11/27/2019 Article
- general characteristics
- Table "Do's and Don'ts"
- Menu for the week
The “6 table” diet is used in the treatment of urological diseases. Indications for using the diet are:
- gout,
- urolithiasis with the formation of stones from uric acid (uraturia),
- uric acid diathesis,
- oxaluria,
- cystinuria.
The essence of the diet is to limit salts, proteins, fats and exclude products that contain extractive nitrogenous substances, purines and oxalic acid. The diet consists largely of vegetables, fruits and dairy products.
Why is this diet needed for gout?
Excluding foods rich in purines from your diet allows you to:
- dramatically reduce their intake and breakdown in the body;
- reduce the content of intermediate decomposition products (sodium urates).
As a result, the deposition of salts in tissues stops. If a patient with gout constantly adheres to the basic rules of a healthy diet (diet No. 6), the formation of salts will dissolve over time and may disappear completely.
Why follow a diet for gout:
- To speed up recovery during acute periods. In this case, experts recommend strict adherence to dietary rules, taking into account prohibited and permitted foods.
- To prevent exacerbation, the formation of gouty tophi (salt deposits) and kidney stones. During the asymptomatic period of gout, it is enough to adhere to the general rules of diet. Preference is given to vegetable vegetarian dishes, the amount of meat and animal fats is reduced to a minimum. There may be some minor deviations. Menu dishes and their variations can be used as a basis for a healthy diet.
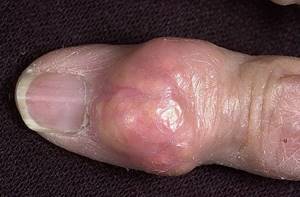
Gouty tophi on the finger
The full menu of table 6, or the Pevzner diet - a list of dishes that can be prepared from permitted products. During an exacerbation of gout and throughout the rest of your life, a weekly menu is necessary to make your diet varied and healthy.
This means that the rice vegetable soup recommended for lunch on Wednesday can be replaced with vegetable stew. The main thing is not to exceed the recommended daily intake of proteins, fats and carbohydrates for gout.
Authorized Products
The diet cannot be called too strict. Permitted products include:
- any soups, but without meat broth, can be made with milk, vegetables, and added cereals;
- cereals are also not classified as prohibited products;
- You should lean on greens and vegetables, you can eat them in unlimited quantities, or at least emphasize them in your diet;
- It is allowed to consume low-fat fish and meat, but not more than 3 times a week, in a volume of 150-160 g;
- you can eat 1 egg per day, no more;
- fruits and berries are also classified as recommended foods that can be consumed in unlimited quantities, they can be raw or processed;
- You can have dairy products, fermented milk: kefir, cottage cheese and even hard cheeses;
- You can have sweets, but without chocolate, for example, jam, jelly, honey pastille and marmalade;
- For bakery products, it is recommended to give preference to products with bran, wheat and rye bread, at least grade 2.
- It is permissible to consume ghee, butter and vegetable oil.
Among the drinks, tea, coffee, but not strong coffee, milk, juices, compotes and even kvass are not prohibited.
Rules and features of the diet
The basic rules of the diet for gout (table) No. 6 concern several points:
- content of chemicals in food;
- energy value of eaten dishes and products (in kilocalories);
- weight or mass of food eaten;
- power mode.
Content of chemicals in the daily diet for gout:
| Substance | Weight |
| Fat – saturated fatty acids | 80–90 g |
| Squirrels | No more than 80 g |
| Carbohydrates | 400–450 g |
| Salt | No more than 8–10 g |
| Liquid | From 2 to 2.5 l |
All food eaten per day, according to the rules of a therapeutic diet for gout:
- divided into 5 parts (techniques - at equal intervals of time);
- energy value does not exceed 2700 Kcal;
- maximum total weight – 3 kg.
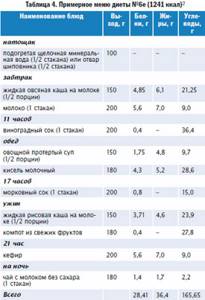
Content of chemicals in foods recommended for gout
Only meat requires special preparation. Before any processing (stewing, baking), boil it for 15 minutes and pour out the first broth (this is necessary to reduce the content of purine compounds).
If you have gout, it is strictly not recommended to fast; it is better to periodically “unload” (for example, eat only vegetables and fruits).
Video consultation
In the following video, a specialist will tell you how to eat so that uric acid does not deposit in the joints, does not cut cells and, thus, does not cause attacks:
The content of purines disrupts the metabolic process in the body, which leads to uric acid retention, salt deposition and gout. To stabilize the condition and prevent exacerbations, you need to follow a diet to reduce the accumulation of uric acid in the body.
Add a comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
What not to eat
Diet number 6 for gout completely prohibits or greatly limits the use of:
- Fatty meat and offal.
- Strong decoctions of meat (broths).
- Pickled, smoked, pickled, canned food.
- Spicy, mature cheeses, sausages.
- Black coffee, tea, alcohol.
- Dried fruits (with the exception of prunes), figs.
- Muffins, chocolate, cocoa.
- Mushrooms, legumes (soybeans, beans), spinach, rhubarb, sorrel.

Menu for 7 days
The complete menu of diet number six (table number 6) for 7 days, scheduled by day of the week. In the left column of the tables is the number of meals, in the right - what to eat at this time.
First day
| 1 | Corn flakes in milk with dried apricots and prunes, a decoction of rose hips or chokeberries |
| 2 | Low-fat cottage cheese cheesecake |
| 3 | Vegetable soup with rice or buckwheat, potatoes stuffed with stewed vegetables, oatmeal jelly |
| 4. | Carrot-beet juice (freshly squeezed juice) |
| 5 | Pancakes or pancakes with banana, vegetable salad with boiled egg, fruit mousse |

Banana pancakes
Second day
| 1 | Vegetable salad (green salad, cucumbers, tomatoes, cottage cheese) with sour cream dressing, bran bread toast with berry marmalade, herbal tea |
| 2 | Biscuits (dry cookies), a portion of yogurt |
| 3 | French vegetable soup with leeks, eggs and croutons, baked beet caviar, fresh apple and banana |
| 4 | Fruit yogurt |
| 5 | Potato croquettes on a vegetable bed, berry marmalade with cottage cheese, herbal herbal tea |

Potato croquettes with vegetables
The third day
| 1 | Millet porridge with pumpkin in milk, tomato juice |
| 2 | Corn flakes with yogurt |
| 3 | Vegetable casserole (potatoes, onions, pumpkin, carrots, bell peppers), steamed chicken meatballs, fresh berry jelly |
| 4 | Toast with berry jam, green tea |
| 5 | Steamed vegetable rolls stuffed with rice and vegetables, cottage cheese, fermented baked milk |

Corn flakes with yogurt
Fourth day
| 1 | Steamed cottage cheese dumplings, fresh berry jelly or mousse, herbal herbal tea |
| 2 | Carrot rice casserole with jam |
| 3 | Fish soup (ukha), mamalyga (corn porridge), yogurt with fresh berries or prunes |
| 4 | Infusion of chokeberry, rosehip, biscuits |
| 5 | Potato boats with vegetables, eggs and cottage cheese, salad and fresh vegetables and flaxseed oil dressing, herbal tea with berry jam |

Fish soup
Fifth day
| 1 | Carrot-curd-pumpkin casserole, corn flakes with milk, fresh tomato |
| 2 | Toast with marmalade, tea |
| 3 | Noodle soup with milk, oven-baked potato balls with sour cream, curd mousse with prunes, fresh carrots |
| 4 | Oatmeal jelly, apple |
| 5 | Vegetable caviar or stew, boiled chicken breast, dried fruit jelly |

Noodle soup with milk
Sixth day
| 1 | Pancakes or pancakes with fruit and berry jam, soft-boiled egg, green tea |
| 2 | Cheesecake or cottage cheese pudding |
| 3 | Borscht or cabbage soup in vegetable broth, fish in a “pocket” of vegetables, baked in the oven, vinaigrette, compote |
| 4 | Yogurt with corn or oat flakes and prunes |
| 5 | Vegetable stew with rice, baked in pumpkin, fruit or berry mousse, tea |

Vegetable stew with rice
Seventh day
| 1 | Cereal flakes with milk with prunes or banana, salad of tomatoes and young cheese with olive oil dressing, tea or compote |
| 2 | Vegetable (tomato) or fruit (carrot-apple) juice |
| 3 | Vegetable puree, steamed chicken rolls, whole grain toast, tea marmalade |
| 4 | Pear with cottage cheese |
| 5 | Dolma (stuffed cabbage rolls in grape leaves) with stewed cabbage and rice, boiled potatoes with dill, toast with berry marmalade or marshmallow, tea |

During an exacerbation, the diet for gout should be completely vegetarian, meat and fish should be completely excluded from the diet.
Recommended Diet
If nutrition is properly organized, then gout will recede. Recommendations for the consumption of products are based on this principle. If uric acid is high, the menu can be varied:
- various vegetable soups, incl. with the addition of cereals;
- marine cephalopods and crustaceans;
- low-fat fish;
- rabbit meat;
- cereals and pasta;
- yoghurts;
- sour cream and low-fat cheeses.
Lunch can be safely flavored with dill, eating wheat or rye bread. Vegetable proteins can be consumed in large quantities.

For gout, foods should not increase the level of purines, and therefore the consumption of vegetables (except those named in the restrictive list) increases:
- apples (especially green ones);
- dried fruits (except raisins);
- honey;
- nuts;
- sunflower seeds;
- citrus fruits;
- berries (except raspberries).
You can diversify the menu for every day:
- marshmallows;
- marmalade;
- jam.

Care must be taken when preparing food. You can cook it with butter or vegetable oil, but you should avoid using animal fat, especially pork and lamb. Preference should be given to boiling, stewing, and steaming. Fried food is allowed only in limited quantities.
An important condition for diet therapy for gout is the organization of weekly fasting days with a strict diet.
On such days, only one type of selected dietary product is consumed, which makes it possible to normalize a certain direction of the metabolic process. You can adhere to a vegetable, fruit, dairy, kefir or cottage cheese diet. The rice-apple diet is popular.
Simple 6 diet recipes for gout
Foods for gout are boiled in water, steamed, stewed or baked. Frying in oil or fat is strictly contraindicated.
For soups, only vegetable broths are used; olive or flaxseed oil, flax seeds, low-fat sour cream, and cream are used as salad dressings.
Several recipes for diet 6 dishes for gout:
- Pumpkin (or broccoli) puree soup recipe. Cut 500 g of pumpkin into pieces, place in a saucepan, pour in 300 ml of low-fat milk, add salt and peeled onion. Boil until tender (the pumpkin is pierced well with a fork and crushes when pressed) over low heat. Remove the onion from the broth (you can throw it away). Place the pumpkin pieces in a blender, add half the milk in which it was boiled, 2 tbsp. l. low-fat sour cream and grind until smooth. Serve with finely chopped dill and croutons.
- Recipe for fish in vegetables. Cut vegetables into pieces: carrots, onions, bell peppers, eggplants, place in a shallow frying pan, add salt and 2 tbsp. l. low-fat sour cream. Simmer over low heat, covered, until half cooked (5-10 minutes). Divide the vegetables into 2 parts. Place one vegetable layer on the bottom of the baking dish, cover the second layer with a piece of fish (150 g pollock or hake fillet). Bake for 15–20 minutes.
- Dolma (stuffed cabbage rolls in grape leaves). Mix minced chicken with boiled rice. To keep the minced meat in shape, add a couple of tablespoons of semolina, add salt, and leave for 1.5 hours. Wash large grape leaves, pour boiling water over them, wrap a small ball of minced meat in them, and place tightly in a saucepan or saucepan. Top each layer with stewed cabbage and 2 tbsp. l. sour cream. Add 1 glass of water, cover with a lid, simmer until cooked (depending on the number of layers, approximately 30–40 minutes).

Stuffed cabbage rolls in grape leaves
Indications
There are several main medical indications, in the presence of which diet 6 is prescribed, these include:
- Gout.
- Uric acid diathesis with an increased likelihood of the formation of insoluble stones in the hollow structures of the urinary tract.
- Uraturia is an increased excretion of insoluble urate salts in the urine.
- Urolithiasis - diet 6 is a prerequisite for successful treatment of the formation of insoluble stones in the hollow structures of the urogenital tract, as well as for the prevention of the pathological condition.
- Oxaluria is an increase in the concentration of insoluble acid salts of oxalates in the urine, which is the initial stage of the development of urolithiasis.
- Cystinuria is an increase in the level of certain insoluble salts in the urine that have an acidic reaction. The pathological process in most cases is of hereditary origin.
The effectiveness of this diet for gout
Doctors believe that the effect of diet No. 6 on the successful treatment of gout is somewhat exaggerated. Recent studies have shown that nutritional therapy reduces uric acid levels in the body by 15%. A proper diet for gout is effective only in combination with the following recommendations:
- get rid of excess weight;
- do not give up vegetable protein (legumes, mushrooms, corn), as it is absorbed more fully and is not capable of causing an increase in intermediate breakdown products (urates);
- add more unsaturated fatty acids (vegetable oil) to your diet - they indirectly affect glucose levels and reduce the risk of diabetes (and the associated risk of increased uric acid).
Controversial issues remain regarding the use of such products as:
- Alcohol – Some experts believe that red wine for gout regulates sodium urate levels and prevents the formation of stones.
- Coffee is a drink that has diuretic properties and promotes intensive urine excretion.
- Animal proteins - it is believed that they are not so dangerous and their norms in the diet of gout patients need to be reconsidered.
Consult your physician before following the latest nutritional recommendations.
Fully or partially limited products
First of all, the diet should not contain fish or meat broth. You will have to give up marinades and pickles. Legumes, sorrel and all vegetables containing high amounts of oxalic acid are prohibited. Consumption of offal, raspberries and cranberries is unacceptable. You should not eat baked goods or baked goods with powdered sugar. Sausages, mushrooms, hot peppers, seasonings, or rather mustard and horseradish, are prohibited.
Naturally, no alcohol should be present during treatment.
Despite the fact that you can drink milk, you should not get too carried away during the day and drink more than 500 ml. The same goes for potatoes; you can eat no more than 1 serving during the week, regardless of the cooking method. Sweets should also be consumed in moderation, at the rate of 4 tbsp. l. sugar throughout the day.
Forecast
Despite conflicting data and studies on the need for table No. 6, any drug therapy for gout is not effective enough without following the rules of proper nutrition.
With the diet, the patient’s well-being noticeably improves. 70% of patients switch to a maintenance dose of medications 2 times faster.
Experts recommend following a strict diet during periods of exacerbation - during inflammation and pain. In the future, it is enough to follow its basic principles (give preference to plant foods, reduce the content of animal protein).
Since gout is an incurable disease, a more or less strict diet will have to be followed throughout life.
Doctor's opinion
Diet 6 was developed by physician Pevzner to improve the metabolism of uric acid in gout. At the same time, first of all, it was possible to achieve a decrease in the flow of nucleotides into the human body, which accordingly affected the course of gout. Within a few days after starting food intake, the patient’s general condition improved, and the frequency, duration and severity of gout attacks decreased. By reducing the functional load on the digestive organs, their work improves, dyspeptic symptoms, including bloating (flatulence), stool disorders, and discomfort in the stomach, are reduced. In the presence of concomitant obesity, the use of a modified diet 6 made it possible to reduce the patient's body weight. Dietary recommendations can be carried out in a medical hospital or at home. Table 6 is recommended for people with a hereditary predisposition to the development of gout to prevent pathological disorders of nucleotide metabolism.











