The correct starting position for starting this exercise is lying on a bench, legs on the floor, resting with the entire foot (shin perpendicular to the floor). Lift the barbell from the rack with your arms straight. Lower the barbell to the middle of your chest. Raise (Press) the barbell up until your elbows are straight. Keep your pelvis on the bench. The bench press consists of 5 repetitions in a 5x5 program (workout A).
how to properly perform a bench press (on a bench): lower the barbell to the middle of your chest. Press (raise) the barbell upward until your elbows are straight.
To avoid shoulder pain, keep your elbows at a 75º angle when lowering the bar. Do not try to stretch your chest by raising your elbows to 90º. You injure the shoulder joint when the base of the forearm is perpendicular to the body. Keep your elbows apart (keep your elbows) at a 75º angle to avoid pain.
Unlike the squat or deadlift exercise, the barbell does not move in a vertical plane when you perform the bench press correctly. It moves diagonally to the middle of the chest above the shoulders. Thanks to this, you can avoid shoulder injury. This is the most effective way to perform a bench press with a heavy weight.
Introduction. How to do a bench press (on a bench)

lie down on a bench, grab the barbell, remove it from the rack, lower the barbell to the middle of your chest, and raise it back up.
Perform the bench press on a special machine (power rack) for maximum safety. Set the restraints at a comfortable height so that they will support the weight if you are unable to lift it. You don't need an assistant if you do the exercise on the same machine as I do. If you do not have a special rack (power rack), ask someone in the gym to support you while performing this exercise. Follow these 5 simple steps to do the bench press correctly.
- Preparation. Lie down on the bench so that your eyes are under the barbell. Raise your chest and squeeze your shoulder blades together. The entire foot rests on the floor
- Grip . Place your little finger on the indicated (ring) places. Hold the barbell at the base of your palm with a full grip without bending your wrist
- lifting the barbell. Take a deep breath and grab the bar with straight arms. Bring the barbell over your shoulders without bending your elbows.
- Lowering the bar . Lower the barbell to the middle of your chest, keeping your elbows at a 75º angle to your torso. After lowering the bar, take a short break.
- Lifting the barbell . Press the barbell from the middle of your chest to the starting position (above your shoulders). Keep your pelvis on the bench. Straighten your elbows. Take a breath.
Place the barbell on the rack after completing the 5x5 power lift exercise. For the final rep, lift the weight from your chest until your elbows are straight. Then, install the barbell on the power rack. As soon as you touch the rack, bend your elbows to lower the bar into the racks.
Bench press on a horizontal bench. Vertical Bench Press

Introduction - Bench press on a horizontal bench. Vertical bench press .
Yes, this is Arnold’s favorite exercise, Ronnie Coleman’s favorite exercise, and in general the favorite exercise of almost every bodybuilder and person who works with weights - the bench press. What could be cooler than lying on a horizontal bench and squeezing out the weight? Here you will not have injuries 90%, because klutzes will always find ways to harm themselves and their health. But that’s not what we’re talking about now. The fact is that in many disputes everything is decided precisely by the weight category of the bench press - if you press more, it means you are stronger. And there are no accusations about weight and so on. If you want to say something, object, then go and get more, understand?
This is exactly the tone that those who bench press over 150 can speak in. But you and I are still mere mortals and want to learn how to bench press correctly, and the weight will come by itself. Of course, without proper training, no barbells will grow. Therefore, to begin with, think like this - warm-up with a bar, then 40 kg, then 50 kg. If after such a pyramid you do not feel tired, then you are completely ready for bench press exercises. If not, swing on the uneven bars for now until you do it 30 times.
Tips from those in the know - Bench press on a horizontal bench. Vertical Bench Press
It is best to do the exercise with a partner, because while you are just a beginner, additional insurance will not hurt. Imagine this situation - you pressed for the last time, but it went very easily for you, then you think - let me press one more time. And then, as soon as you start pushing the barbell, it no longer moves. And, of course, all this mass falls on your body. Certainly. You can get out of any situation, but why struggle if you can just ask someone to “insure me.”
Technique, continued - Bench press on a horizontal bench. Vertical Bench Press
The bench press itself is very simple - lower it to the middle of your chest, approximately at that level. where your shoulders begin, but a little closer to your stomach.
Next, you need to slowly lower the barbell, and then with a quick and sharp upward movement, raise it to its original position. The main thing you must remember is do not throw the barbell down. It is necessary to lower it as slowly as possible and to raise it as quickly as possible. Only with such observance can the maximum effect be achieved.
As you can see in the figure, the result is an up and down movement. This is exactly how you should press the barbell. Don't rush with the weights - you'll still bench more than your girlfriend. To begin with, this will be enough for now. If they start laughing, don’t pay attention. Everyone was such a sucker at first. The main thing is the desire to improve the bench press technique, and then add weight.
Video on the topic - Bench press on a horizontal bench. Vertical Bench Press
Video on topic 2 - Bench press on a horizontal bench. Vertical bench press .
We recommend reading:
- The best exercises for biceps. Biceps pumping. How to properly pump your biceps In fact, few athletes (we are talking about beginners) [...]
- Exercises for the chest muscles. Pectoral muscle Target muscles: Chest Type of exercise equipment: BarbellLevel […]
- Technique for performing the bench press The bench press is considered the second most important exercise in […]
- Deadlift technique. Deadlift video. How to do a deadlift One of the most effective and beautiful exercises in [...]
- Barbell squats. Squat technique Today we will talk about one of the most dangerous exercises [...]
- How to pump up your shoulders. How to pump up deltoids Target muscles: Shoulders Type of exercise equipment: Dumbbells Level […]
Preparing to perform the bench press (on a bench)
How to prepare for the bench press exercise (on a bench): sit on a bench, lie down, squeeze your shoulder blades together, grab the barbell, put your feet in the correct position.
Before performing the exercise, install the necessary equipment. Set the restraints to the appropriate height so that they will catch the weight if it falls. Position yourself strictly in the center of the bench. Take the correct starting position before you remove the weight (start the exercise). Your wrist will bend if you grip the bar incorrectly. Your shoulders will begin to move unless your shoulder blades are strongly retracted. You won't be able to correct their position mid-exercise, which can cause the weight to fall on you. Compliance with these rules (recommendations) will contribute to the successful completion of the exercise and the development of the chest muscles.
- Lying position (on a bench). To begin, sit on the edge of a flat bench. Lie down with your back flat on the bench. Lie down so that the barbell is at eye level.
- Reduction of the shoulder blades . Push your chest forward, tense your upper back, squeeze your shoulder blades as far as possible and lower them down.
- Grip . The little finger is on the inside of the ring marks. Hold the barbell tightly with your hand so that he cannot change position.
- Leg position . The legs stand straight (flat with the entire foot) on the floor, under the knee there should be an angle of 90º with respect to the floor.
- Removing the rod . Using straight arms, remove the barbell from the holders. Bring the barbell to shoulder level. Ready.
Perform this preparation before each bench press. Thorough and consistent preparation for the exercise will help you successfully cope with weight. By developing your technique, you increase the effectiveness of the exercise. When preparing, pay attention to the weight you will be working with. Follow the rules when preparing to warm up or perform basic strength exercises.
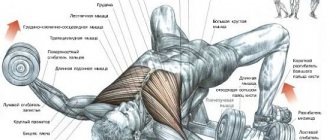
Chest press in the simulator to pump up the pectoral muscles

One of the simplest and most effective exercises for the pectoral muscles is the chest press in a machine. Good for beginners. The work includes the chest muscles, front deltoids, triceps of the arms, and a little biceps.
The pectorals are the target muscles in the exercise.
Chest press in the simulator: video
How to do the exercise? Technique
- Set the seat height of the exercise machine to the correct height for you. Sit tightly on the bench. Grab the handles. Raise the weight until your arms are actually straight. This will be the starting position.
- Lower the handles, moving your elbows back as low as possible. As you lower, inhale.
- Press from your chest to the starting position. Under load, when you press, exhale.
- Repeat the range of motion 15 times for 3 sets.

How to do a chest press in a machine? Technique
Application of the exercise
For whom . Any level for girls and men. Recommended for beginners to practice and consolidate the movement - chest press.
When . The machine chest press is best done at the beginning of training the pectoral muscles. After the press, do incline dumbbell flyes and triceps extensions from the upper block.
How many . For beginners, do 3 sets of 15 repetitions. For more experienced athletes to work on weight - 4 x 10 times.
Advice! If you come to the gym to pump your chest, and your favorite horizontal bench for barbell press is occupied. The machine chest press is a great alternative to the basic barbell press.
Exercise options
- Basic and basic. A medium grip or when the seat height is so that the arms are at the level of the middle of the pectoral muscles. Then the load is precisely distributed over the pectoralis major muscle.
- An option for greater development of the upper pectoral muscles. Overhand grip or when the seat height is so that the hands are at shoulder level.
- Alternate chest press in the simulator. For uniform training and targeted concentration on the muscles. Use this version of the exercise.
There are block and lever chest press machines. There is not much difference in the range of motion and the development of muscle groups. Use what you have in the gym.

Chest press. Block and lever trainers
Recommendations for execution technique
- Often, exercise machines have an additional lever for the legs. To help move the handles to a comfortable starting position. Use it by pressing with your feet. If there is no lever. For help, you can turn to your partner in the gym. Ask him to throw the heavy weight into the starting position for the press.
- Perform a movement that is comfortable for your shoulder joints. If flexibility is good, lower the levers of the machine low; if flexibility is not enough, work in the upper range of motion.
- You can choose the load in the exercise depending on the purpose of working out muscle groups. When you spread your elbows to the sides, perpendicular to the body, the pectoral muscles work more. When the elbows are brought together and are closer to the body, the triceps muscles of the arms are more involved in the work.
- An exercise similar to a horizontal barbell press. Good for beginners. Since the movements in the simulator are predetermined and do not need to be coordinated. Unlike horizontal bench presses with barbells or dumbbells.
Common mistakes
- Lifting your back off the backrest and moving your shoulders forward. Keep your back close to the backrest and your shoulders level with the shoulder girdle. Concentrate on your chest muscles.
- Full arm extension. Always keep your arms slightly bent in the final position. This way you will protect your joints from premature wear and aging.
- Incorrect breathing. Under load, when you press up, exhale. When you lower it, inhale.
- Jerks and fast movements. Make clear movements. Try to do lowering slower than lifting.
Did you like the article? Subscribe to us on social networks and be the first to know about new products!
Bench Press 101

The effectiveness of the bench press depends on your body type. The wider your shoulders, the wider your grip should be. The longer your forearms, the closer your elbows will be to your torso in the lowest position. Do not try to repeat the technique of performing this exercise after another person until you have a similar physique. Instead, stick to the basic rules of doing the bench press; As you gain experience you will improve your form.
- Grip . Hold the barbell firmly at the base of your palm.
- grip width _ the palms are within (inside) the circular marks. When lowering the barbell, your forearms should be vertical.
- Thumb . _ _ The thumb should wrap around the barbell.
- Brushes . The hands should be straight from the bar to the elbow. Do not bend your wrists - this can cause pain.
- Elbows . In the lower position, the elbows should be at an angle of 75º relative to the body. They should not touch the body or move apart (“fly apart”) at an angle of 90º.
- Forearms . Must be vertical to the floor.
- Shoulders . Don't lift your shoulders off the bench. Do not push your shoulders forward when the bar is in the top position.
- Upper back . _ Squeeze your shoulder blades together to provide maximum stability as you press.
- Breast . lift your chest towards the ceiling. The bar should touch your chest when in the lowest position.
- Head . when lying down, the bar should be at eye level.
- Lower back . A natural curve that allows you to move your hand freely between the bench and your back.
- Pelvis . Keep your pelvis on the bench. Don't try to cheat by lifting your pelvis off the bench.
- Feet . They are located flat on the floor, strictly at the knees, at an angle of 90º, shoulder width apart.
- Removing the rod . Remove the barbell (with weight) from the holders, straightening your elbows. Move the barbell over your shoulder joints.
- Lowering the bar . Lower the bar to the middle of your chest. Place your elbows at a 75º angle in the down position.
- Bottom position. The hands are straightened, the hands are vertical. The elbows are turned towards the body, not away from it.
- Lifting the barbell. Do not pause in the down position. Press the barbell to the top position (above your shoulders). Lock your elbows at the top.
- Fixing the bar in the upper position (“lockout”). Lock the barbell in position above the shoulder joint. Lock your elbows in the upper position. Don't rush to bend your elbows back.
- Returning the bar to the holders. With your elbows straight, bring the barbell to the rack and slowly lower it onto the holders.
- The trajectory of the rod. A diagonal line from the middle of the chest to a position above the shoulders. Incorrect - a straight vertical line above the shoulders, neck or chest.
- Breath. Take a deep breath in the top position, hold your breath while lowering the bar and in the bottom position. Exhale in the upper position.
How to do bench presses for the upper chest. Method of training the pectoral muscles
Starting position – sitting in the simulator. We select the seat height so that the upper chest is slightly higher than the handles of the exercise machine. Grasp the handles with a wide straight grip, keep your elbows pointing to the sides at all times; if there is a foot lever, press it:
— inhale and press the weight up until your arms are almost completely straightened at the elbows;
- lower the weight to the starting position, exhaling, until the pectoral muscles are slightly stretched.
Performing the exercise
- Initial position.
- Highest point of movement.
This exercise is perfect for working the upper muscle fibers of the pectoral muscles . The front deltoids and triceps are also included in the work.
Notes.
1. At the top point of the movement, do not straighten your arms at the elbow joints to the end, leave a minimum reserve of movement. This will help remove stress from the joints and prevent microtrauma and unwanted damage.
2. All kinds of machine presses are great for entry-level athletes. We recommend starting your first steps with them.
Video for the bench press exercise for the upper chest
Muscles and approximate effectiveness of the exercise for working muscle fibers: *
- Chest: 100%
- Front deltoids: 70%
- Treceps: 30%
*Subjective assessment based solely on personal training experience.
Application of the press exercise in the simulator for the upper chest
To whom: Everyone from beginner to master.
When: At the beginning or in the middle of a chest workout. Before the bench press in the simulator, perform a dumbbell bench press; after the press in the simulator, do a pullover with a dumbbell.
How many:
- Endurance – 3-4 sets of 20-25 reps
- Relief/drying – 3-4 sets of 15-20 repetitions
- Weight – 4-6 sets of 6-10 reps
- Strength – 4-6 sets of 3-6 reps
Safety

How to urgently complete a bench press: lower the barbell to the middle of your chest, flatten your chest (exhale) until the barbell touches the holders (frame). Crawl out from under the bar.
You will never get stuck under a barbell with weight if you bench press inside a power rack. The power rack has horizontal holders that can pick up the weight if the barbell fails to lift. Install the horizontal holders slightly below the extreme lowering point of the bar. If repeated successfully, the holders will not interfere with you. If you fail to lift the weight. In this case, lower the weight to the middle of your chest, flatten your chest (exhale) to lower the barbell onto the holders (frame). The power rack bench press is the safest way to perform this exercise.
Performing a bench press without a power rack or an assistant is dangerous. If you are crushed (stuck under) a barbell, then the only way to get out from under it is the “Bundle of Shame”. Lower the barbell to the middle of your chest, “roll” it to your stomach, then raise your body and lift the weight (the article says - do a deadlift). This will not be very pleasant and may leave bruises on your stomach. An alternative way is to do the bench press without weight clamps, in which case you can tilt the bar to one side and drop some of the weight (plates) onto the floor, although by doing so you will violate the rules of the gym by roughly dumping the weight on the floor.
The dumbbell bench press looks safer, but it's not entirely true. Although it should be noted that you will never get stuck under the weight. But if you fail to lift the heavy dumbbells, they may fall on your face and seriously injure you, or you may throw the dumbbells on the floor, which will also not please the general manager. The power rack bench press is the safest way to perform this exercise because the horizontal holders can catch the weight if you fail to lift it (if you get stuck under it). The power rack will also prevent the barbell and weights from falling to the floor. But even a power rack won’t help if you can’t handle the weight of the dumbbell.
It's normal to be afraid of hurting yourself while doing the bench press. People die from barbell accidents. To avoid this, always hold the barbell with a full grip (your thumb should be opposed to the others), this will eliminate the possibility of the barbell rolling and falling onto your chest. Do not bench press with heavy weights without a power rack. Start with light weights, focus on the technique of performing the exercise, and only then gradually increase the weight. Following safety rules will give you confidence and you will overcome fear. Don't forget to position the horizontal holders even if you think you can handle the weight.
Seated press in the simulator: correct exercise technique
In almost every gym, the free weights area is a mass gathering place for athletes. Here they patiently wait their turn to do the bench press, and strive to get a bar to pump up their shoulders in the standing press. Sometimes in such situations it is possible, without wasting time waiting, to perform a seated bench press in a special machine.
- Seated press in a simulator: training features
- Muscle activation in the seated press
- Benefits of Exercise
- Varieties of seated press: correct technique and significant nuances
- Bench press in a special machine
- Video: Technique for performing seated bench presses in a machine
- Hammer Seated Press
- Video: How to properly perform a bench press in a Hummer
- Smith machine press to work the pectoral muscles
- Press sitting in front of you at an angle in the Smith machine
- Video: Press sitting in a Smith machine in front of you - pumping up the chest and shoulder muscles
- Smith machine overhead press
- Video: Correct technique for performing seated overhead presses in a Smith machine
- Recommendations for performing the exercise effectively
Seated press in a simulator: training features
Pressing exercises with free weights are the best for upper body development. They can be supplemented or replaced (if for some reason you can’t exercise with a barbell or dumbbells) with similar movements in special simulators. Gyms offer a variety of modifications of such devices that allow you to perform presses at different angles and shift the working emphasis to certain muscle groups.
Muscle activation in the seated press
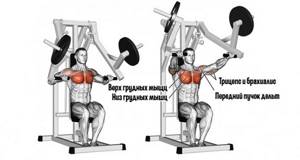
Compared to basic presses, the exercise in question works the target muscles more concentratedly, since stabilizers are not involved in the work.
When performing a pressing movement in a machine, an athlete loads the following muscle groups:
- pectoral muscles;
- anterior bundles of the deltoid muscle;
- arm muscles (mostly triceps), receiving auxiliary load.
Depending on which simulator and at what angle the exercise is performed, the working emphasis will shift to the pectoral or deltoid muscles.
Benefits of Exercise
The press performed in the simulator is ideal for those who, for various reasons, cannot or do not want to do this exercise with free weight (girls, beginner athletes, athletes recovering from injuries).

In the exercise under consideration, the athlete does not need to be distracted by the work of the stabilizer muscles, so it will be easier to concentrate on contracting the target muscles and “hone” the ideal technique.
The press in this version is more gentle on the back and shoulder joints, which are very susceptible to injury. If there are problems in this area, it is advisable to train the upper body in this way.
An important advantage of bench presses in simulators is optimal load distribution. When working with free weights, the athlete's arms undergo natural, from an anatomical point of view, vibrations, and this can lead to incorrect load distribution and muscle asymmetry. The design of bench press machines provides for movement along a fixed trajectory, so the work emphasis will be distributed evenly.

Even beginners can perform this press without the help of a partner. There is no risk that the projectile will fall on the chest or head.
Varieties of seated press: correct technique and significant nuances
In gyms there are various modifications of devices for performing pressing movements. They can be either load-bearing or loadable. You can train in them at an angle, as well as do horizontal and vertical bench presses: it all depends on the design of the particular simulator.
All such simulators are characterized by a common algorithm of actions.
Before starting the class, you should warm up your upper body, paying special attention to your shoulder joints. Before the first approach, install a small weight: this will be a warm-up set.

Bench press in a special machine
Many gyms have press machines that allow you to move upward at an angle, as well as horizontal presses. They are used in complex training of the upper body.
Almost all such devices provide the ability to adjust the seat - you need to use it by adjusting the height to suit your height. Having settled down while sitting, press your body tightly against the back, straighten your shoulders and slightly lean your chest forward. Legs spread apart rest firmly on the floor.
Holding the handles with a comfortable grip, remove the weight and hold it with your hands (if there is a special pedal for bringing the weight to the starting position, this will make the task much easier). The shoulder blades are in a flattened state, the elbows are apart.
- Exhaling, with a powerful effort, squeeze the weight in front of you until your arms straighten, maintaining a slight bend in the elbow joints (“soft elbows”).
- They are fixed in this position for a couple of seconds: the target muscles are statically tense.
- As you inhale, maintaining tension in the muscles, slowly return the handles to their original position.

Do 12 times in 3-4 sets.
Video: Technique for performing seated bench presses in a machine
Hammer Seated Press
For performing the seated press, an ideal machine is called a “Hammer” in the sports community, after the manufacturer of such devices.
This lever type machine is simple and efficient, being operated by pushing out a lever to which a weight is attached. It was originally created to reduce the load on athletes’ joints during pressing movements.

The halls feature a variety of modifications of Hummers, allowing you to shift the working emphasis in the presses:
- A vertical press device that simulates similar movements with free weights. The deltoids receive the main load here.
- Angle press machine. It activates the pectoral muscles with an emphasis on its upper zone.
Before starting the lesson, the selected device must be adjusted to suit your height. The seat is installed so that the handles are placed at mid-chest level or slightly lower. The optimal weight is placed on the machine.
Having settled down on the seat, you need to press your back tightly against its back: there should not be a large distance between the exercise machine and your lower back. Feet rest on the floor.
Holding the handles of the Hummer, squeeze your shoulder blades together, spread your elbows to the sides and take a deep breath. With an optimal grip width, the forearm at the lowest point will be perpendicular to the body.
- With a powerful muscular effort, while exhaling, squeeze the weight in front of you, straightening your arms (the elbows remain “soft”, without “snapping” in the joints). Shoulders are pressed against the back, elbows pointing to the sides.
- At the top point you need to fixate for 1-2 seconds, focusing on the static contraction of the target muscles.
- While inhaling, slowly and smoothly lower the handles to their original position.
Do 12–15 repetitions in 3–4 approaches.

When practicing the Hummer, during the positive phase of the movement, you need to learn to resist the instinctive arching of your back. This is important, since with this technique the back muscles will take on a significant part of the load, and the spine will be subject to undesirable effects.
The lowering of the handles lasts longer than the pressing movement. Here you need to avoid sharply “throwing” your arms down, moving them under control and maintaining tension in the muscles.

The correct biomechanics of movement in this device implies a contracted position of the shoulder blades and a protruding chest at all points of the trajectory. There is no need to concentrate on pushing the weight out (similar to a barbell bench press). What is important here is a smooth and leisurely straightening of the arms; you should seem to be moving the weight, not pushing it.
Video: How to properly perform a bench press in a Hummer
Smith machine press to work the pectoral muscles
You can specifically work the target muscles without spending additional effort on the work of the stabilizer muscles in a Smith machine. As with other bench press machines, the Smith uses the same movements as in a free weight class, but in a more focused manner. This is due to the fact that the bar here goes strictly along the guides, the trajectory of its movement is set initially.
Press sitting in front of you at an angle in the Smith machine
First you need to set the desired angle of the bench and place it directly under the bar. It is advisable to determine the exact placement on an individual basis by performing several trial repetitions without weight. After this, the optimal weight is set.
After sitting down on a bench (the bar is in front), you need to fix the position of the body: your feet rest on the floor, your pelvis and back are pressed against the seat). The bar is taken with a straight closed grip with a wide stance of the hands, by turning it, remove it from the stoppers and lower it to approximately the level of the chin.
- As you exhale, squeeze the bar above yourself. The arms are not fully straightened, leaving a slight angle at the elbow joints.
- At the top point, pause for a second, concentrating on peak muscle contraction.
- As you inhale, lower the bar under control to its original position. There is no need to put it on your chest.
Perform 10–12 times in 3–4 approaches.

During movements, you should not arch your lower back - this will overload the spine and change the emphasis of the load.
Video: Press sitting in a Smith machine in front of you - pumping up the chest and shoulder muscles
Smith machine overhead press
Before you begin this exercise, you need to thoroughly warm up your shoulder joints, since they have serious work ahead of them: the overhead press is more dangerous than other similar movements.
In the Smith machine, the bar is placed in the top position, so that it can be comfortably grasped with straightened arms. A weight is placed on it. A bench with a vertical backrest is placed under the bar (if it is not available, a regular gymnastics bench will do). You should position yourself on it so that the bar is positioned exactly above your head. The abdominal muscles are statically tense, the feet rest firmly on the floor. Raising your hands, grab the bar with a grip wider than your shoulders and remove it from the stoppers.
- Inhaling, in a controlled movement, bring the barbell behind your head to approximately the middle of your head or slightly lower. In the lower position, an angle of 90 degrees should form between the joints of the shoulder and elbow. This is an average indicator; the level of lowering of the bar is determined by the flexibility of the athlete’s joints. It's important not to overdo it here.
- There is a second pause at the bottom.
- As you exhale, push the bar up with a powerful movement, avoiding “snapping” in the elbow joints.
Do 8-10 times in 3 sets.

To make launching the projectile more comfortable, it is permissible to tilt your head forward slightly, without allowing your back to lift off the back of the bench. The bar must move strictly along a vertical trajectory without deviation to the sides.
It is not recommended to work with heavy weights in this exercise: this increases the risk of injury to the shoulder joints.
Video: Correct technique for performing seated overhead presses in a Smith machine
Recommendations for performing the exercise effectively
Seated presses are the ideal finishing movement for an upper body workout day. It is advisable to include it in the lesson plan after basic exercises on the chest and shoulders and perform it in a multi-repetition mode: this way the target muscles will receive high-quality development. This is especially true for experienced athletes who have already built up muscle mass. In addition, here you can work to failure without fear of being crushed by the barbell.
The design of such simulators allows you to do presses with one and the other hand alternately. This may be relevant if there is pronounced muscle asymmetry and correction of the load is required in relation to one of the arms.

Presses in simulators allow you to change the emphasis by changing the grip. For example, when training the pectoral muscles, a wide grip more actively engages its outer area, while a narrower grip activates the inner part of the pectorals and triceps.
If an athlete has an injured shoulder joint, it is not recommended for him to do a full-amplitude bench press: in the lower position, the elbows should not extend beyond the plane of the body. In such situations, it is advisable to train in devices with a special lever for applying weight.
Seated presses in simulators will complement the training program for the development of the upper body: performed in combination with basic exercises, they will significantly increase the effectiveness of the training. Pressing movements in special devices can become the basis of a training program if the athlete does not plan to gain muscle mass or is recovering from a shoulder girdle injury.
Bench press technique
Grip technique

left: grip with the middle of the palm - the hand will bend and hurt. In the middle - grip with the lower part of the palm, the hand will not bend. On the right - green indicates the correct position of the barbell in the palm.
Full grip . The thumb wraps around the barbell. This is the safest and most effective way to hold a barbell. Clamp the bar so that it cannot move during the exercise. The muscles of the arms, shoulders and chest will have a harder time contracting, which will increase the load during the exercise (hyper load). Do not relax your arms (palms) during the bench press. Hold the barbell as tightly as possible.
Incorrect grip . The thumb should be opposed to the other four, which creates a lock that prevents the bar from rolling and falling onto the chest. If the bar slips out of your hand and no assistant will have time to help you, the bar may fall on your chest, throat or face. This may result in an accident or death. If your hand (wrist) hurts, take the barbell closer to the base of your palm; this position will prevent your hand from bending.
Bulldog grip. The easiest way to properly grip a barbell is to use a bulldog grip. Grasping the barbell, rotate your palm around it to get a better grip on the bar. Grip tightly with your palm so that the bar cannot move. This grip will prevent the bar from slipping out of your hands. Try this grip variation for a few workouts and you will get used to it.
Grip width

Left: Grip too wide, forearms at an angle. Middle: The grip is too narrow, emphasizing the triceps. Right: The most efficient way to press.
Medium grip . Grasp the barbell with your little fingers inside the designated area. your forearms should be vertical when lowering the bar. Your body type determines your grip width. A narrower grip is not effective for developing the pectoral muscles as it engages the arm muscles, focusing on the triceps.
Vertical forearms . Your forearms should be vertical, in other words, perpendicular to the floor. If your elbows are on the outside of your hands as you lower, you'll have a harder time lifting the weight (you'll also be recruiting your triceps). If your elbows are inside your hands, you put stress on the shoulder joint. Maintaining a vertical forearms position as you lower the bar helps determine the correct grip width.
Brushes

Straight brushes . Straight hands are the safest way to perform a bench press (straight vertical line - barbell, hand, elbow when the bar is in the lower position). Remember, if you do the bench press with bent wrists, they will hurt. A sports tourniquet (special bandage) will not help solve this problem. Straighten your hand, positioning the barbell correctly in your hand (closer to the base of the palm).
Grip with the bottom of your hand. Don't hold the bar in the middle of your palm or close to your fingers as in a deadlift. Gravity will pull the bar down, and this will lead to flexion of the hands and pain; to avoid this, hold the bar closer to the base of the palm. As you prepare to perform the exercise, grab the barbell with a bulldog grip and twist your palm to tighten your grip on the barbell.
Elbows
Spreading elbows when lowering the barbell can lead to sharp pain in the shoulder (Shoulder impingement syndrome , the syndrome is based on a mechanical impingement of the tendons of the rotator cuff muscles and the anterioinferior part of the acromion, especially when the shoulder is bent forward and turns inward)
Elbow grouping (correct position of the elbow joint). When lowering the barbell, you need to bring your elbows together a little. Your body type will determine how close your elbows should be (the optimal angle at which you should keep your elbows in relation to your body is 75º). Your shoulders (anatomical) should not be strictly perpendicular to your torso when the bar is in the lower position. It is also necessary to remember that excessive reduction of the elbows (until they touch the body) will negatively affect the effectiveness of the bench press. Remember that the safest and most effective way to perform this exercise is to keep your forearms strictly vertical (perpendicular to the floor) in the down position.
Do not touch the torso . When the elbows touch the body, they are “inside” (relative to the hands). The weight will be harder to lift and this will put additional stress on the joints. Professional powerlifters use compression shirts. But we don’t use such shirts, so our hands and elbows must be in the same vertical line for the bench press to be as effective as possible. Do not place your elbows out to the sides when the bar is in the lower position.
Do not open (do not spread) your elbows . We advise you not to lower the bar if your elbows are more than 90º apart. We also do not advise you to perform a bodybuilder-style bench press with your elbows perpendicular to your torso in a lower position. You injure your shoulder joint in an attempt to stretch your pectoral muscles further. The upper arm will “hit” the rotator cuff opposite the acromioclavicular joint with each repetition. The shoulder joint will become inflamed and painful. In the lower position, keep your elbows at a 75º angle to your body.
Keep your elbows out when lifting the weight only . The lifting of the weight should mirror the trajectory of the lowering of the barbell. You should keep your elbows out as you lift the weight and bring the barbell to a position above your shoulders. Otherwise, you will lift the barbell directly above your chest. This lifting trajectory is considered ineffective when working with heavy weights. “Push” the weight from the middle of your chest to a position above your shoulders, keeping your elbows out.
Vertical (perpendicular) forearms . The most effective way to perform a bench press is to keep your forearms perpendicular to the floor with the bar touching your chest. A straight, perpendicular line from the hand to the elbow will create effective leverage for lifting heavy weights without pain in the hands. If your elbows are too close or too far, grab the barbell (the barbell should be held at the base of your palm, bulldog grip) and change the grip width.
Fixing the rod in the upper position. Return the barbell to the machine with your elbows straight. Straighten and maintain this position every time you lift the bar. The bench press is not performed correctly if you do not straighten your elbows at the top position because: firstly, the repetition will not be counted; secondly, you can drop the barbell and injure yourself; thirdly, it is safe to fix the elbows in a straight position with a full range of motion.
Forearms

Left: Vertical forearms with bar on shoulders, causing damage. There are two in the middle: the forearms are not vertical, it touches the chest too high/low. Right: vertical forearms, the most effective method.
When viewed from the side (side), the forearms should be vertical (parallel and perpendicular to the floor). Your forearms should be vertical (parallel and perpendicular to the floor) when the bar touches your chest. From the side, a strict vertical line should be visible - barbell, hand, elbow. This is the safest and most effective way to perform the bench press. If your wrists are bent (backward), grab the barbell with a bulldog grip. Make sure that your elbows are in the correct position (at an angle of 75º relative to your body). Lower the barbell to the middle of your chest.
Vertical from the front. Your forearms should be vertical (parallel and perpendicular to the floor) on either side (front or back). It is not recommended to tilt your forearms because... this will negatively affect the effectiveness of this exercise. The close grip bench press will engage the triceps more. If you bench press with a grip that is too wide it will cause problems for your shoulders (shoulder injury).
Head position

Eyes under the barbell. Lie down on the bench so that your eyes are under the barbell. This position minimizes the distance between the power plant and the shoulders. Do not lie far from the holders - it will be inconvenient for you to remove and return the barbell to its place, it will require a lot of your strength, and it will also be unsafe. Therefore, the bar should be above your eyes when you lie on the bench and look straight at the ceiling. If you hit the racks while lifting the barbell, you are lying too close.
Do not rest your head (press) on the bench. Your neck will hurt if you rest your head on the bench while bench pressing. Tighten your neck muscles without putting pressure on the bench. The easiest way to avoid this is to avoid touching your head to the bench. The muscles will be tense if the head does not touch the bench. Your neck will not be harmed because you will be pushing it into the bench.
Keep your head in a neutral position (flat). Do not turn your head to look at the posts, otherwise you will injure your neck. Do not raise your head to check if the bar is touching your chest. Keep your head level (neutral) and your eyes looking at the ceiling. At the end of the approach, secure the barbell above your shoulders and return the bar to the power unit. When you have returned the bar to the holders, bend your elbows and lower your arms.
Shoulders
Shoulders should be kept on the bench. Keep your shoulders on the bench. Don't push them forward while pressing. If your shoulders are pulled forward, your arms will be higher than they should be. Therefore, it will be much more difficult for you to perform this exercise. When preparing to perform the bench press, lie down with your shoulders on the bench.
Don't push, push. The best way to keep your shoulders on the bench is to imagine that you need to push the barbell away from you (away from your chest). Imagine that you are doing push-ups and pushing off the floor.
ask someone to help you. Your shoulders may move forward when you remove the barbell from its holders. Some power frames do not have enough markings for the holes, so the posts may be too high or low. When the holders on the stand are too low, it can cause strain on the arms. If the racks are too high, you will have to lift your shoulders off the bench to reach and return the bar to its place. To avoid these situations, ask someone to help you.
Upper back

Squeeze your shoulder blades together as if trying to hold a handle between them. This will give you a better bench press position.
bring your shoulder blades together. While performing the bench press, keep your upper back toned (don't relax). Imagine that you have a handle clamped between your shoulder blades and you need to hold it. This will straighten your upper back and increase stability when you lie on the bench. You can press your upper back into the bench, this will increase the effectiveness of the exercise. Be sure to squeeze your shoulder blades together before removing the bar from the rack.
Stay on your toes (don't relax). do not stick your shoulders forward (up). You'll lose tension in your upper back, your pectoral muscles will weaken, and your arms will rise higher than they should - you'll struggle. Keep your upper back toned, pull your chest forward and shoulders back. Do not lose tension even when you are helped to remove the weight or return it to the rack. Remember to press your upper back into the bench with each repetition.
Breast

Raise your chest toward the ceiling as you press. Notice that my T-shirt is thicker on the right. My breasts are fuller. This is a more efficient way to bench press
Raise your chest. When preparing to perform the exercise, squeeze your shoulder blades together. Lift your chest. Do this by arching your lower back (lower back) and rotating your ribcage upward. Keep your pelvis on the bench. Contract (tighten) your latissimus dorsi muscles to maintain the correct position. This position shortens the stroke of the rod and reduces the movement of the rod in the horizontal plane.
The chest should not remain flat. By performing the bench press with a flat chest, you force the barbell to touch your chest at a very low point. The farther the barbell is from your shoulders, the harder it is to lift it. If your chest is flat, you risk dislocating your shoulder joints and injuring them. You will not “cheat” the range of motion by pushing your chest forward; on the contrary, you will do the exercise more effectively and safely.
Lower Back

Bend in the lower back. Do bench presses with an arched back. Lie down on the bench so that there is a natural arch in your back. Your palm should fit freely between your lower back and the bench. The curve will help you lift your chest. It will increase the effectiveness of this exercise. When bending your lower back, do not forget to keep your pelvis strictly on the bench.
Don't overdo it. The curve in the lower back should not resemble a horseshoe. Still, some athletes bend excessively to cope with the heavy weight. We do not recommend that you do this - as it injures the spinal discs. Some people believe that excessive arching in the lower back is “cheating” because... this reduces the distance of movement of the barbell. Remember that the curve in the lower back should be natural.
You cannot do the bench press with a flat and even back. Our goal is to do the bench press with your chest up. This position is safer for the shoulders and helps to cope with heavy weights. A flat back will not allow the chest to rise up and pull the shoulder blades together. Maintain a natural arch in your lower back to stay toned (keep your muscles tense). Excessive bending can lead to pain.
Pelvis

Do not lift your heel off the bench.
The pelvis should always be on the bench. During the bench press, keep your pelvis on the bench. Your lower back can be lifted off the bench, unlike your pelvis, otherwise the repetition will not count. During the bench press, your feet should rest on the floor, and your upper back and buttocks should rest on the bench.
Never lift your pelvis off the bench. Lifting your pelvis off the bench is cheating. This simplifies the press by reducing the trajectory of the barbell. During a pelvic lift competition you get 3 red lights. In addition, you risk injuring your lumbar spine if you overbend your back. If you lift your hips while doing a bench press, the rep doesn't count.
Legs

Keep your feet flat on the floor. Do not place your feet on the bench or elevate them while bench pressing. This puts you in an unstable position and is ineffective when lifting heavy weights because... you cannot use support in your legs. Keeping your feet on the floor increases your stability, balance and strength. This will help you maintain the correct position of the chest (up) and the natural arch in the lower back.
Heels on the floor. Do the bench press only when your entire foot is on the floor. Don't lift your heels off the floor as this reduces your stability. The larger the area of support, the better you maintain balance during the exercise. Some athletes bench press with their heels raised, but the World Bodybuilding Organization does not allow this.
Squat with a barbell. During the bench press, your feet (heels) should be shoulder-width apart. Use the same position when doing barbell squats. Do not bench press if your feet are narrower than shoulder width; this position is less stable. If your hips hurt or cramp, your feet (legs) are too wide apart. Place your feet narrower, shoulder width apart. Rotate your feet 30º so they are in line with your hips.
Knees over ankles. This means your knees are bent at a 90º angle and your shins are vertical. Don't bench press with your ankles in front of your knees, this will prevent you from pushing off the floor and will reduce your strength. Your ankles can be slightly over your knees as long as you don't lift your heels off the floor or make an excessive arch in your lower back.
Seated press in the simulator. We study all the subtleties and secrets.
Hello again! Today on the agenda is the seated bench press. After reading, you will learn everything about the muscle atlas, the advantages and technique of performing the exercise, we will also conduct some comparative analysis and find out the degree of its effectiveness and advisability of using it in your training program.

So, make yourself comfortable, let's begin.
Seated press in the simulator. What, why and why?
Do you know what Monday is in any gym? And I’ll answer you - this is bench press day. Somehow it so happened that the first day of the week, gym goers devote themselves to the horizontal bench and the classic exercise, bench press. If a horde of newcomers comes to your gym, then rest assured that you won’t be able to see the bench like your ears :). However, the latter is not at all a reason to take off your uniform, pack your bag and head home, no. You can always find an alternative, and on the pages of the project we always try to present our audience with different, sometimes very extravagant, exercises. Today on the agenda is just one of the alternatives to the classics of the genre - bench press - seated press in a machine. This is what we will talk about later in the text.
Note: For better assimilation of the material, all further narration will be divided into subchapters
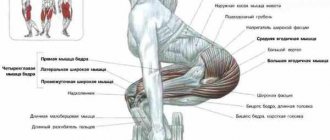
Muscle atlas
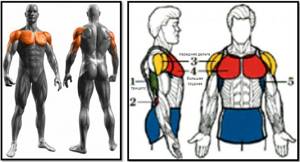
The exercise belongs to the multi-joint class with a push type of force and has as its main goal working the pectoral muscles.
The muscle ensemble includes the following units:
- targeted – pectoralis major (sternal head);
- synergists – pectoralis major (clavicular head), anterior delta, triceps;
- dynamic stabilizers – biceps (short head).
A complete muscle atlas looks like this.
Advantages
By performing the seated press exercise in a machine, you can expect to receive the following benefits:
- targeted work/isolation of the middle of the pectoral muscles;
- increase in chest muscle mass;
- blood filling (pumping) of the central pectoral region;
- allows you to eliminate chest asymmetry (together with other exercises);
- good pectoral stretch;
- the ability to perform in case of problems with the classic bench press;
- safety and the ability to work without an insurance partner;
- the ability to work with increased weights in the negative phase;
- increased working weight, due to a fixed trajectory of movement and lack of use of stabilizer muscles;
- improving the shape of the bust without the risk of pumping up the breasts (relevant for girls).
Execution technique
The seated press in the simulator is an exercise of entry-level complexity. The step-by-step execution technique is as follows.
Step #0.
Set the required weight and sit in the bench press machine, firmly resting on its back and legs slightly apart. Without lowering your elbows down, place your hands (with an overhand grip) on the handles and pull them towards you until your shoulder blades are slightly brought together. This is your starting position.
Step #1.
Inhale and as you exhale, straightening your arms at the elbow joints, press your arms forward (using your chest). At the end point of the trajectory, hold for 1-2 counts and perform a peak contraction (additionally squeezing your pecs). Return to IP. Repeat the specified number of times.
In the picture version, all this disgrace looks like this.

Variations
In addition to the classic version of the seated bench press, there are several variations of the exercise, in particular:
- bench press with handles on top;
- bench press from the lower block of the crossover.

Secrets and subtleties
To get the most out of the exercise, follow these guidelines:
- at the starting point of the trajectory, try to further stretch your chest;
- at the end point of the trajectory, additionally squeeze the chest;
- do not lower your elbows down, they should be in line with your wrist;
- during the bench press, do not lift your back from the support of the machine;
- the height of the seat of the simulator should be such that the arms extended forward are at the same level as the chest muscles;
- slowly “pull” the machine towards you and quickly/explosively press the weight away from you;
- breathing technique: inhale to bring the simulator towards you, exhale to force/squeeze the weight;
- numerical training parameters: number of approaches/repetitions – 4-5x15-20 .
We're done with the theoretical side, now let's look at some practical points.
Bench press VS seated press. What to choose?
The machine press is an excellent option for beginners and especially girls who do not like barbells and free weights. In addition, the seated press, when performed, does not create a significant increase in pressure in the head, which cannot be said about the bench press. Therefore, the sedentary option is more preferable for people suffering from high blood pressure (hypertension).
In the seated press, the movement is carried out along a strictly defined trajectory, and the athlete does not need to connect stabilizer muscles to “catch” his technique. In addition, it has a more gentle effect on the anterior delta, allowing it to be avoided from injury. In turn, the horizontal press is preferable for those athletes who want to enlarge their chest and who do not have problems with joints and ligaments. It is better for beginners and girls to practice seated bench presses in a machine.
Is the seated press an effective chest exercise?
This can be determined by the electrical activity of the muscles, and this is the data obtained by researchers from the University's Department of Exercise and Sport Science (USA, 2016 ) in their analysis of various chest exercises. The following EMG values were recorded in the experimental groups:
- bench press - 100;
- bringing your arms together in the butterfly simulator - 98 ± 26.4;
- seated bench press - 79 ± 22.4;
- push-ups on parallel bars - 69 ± 15.8;
- classic push-ups - 61 ± 20.6.
Data suggests that the seated press is a fairly effective exercise for chest development, and coupled with its technical simplicity and safety, it can become simply irreplaceable for some categories of athletes.
Actually, we’re done with the substantive part, all that remains is to summarize.
Afterword
Are you tired of the classic bench press and want new sensations for your chest? Then include the seated bench press in your training program and soon your little ones will start playing in a new way :).
With that, let me bow out, bye-bye, until Friday!
PS: do you often use exercise equipment in your classes? Which?
PPS: did the project help? Then leave a link to it in your social network status - plus 100 points for karma is guaranteed :).
With respect and gratitude, Dmitry Protasov.
Lockout (straightening arms with apparatus on racks)

Barbell over shoulders . The barbell is in a balanced position when you hold it above your shoulders. Holding the barbell above the chest is more difficult - it is similar to a pullover (sports exercise). Test it (check it yourself): fix the barbell without weight on your outstretched arms above your shoulders. Move it to a position above your chest, then above your face, then back above your shoulders. You will notice that the latter is the easiest to hold the barbell because it is the balance point. Remember to straighten your elbows after each repetition.
Fix the position of your elbows . Finish each repetition by locking your elbows. Do not leave them in a bent position to further strain the muscles. You might fail and drop the barbell on your face and die. Keep your elbows straight so your skeleton, not your muscles, supports the weight. Take care of your elbows - don't overuse them.
Rod movement trajectory

Diagonal line. The correct trajectory of the barbell movement during the bench press is a diagonal line from the position above the shoulders to the middle of the chest and back. This trajectory is longer than a straight line (from the middle of the chest straight up), but it protects the shoulders from shoulder injury. The elbows should be positioned at a 75 degree angle to the torso in a downward position to allow mechanical impingement of the rotator cuff tendons and the front of the lower acromion. The barbell should be fixed on straightened arms in a position above the shoulders (at the balance point). To do this, you need a diagonal trajectory.
Not a vertical path. Unlike the squat and deadlift, the vertical movement of the barbell does not work and is not encouraged in the bench press. If you lift the barbell strictly vertically, it forces your elbows to spread 90 degrees. This injures your shoulders and makes the exercise more difficult. The safest and most effective way to perform a bench press is to maintain a diagonal trajectory from above your shoulders to the middle of your chest and back.
Raise your chest. The trajectory of the barbell cannot be vertical during the bench press. Otherwise, you place your elbows wide and raise the bar directly above your chest. It is not safe for your shoulders and is ineffective. Push the barbell from your chest in a diagonal path, then make the path more vertical by lifting your chest. Lower the bar to the middle of your chest (chest up). Keep your pelvis on the bench.
Breath
Inhale. Remove the barbell from the rack while holding it above your shoulders. Inhale, hold your breath and lower the bar. Inhalation will help you keep your muscles toned (tensed). This will also help you keep your chest up, your shoulder blades retracted, and your lower back arched. Don't inhale (breathe) when you lower the bar, your muscles won't be tense (you won't be toned).
Hold your breath in the lower position. Do not exhale when the bar is in the down position. Your chest will deflate like a balloon, you will lose tone and it will be very difficult for you to lift weights. Hold your breath as you lower the barbell down. Your blood pressure will rise, but it will return to normal when the exercise is over. And muscles trained by the bench press will help lower blood pressure because there will be less load on the heart (literal translation - I seriously doubt the reliability of the information).
Exhalation. Exhale as soon as you fix the weight on straightened elbows above your shoulders. But don't exhale completely between reps - you'll lose muscle tone. Experienced athletes do several repetitions on one breath. take a deep breath before doing your first rep. Don't breathe deeply between repetitions to avoid losing muscle tone. You can exhale slowly through the glottis (anatomical) while raising the barbell, provided that your pressure is too high.
Seated bench press. Exercises for the pectoral muscles
- July 5, 2018
- Workouts in the gym
- Tatiana Udalova
An age-old question among bodybuilders: which is better for building muscle - machines or free weights? Why not use both? In this article we will look at the best exercises for the chest muscles that can be performed in specialized machines.
Exercises
All chest muscles can be roughly divided into three parts - upper, middle and lower. Each part is better stimulated depending on the change in angle at which you perform the exercise.

- For the upper part, exercises performed on a bench at an upward angle of 30-45% are best suited.
- For the middle part, exercises performed on a flat bench are best.
- For the lower part, exercises performed on a bench at a downward angle of 30-45% are best suited.
All chest exercises must be performed with perfect form because poor form can become a habit that will lead to lack of progress or worse, injury in the future. The following are exercises you can do to train your chest muscles, and a step-by-step guide will help you achieve perfect technique.
Seated bench press
There are various options for simulators for performing this exercise. However, absolutely all of them are designed to work the pectoral muscles. The trajectory of movement that the machine sets allows you to focus on the target muscle group while minimizing the involvement of the shoulder muscles.

The horizontal bench press allows you to work the muscles from different angles compared to the standard vertical bench press. Some exercise machines allow you to adjust the seat height, which allows you to shift the emphasis to the upper or lower part.
- Get on the machine and choose the weight that's right for you. Hold the handles of the machine with your palms facing down and raise your elbows so that your upper arms are parallel to the floor. Push the handles forward and extend your arms. This is the starting position.
- As you inhale, pull the handles of the exercise machine towards you. As you exhale, push them away from you. Hold the squeeze for a second before returning to the starting position. Try to keep your shoulders and back on the bench.
- Do the recommended number of repetitions. Slowly return the handles to place when you finish your set.
Do 3 sets of 10-12 reps, resting 45 seconds between sets.
Seated Angle Press
This exercise is almost identical to the classic bench press in a seated machine. However, the machine in which it is performed has an incline bench, which allows you to better focus on the upper part of the pectoral muscles.

- Start by adjusting the seat of the bench so that the arms of the machine are in line with your upper chest. Also set the appropriate load. Sit on a bench and grab your hands. This will be your starting position.
- As you inhale, begin to slowly push the handles of the machine forward until your arms are fully extended. You should feel a stretch in your pectoral muscles. Hold this position for a couple of seconds and then slowly return to the starting position.
- Do the recommended number of repetitions.
Seated bench presses on the pectoral muscles will allow you to effectively work out your muscles. Do 3 sets of 10-12 reps, resting 45 seconds between sets.
Smith machine chest press
This exercise is perfect for beginner athletes who are just learning to feel their muscles. The bench press with free weights allows you to move through a greater range of motion, but it is not as safe. The Smith machine has hooks that you can use to secure the barbell if you feel like you can't complete a rep.

If you are new to this exercise, ask a trainer or friend to guide you. If this is not possible, then do not lift heavy weights to avoid injury.
- Place a flat bench under the machine. Then set the barbell to such a height that you can reach it with straight arms from a lying position. Once you have established a weight that suits you, lie down on a flat bench. Place your hands on the barbell at a shoulder-width distance apart, using a pronated grip. Remove the bar from its safety catches and hold it straight above you with your arms extended. This will be your starting position.
- As you inhale, gradually lower the barbell until it rests on your mid-chest. As you exhale, after a short pause, return the barbell back to its original position. Hold at the top for a second, and then begin to slowly lower the barbell down again.
- Do the recommended number of repetitions. When you're done, lock the barbell into the machine.
Do 3 sets of 10-12 reps, resting 45 seconds between sets.
Hand curls in the simulator
To train your chest, it is important to combine two types of movements: compression and deep stretching. The hand pinch machine helps you do both of these. The butterfly exercise (peck-deck) is an isolating exercise that allows you to strongly compress the chest muscles and then stretch them in a negative phase.

- Set the weight that suits you. Your shoulders should be parallel to the floor, so adjust the machine accordingly. Sit with your back resting on the exercise pad. Take your pens. This will be your starting position.
- As you exhale, slowly begin to bring your arms together, squeezing your chest muscles. Hold the contraction for a second at the peak point. As you inhale, return under control to the starting position until your pectoral muscles are fully stretched.
- Do the recommended number of repetitions.
A good training option would be to combine hand presses in a machine with push-ups. Once you complete 20 reps, move on to 20 push-ups. Perform 3 supersets in this manner, taking a 60-second break between exercises.
Mistakes in training the pectoral muscles
The two biggest mistakes most people make in their training are:
- Focusing on the wrong exercises. Many people pay excessive attention to machines and isolation exercises, which have a secondary role in creating impressive muscle mass in the chest muscles.
- Lots of repetitions. Repeated training will only tone the muscles, but not build them.
The more you perform compound movements with heavier weights (80-85% of your maximum and above), the better your results will be.
Conclusion
So, we've looked at the basic exercises you can do to pump up your chest muscles. Be sure to try incorporating them into your next upper body workout. However, exercise machines are not a panacea, so try to make your training voluminous and varied, also working with free weights.
Narrow grip

Close grip bench press. Set up the bench in the same way as for a regular bench press. Lie down on the bench. Raise your arms up. Take the barbell with a narrow grip (hands shoulder-width apart). In the upper position, the hands should be above the shoulders, and in the lower position, next to the body. This is the same grip you use when doing overhead presses. Lower the barbell to the middle of your chest and press it back up.
The bench press with a narrow grip is more difficult to do than with a medium grip. The trajectory of the barbell is longer because in the top position your arms are vertical. This is an exercise to develop the triceps, so the pectoral muscles work less. While using the same muscles, the close-grip bench press puts 20% less stress on the chest muscles.
The close grip bench press is a good complementary exercise. A close grip keeps the elbows close to the body. If your shoulders hurt when doing the bench press correctly, change your grip to a narrower one. Many people who suffer from shoulder pain with a medium grip can perform the bench press with a close grip without pain. You'll lift less weight, but it's better than not bench pressing at all.
Just don't grab the barbell with a too narrow grip. Your hands should not touch each other. In this case, your hands are too far from your forearms - your hands will hurt, and it will be difficult to keep the barbell in balance. With a narrow grip, your hands should be approximately shoulder-width apart.
Incline Bench Press
The incline bench press is done on an incline bench.
Set the bench at an incline of 45. Lie on the bench with your feet on the floor and grab a barbell with a medium grip. Remove the bar with straight arms, lower the bar to your upper chest, and then raise it to a position above your shoulders. Do not lift your pelvis off the bench, maintaining a natural arch in your back. We recommend performing this type of bench press in a power rack to avoid injury if you cannot handle the weight. Many people do this exercise to tone up their upper chest. But you can’t isolate any specific part of the muscle. The pectoralis muscle is a biceps muscle, part of which attaches to the collarbone and the other to the ribs. They always work together no matter what bench you do, you won't be able to isolate one of them.
The best way to build (pump up) your upper chest is to do (improve) the bench press and overhead press. The bench press engages all of the pectoral muscles, while the overhead press puts more emphasis on the upper chest because it is somewhat similar to the bent press. The stronger your pectoral muscle (pectoralis), the larger it becomes.
It also promotes the development of external and internal chest muscles. The minor pectoralis muscles are located under the major pectoralis muscles, so they are not visible. The main muscles you work with are the main pectorals. And the best way to pump them up is to improve your bench press.
Bench press on an incline bench
The incline barbell bench press targets the upper portion of the pectoralis major muscle. In this version of the exercise, you need to lower the barbell to the top of your chest.
Main working muscles:
- Chest muscles (upper part to a greater extent than with a bench press)
Additional muscles worked:
- Deltoid muscles (anterior bundle)
- Triceps
Initial position:
Lie on an incline bench (45 degree incline) and grab the bar with a grip slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. The shoulder blades are retracted. There is a deflection in the lower back. The legs rest firmly on the floor.
Exercise technique:
- Smoothly, while inhaling, lower the barbell until it touches your upper chest.
- As you exhale, press the barbell up, returning to the starting position.

Reverse Bench Press
Position the bench so that your thighs are higher than your head.
You need a bench with a reverse incline and a leg lock so that you do not slip into them during the exercise. Lie down on a bench, grab a barbell, lower it to your chest, and then press it up. We recommend performing this variation of the press with an assistant who can pick up the weight if the repetition fails. Many people do reverse bench presses to tone their lower chest. The reverse bench press is a waste of time. You won't be able to isolate the lower chest because the chest muscles act as one unit. It's like doing half a squat. Just improve your bench press and your lower chest will grow.