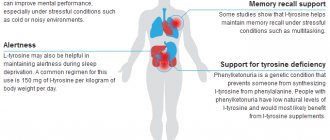
Tyrosine is an important precursor to neurotransmitters and substances such as adrenaline, norepinephrine and dopamine. This means that it helps the body produce chemicals that support the thyroid gland and increase energy and mood. This is why some people claim that taking this amino acid can help “boost your metabolism.” As you can see, the health benefits of tyrosine are obvious!
Tyrosine is found naturally in foods, and there is a lot of it in cheese. Soy products such as tofu, tempeh and soy milk are especially high in it. Nuts, seeds and eggs are also good sources of tyrosine. Chicken, beef and seafood also contain decent amounts.
Tyrosine is also available in supplements, which some people take when trying to lose weight.
Levels of the amino acids tyrosine and tryptophan fluctuate depending on the consumption of protein or carbohydrate-containing foods. This means that for most people, it's best to include both types of these macronutrients in your diet. While eating complex carbohydrates can increase feelings of calmness and even sleepiness, thanks in part to tryptophan, which increases serotonin levels. Eating protein tends to increase alertness and the ability to concentrate due to increased tyrosine levels.
What is tyrosine needed for?
Tyrosine, or L-tyrosine, is one of 20 amino acids that are involved in protein building. L-tyrosine is considered an "essential amino acid." The body can produce tyrosine on its own—provided it has enough building blocks. These building blocks are the amino acid phenylalanine and nutrient cofactors such as vitamin C and vitamin B6. The body needs tyrosine in large quantities during times of stress, and its natural reserves in the body are depleted with age.
What are the health benefits of L-tyrosine?
The health benefits of L-tyrosine include fighting fatigue, depression, poor cognitive function, and possibly weight gain.
Does tyrosine increase dopamine?
Yes—the production of dopamine and norepinephrine is affected by the amount of tyrosine you eat or get from supplements. Dopamine and norepinephrine are produced from tyrosine with the help of a number of other nutrients such as folate, B vitamins , copper and magnesium .
general characteristics
Tyrosine, also known chemically as 4-hydroxyphenylalanine, is one of the 20 amino acids required for protein synthesis.
And since the human body is able to independently produce this substance, it is considered a non-essential amino acid. This means that a healthy person does not need additional supplements to provide themselves with the required amount of tyrosine. This amino acid affects many processes in the body, including the production of neurotransmitters.
The word "tyrosine" comes from Greek and is translated as "cheese". The amino acid received its name in 1846, when it was first discovered by the German chemist Liebig in casein, a protein found in cheese. And its chemical name indicates that tyrosine can also be synthesized from another amino acid - phenylalanine.
There are 3 forms of tyrosine: L-tyrosine is an amino acid, found in the proteins of all living organisms, D-tyrosine is a neurotransmitter, found in enzymes, DL-tyrosine has no optical energy.
Health Benefits of Tyrosine
Tyrosine for depression and stress
What does tyrosine do for the brain?
Tyrosine helps the brain produce neurotransmitters. These are biologically active substances that transmit electrical impulses between neurons. Neurotransmitter production is affected by diet, especially the amount and types of amino acids you eat. Tyrosine affects dopamine levels, which regulate your satisfaction, pleasure and adrenaline centers. Adrenaline is responsible for your fight-or-flight response when you are under stress. Stressful situations increase the release of catecholamines, which can lead to their depletion in the body.
Eating more tyrosine is beneficial for people who are under a lot of stress or suffering from depression. This is because when dopamine and norepinephrine levels decrease, irritability, fatigue, and moodiness increase. A 2016 paper published in the Annals of Neuroscience states:
Hydrochloric acid in the stomach separates vitamin B12 from the protein it is attached to in food. Vitamin B12 in the body then combines with a protein produced by the stomach called intrinsic factor and is absorbed by the body.
There is evidence that higher levels of tyrosine in the body can improve mood and increase alertness. And also improve stress resistance and overall cognitive functioning. According to research, tyrosine is also beneficial during physical activity. This is especially true for the military. For example, when soldiers are exposed to stress at high altitudes or while awake for long periods of time.
However, some experts believe that tyrosine is not effective enough to truly reduce stress in most people. And not all studies have shown that this amino acid has a significant antidepressant effect.
Benefits of Tyrosine for Increased Energy and Mental Performance
Does Tyrosine Make You Drowsy?
As a rule, no. In fact, tyrosine tends to do the opposite. While tryptophan is known to increase sleepiness, tyrosine is thought to improve concentration and productivity.
How does tyrosine provide energy?
Research shows that during stressful situations, tyrosine can reduce mental stress and help with cognitive functions, including memory. Tyrosine is useful because it has a stimulating effect. In this regard, it is recommended to use it during intense training loads, and also as an invigorating remedy for fatigue.
One noteworthy effect of taking this amino acid is increased alertness when sleep deprived. One study found that tyrosine helped increase alertness for about three hours. Observations were made among people who were deprived of sleep due to night work. Study participants were awake throughout the day when the experiment began and were awake for more than 24 hours by the end of testing. Six hours after the start of the experiment, half of the subjects received 150 mg per kilogram of body weight of tyrosine (in a divided dose), and the other half received a placebo.
Benefits of Tyrosine for Weight Loss
Will tyrosine help with weight loss?
According to the Medical University of Michigan
there are no studies specifically showing that L-tyrosine promotes weight loss
However, there is evidence that tyrosine may help overweight people with weight loss, although only slightly. This is possible when using tyrosine in combination with other natural fat-burning substances such as cayenne, green tea and caffeine. A 2007 study showed a small weight loss of about 0.9 kg when tyrosine was taken along with capsaicin, catechins and caffeine.
Can tyrosine cause weight gain?
There is no weight gain from taking tyrosine. However, there is evidence that tyrosine may help improve appetite among people who need to gain weight. For example, those who are recovering from anorexia.
Tyrosine for Metabolism and Thyroid Health
What does tyrosine do for the thyroid gland?
Tyrosine is used to produce thyroxine, a thyroid hormone. Thyroxine is the main hormone that is released into the blood by the thyroid gland. It helps regulate metabolism and control levels of thyroid hormones T3 and T4. It is important to have enough thyroxine in your body because it helps reduce symptoms of an underactive thyroid gland (hypothyroidism). Hypothyroidism causes a sluggish metabolism, fatigue, sensitivity to cold, weight gain, constipation, moodiness and weakness.
On the other hand, people with an overactive thyroid gland, including hyperthyroidism and Graves' disease, should not take tyrosine. In this case, taking tyrosine can greatly increase thyroxine levels. This may affect how your medications work and make your symptoms worse.
Tyrosine to reduce alcohol and heroin withdrawal symptoms
Research has shown that the "highs and lows of dopamine" can make people more vulnerable to addiction. The Integrative Psychiatry website states:
Dopamine, adrenaline and norepinephrine (catecholamines) are responsible for motivation, energy, interest, sexual functioning, pleasure, drive, attention and concentration. They are associated with positive stress conditions such as love, playing sports, listening to music and sex. Deficient levels contribute to depression, poor concentration, low energy and lack of motivation. Habits such as alcohol, drug use, cigarettes, gambling and overeating may also occur.
Current research suggests that tyrosine may be useful in treating heroin and alcohol withdrawal symptoms. As well as reducing alcohol consumption when used together with the drug naltrexone. A combination of tyrosine, 5-hydroxytryptophan (HTP), phosphatidylcholine and L-glutamine has been shown to improve mood and sleep ability in heroin and alcohol addicts. This is due to tyrosine's ability to balance catecholamine levels.
Why is tyrosine needed?
Tyrosine is an amino acid that is a precursor of adrenaline, norepinephrine and dopamine - mediators responsible for the conduction of nerve impulses. It is thanks to this organic compound that people experience muscle flaccidity after physical activity. In addition, tyrosine improves the functioning of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands and pituitary gland, suppresses appetite, and helps minimize fat deposits. Tyrosine is especially needed by people who subject themselves to long physical training.
Tyrosine in foods
Tyrosine is found in foods such as meat and eggs, as well as some plant foods, but in smaller quantities. Tyrosine is found to a greater extent in foods such as:
- Organic dairy products such as raw milk, yogurt or kefir
- Meat and poultry
- Fish
- Eggs
- Nuts and seeds
- Beans and legumes
- Whole grains such as oats, etc.
- Protein powders
In order for tyrosine to be converted into neurotransmitters, you need to consume additional nutrients such as vitamin B6, folate and copper. This means regularly including foods high in these nutrients in your diet. These include eggs, beef, greens, asparagus, oranges, legumes, nuts, sunflower and chia seeds. As well as whole grains such as quinoa and wheat germ, avocado and broccoli.
Unlike the amino acid tryptophan, which can have the same stimulating effect as tyrosine, tyrosine levels increase. This happens if you eat high protein foods or take supplements. Tryptophan and tyrosine actually compete with each other in the body. This means that when the level of one increases, the content of the other usually decreases.
Useful properties of tyrosine
In order to understand how important tyrosine is for our body, let's consider its basic properties. So:
- tyrosine is a source for the formation of hormones, neurotransmitters and neurotransmitters,
- with a sufficient amount of zinc and copper ions, it participates in the production of melanin - the main protector of the skin from ultraviolet radiation,
- Without tyrosine, normal functioning of the thyroid gland is impossible,
- it optimizes metabolic processes, promotes weight loss,
- reduces the number of allergic manifestations,
- increases the body's endurance during intense physical activity,
- helps to quickly restore strength,
- L-tyrosine also has a positive effect on concentration,
- improves the functioning of the vestibular apparatus,
- has a pronounced effect of detoxifying the body,
- is a powerful antidepressant,
- Tyrosine affects the intensity of heat exchange in the body,
- improves adrenal function,
- relieves PMS symptoms.
Tyrosine Supplements and Dosage Information
Tyrosine is available in powder form, capsule form, and is also found in some supplements for athletes. What are the reasons for taking a daily tyrosine supplement? Some of the most common reasons for taking tyrosine are to manage mood and symptoms of depression. And also increase energy and support weight loss.
Another reason to use a tyrosine supplement is to treat an inherited disease called phenylketonuria (PKU). In this condition, the amino acid phenylalanine cannot be properly converted into tyrosine, resulting in low levels. For people with PKU, it is best to get tyrosine from food and supplements. But there is very little phenylalanine in supplements because it cannot be artificially processed. Four to six grams of tyrosine per day is usually recommended for the treatment of PKU. Pregnant women with PKU should consume even more, up to 7.6g per day.
How much tyrosine should you take?
In most studies, adults safely took 100 to 150 mg per kg of body weight, which is equivalent to approximately 7 g per day for an adult. In some situations, higher dosages are recommended. For example, in stressful situations, to improve mental abilities, it is better to take 300 mg per 1 kg of body weight.
To increase alertness and prevent fatigue, it is recommended to divide the dose and take it in several stages. Depending on your health condition, your dosage may be individual. Therefore, it is better to start with a low dose and increase it as needed.
How much tyrosine should you take for depression?
The dosage of tyrosine for a person weighing 90 kg is 9–13.5 g and 7–10 g for a person weighing 68 kg.
When should you take tyrosine?
For greater benefit, tyrosine should be taken on an empty stomach before meals. Because eating other amino acids may interfere with its absorption. Tyrosine may stimulate and potentially reduce sleepiness. Based on this, it is best to take it in the morning, and not in the evening before bed, and especially in large quantities.
How long does it take for tyrosine to take effect?
The effects of tyrosine in supplements can be felt in as little as 30-60 minutes, depending on the dosage and timing of the meal. Consuming this amino acid on an empty stomach has a faster effect.
How to take tyrosine, dosage
Tyrosine is available in powder form, capsule form, and is found in some workout supplements. Why do you need tyrosine on a daily basis, what are the indications? Some of the most common reasons are to improve mood and alleviate symptoms of depression, as well as increase energy and for weight loss.
Another use of tyrosine supplements is to treat an inherited disease called phenylketonuria (PKU), in which the amino acid phenylalanine cannot be properly converted into tyrosine, resulting in low levels. For people with PKU, it is best to consume tyrosine from foods and supplements, but very little phenylalanine from these as it cannot be processed. For the treatment of PKU, 4 to 6 grams of tyrosine per day is usually recommended. Pregnant women with PKU should consume even more, up to 7.6 grams per day.
Tyrosine Supplements for Mood
Dopamine increases motivation and also gives us a feeling of pleasure. Your dopamine reserves may be low if you are detached from your career and setting goals for yourself. At the same time, you feel unsatisfied.
The first step to increasing dopamine levels is to replenish tyrosine. This may take up to a month of continuous L-tyrosine supplementation. Although you will probably feel some improvement within a week.
Moderate doses of 500 to 1000 mg per day are considered a therapeutic dose. There is no need to take it in large dosages - the body strictly controls the amount of dopamine. Therefore, taking a large amount of tyrosine at one time will not cause a huge surge of health-promoting chemicals.
For example, a 2021 study found that blood tyrosine levels can influence social behavior. High levels of tyrosine were associated with study participants exhibiting more distressing behavior. While low tyrosine levels correlated with participants choosing punitive measures.
Application and dosage[edit | edit code]
The single and daily dose of tyrosine is largely determined by the purposes of use. It is necessary to follow the recommendations indicated on the packaging, and it is also advisable to consult with your doctor or pharmacist regarding the dosage regimen.
People who suffer from insomnia and take tyrosine in the morning after a sleepless night may need 1500 mg of tyrosine per day. This is the maximum dose that is usually prescribed to adults. The duration of the course is approximately 3 months.
For phenylketonuria, the recommended dose of tyrosine can vary over a wide range and reach 6 grams for every 100 grams of protein consumed. It is important to consult with your doctor to select the appropriate dose for the treatment of phenylketonuria and at the same time avoid the development of unwanted side effects.
Some manufacturers of tyrosine preparations recommend taking 5 grams of this amino acid twice a day, but the feasibility is extremely questionable.
Tyrosine Supplements for Liver Support
Amino acids are essential for liver health and function. Tyrosine and its precursor, phenylalanine, are known as aromatic amino acids.
An imbalance between aromatic and other amino acids is observed in liver failure. Supplementation studies have not been conducted, but it is possible that taking L-tyrosine may help relieve cognitive symptoms of liver disease.
To further promote liver health and overall wellness, consider supplementing with tudka or even natural curcumin and turmeric.
How does a lack and excess of tyrosine affect the body?
If there is a lack of this amino acid, a person may experience low blood pressure and body temperature, and uncontrolled weight gain. An unhealthy person may experience lethargy and drowsiness, and quickly get tired. In some cases depression appears. People suffering from acquired tyrosine deficiency may experience severe mental and physical impairment. With uncontrolled consumption of tyrosine, a person may experience problems with the stomach, irritability, and increased anger. Tyrosine is not recommended for people with cancer, people suffering from schizophrenia, hypertensive patients, and pregnant women.
Precautions and side effects of taking tyrosine
What are the side effects of tyrosine?
Taking tyrosine supplements is very safe as there are few side effects from taking it. However, consuming large amounts over a long period of time may interfere with the absorption of other amino acids. Therefore, it is better to use only as much as you need.
It is possible that some will experience side effects from taking tyrosine. These may include digestive problems such as nausea, headache, fatigue and heartburn. However, high dosages of up to 20g per day have been used safely in studies on military subjects.
As mentioned earlier, people with hyperthyroidism and Graves' disease should not take tyrosine. This is because of its interaction with thyroid hormones and medications. Anyone taking levodopa (L-dopa), a medicine used to treat Parkinson's disease, should avoid taking this supplement.
Here are other common questions about the safety of using tyrosine:
Is Tyrosine safe for long-term use?
There are few studies showing the long-term effects of taking L-tyrosine, especially in large quantities. For long-term use over several weeks or months, it is best to take less than 1,000 milligrams per day. If you have not consulted a doctor about the duration of use, then it is best to take it for no more than three months. This is to avoid the risk of side effects associated with amino acid imbalance.
Is L-Tyrosine a stimulant?
Although tyrosine may reduce sleepiness, it is not a stimulant and has a milder effect than substances such as caffeine.
Is Tyrosine a concern?
In fact, tyrosine should not cause anxiety. In fact, it may have the opposite effect if it does not increase hyperthyroidism.
Does tyrosine increase blood sugar?
There is some evidence that this is possible. Conducted at the University of Texas Health Science Center. It follows that tyrosine levels are elevated in the blood of obese people with a high risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Or in people who have been diagnosed with this form of diabetes. It is possible that this amino acid affects insulin signaling. More research is needed to determine how tyrosine affects blood sugar levels.
Excess tyrosine
Excess tyrosine cannot be obtained from regular foods. This is a problem with taking high doses of the drug L-tyrosine. The usual dosage for taking this drug is 1.5 - 3 g per day, the highest single dose is 12 g per day. However, such large doses can cause negative reactions.
- From the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite, increased acidity of gastric juice, heartburn; up to stomach ulcers,
- From the nervous system: migraines, increased excitability, anxiety, insomnia, dizziness, or, conversely, increased fatigue, drowsiness.
- From the cardiovascular system: increase (decrease) in blood pressure, increased heart rate, chest pain, feeling of shortness of breath
- Allergic reactions: rash, joint pain
- Thyroid dysfunction, weight loss
If these symptoms occur, depending on their severity, you should either stop taking the drug or reduce the dosage to the recommended or minimum
Tyrosine-rich foods
A person’s well-being directly depends on the food he eats. A lack of nutrients will definitely affect human health. Tyrosine is responsible not only for a person’s mood, but also for metabolic processes in the body. If it is deficient, you may experience poor health, fatigue, and a decrease in body temperature and blood pressure. You can cope with this condition by including seafood, sesame seeds, avocado and almonds in your diet. A high-quality and varied diet will allow you to be in a great mood all the time and forget about depression.
Complete list of foods containing tyrosine
| The product's name | Amount of tyrosine per 100 g of product |
| Meat | |
| Turkey, roasted | 1.18 g |
| Rabbit, stewed | 1.18 g |
| Goose, fried | 1.10 g |
| Rabbit | 0.78 g |
| Calf tongue | 0.77 g |
| Beef liver | 0.73 g |
| Pork liver | 0.71 g |
| Veal meat | 0.69 g |
| horsemeat | 0.69 g |
| Chicken liver | 0.67 g |
| Beef meat | 0.66 g |
| Chicken | 0.64 g |
| Turkey | 0.62 g |
| Goose | 0.55 g |
| Pork meat | 0.52 g |
| Pork tongue | 0.51 g |
| Duck | 0.51 g |
| Beef tongue | 0.48 g |
| Stewed pork, canned | 0.47 g |
| Chicken breast, in the oven | 0.34 g |
| Legumes | |
| Soybeans | 1.06 g |
| Lentils | 0.78 g |
| White beans | 0.66 g |
| Yellow beans | 0.62 g |
| Black beans | 0.61 g |
| Miso | 0.35 g |
| Hummus | 0.13 g |
| Green peas, canned | 0.10 g |
| Cereals | |
| Millet, polished | 0.41 g |
| Oats, cooked | 0.36 g |
| Barley | 0.30 g |
| Manna | 0.27 g |
| Buckwheat | 0.24 g |
| Wild rice | 0.17 g |
| White rice, cooked | 0.09 g |
| Pearl barley, cooked | 0.07 g |
| Nuts | |
| Peanut | 1.05 g |
| Sesame | 0.72 g |
| Gretsky | 0.58 g |
| Hazelnut | 0.56 g |
| Almond | 0.55 g |
| Sunflower seeds | 0.54 g |
| Cedar | 0.51 g |
| Cashew | 0.51 g |
| Dairy | |
| Russian cheese | 1.35 g |
| Cheese Poshekhonsky | 1.30 g |
| Cheddar cheese | 1.27 g |
| Dutch cheese | 1.39 g |
| Swiss cheese | 1.26 g |
| Roquefort cheese | 1.21 g |
| Cottage cheese | 0.88 g |
| Kefir | 0.16 g |
| Cream | 0.14 g |
| Sour cream | 0.12 g |
| Kumis | 0.11 g |
| Milk | 0.11 g |
| Goat milk | 0.11 g |
| Vegetables | |
| Potato | 0.09 g |
| Spinach | 0.09 g |
| Eggplant | 0.05 g |
| Beet | 0.05 g |
| Bulb onions | 0.03 g |
| Tomatoes | 0.03 g |
| Carrot | 0.02 g |
| cucumbers | 0.02 g |
| Radish | 0.02 g |
| Fruits and berries | |
| Jackfruit | 0.10 g |
| Avocado | 0.05 g |
| Strawberries | 0.02 g |
| Figs | 0.03 g |
| Kiwi | 0.03 g |
| Cranberry | 0.03 g |
| Longan | 0.03 g |
| A pineapple | 0.02 g |
| Strawberry | 0.02 g |
| Mango | 0.02 g |
| Mandarin | 0.02 g |
| Peach | 0.02 g |
| Persimmon | 0.02 g |
| Apricots | 0.01 g |
| Orange | 0.01 g |
| Watermelon | 0.01 g |
| Banana | 0.01 g |
| Grape | 0.01 g |
| Pear | 0.01 g |
| Papaya | 0.01 g |
| Feijoa | 0.01 g |
| Cherries | 0.01 g |
| Blueberry | 0.01 g |
| Apple | 0.01 g |